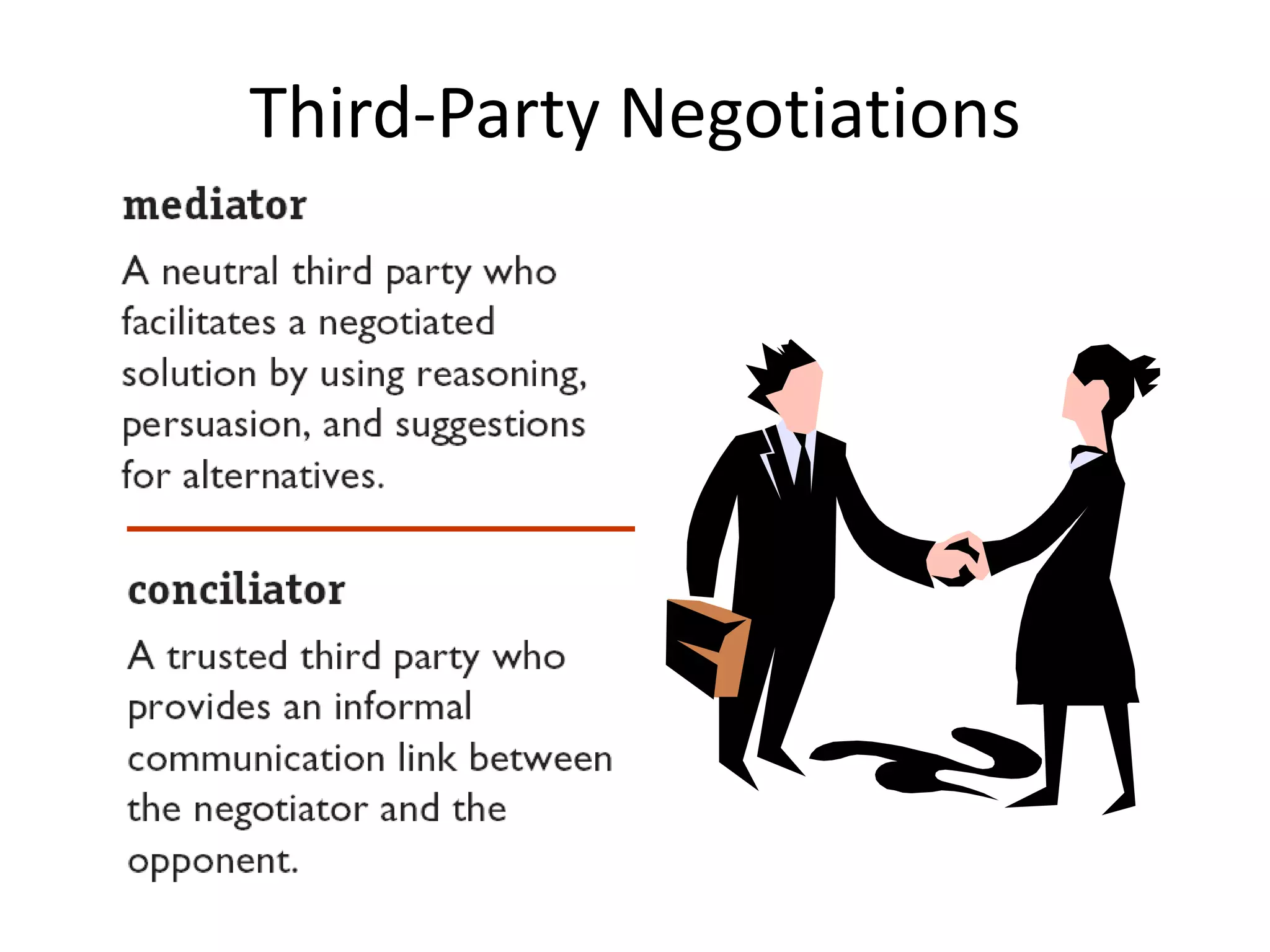
Negotiation involves groups with conflicting interests meeting to resolve differences through offers, counteroffers, and concessions. There are three types of third parties that can be involved - a mediator who helps parties reconcile differences, an arbiter who can impose a solution, or a neutral negotiator skilled in bargaining. Effective negotiation requires planning, understanding different strategies like distributive and integrative bargaining, properly handling the negotiation process, and avoiding common mistakes like poor preparation.