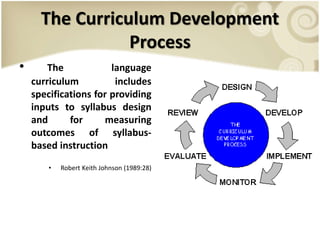
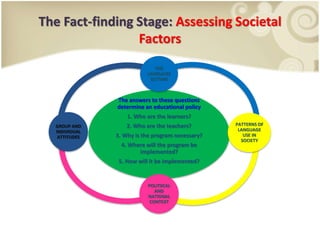
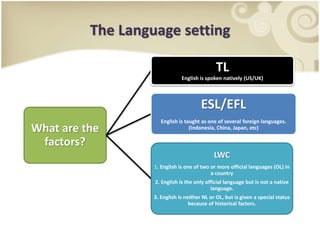
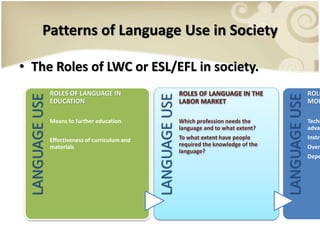
This presentation discusses the importance of assessing societal factors when developing an English language curriculum for Indonesian students. It outlines the curriculum development process and the key societal factors to examine, including the language setting, patterns of language use in society, attitudes toward the language, and the political/national context. Practical examples of interview questions are provided to help gather information about learners' needs, attitudes, and whether English courses are sufficient. The conclusion emphasizes that understanding these societal factors is essential for designing an effective new language program.