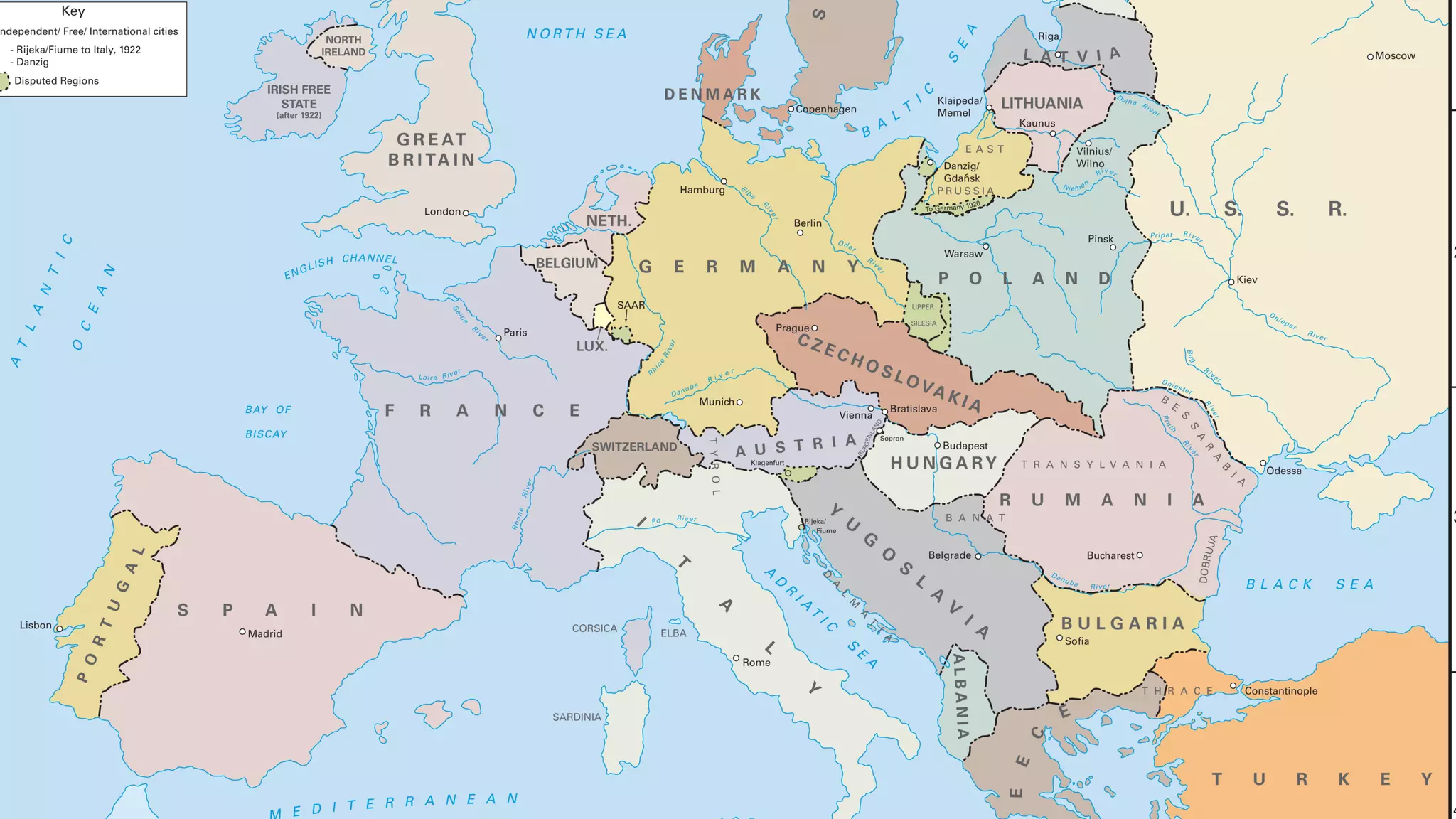
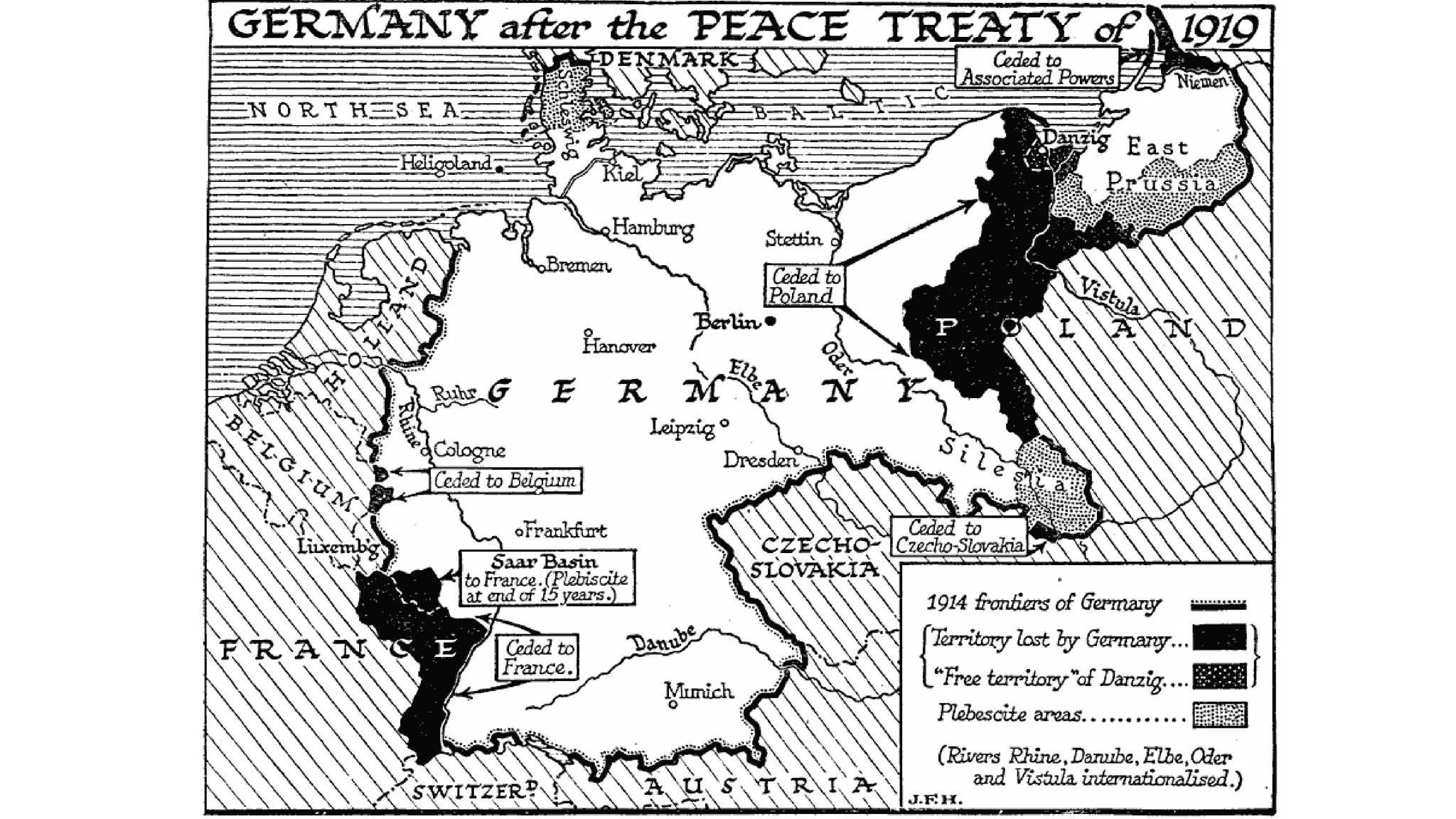
The document summarizes the end of World War I and its effects. It discusses the Russian Revolution and Lenin taking Russia out of the war. It describes conscription in Canada causing tensions between French and English Canadians. Women gained new roles in the war effort and were eventually given the right to vote. The Armistice was signed in 1918 and the Paris Peace Conference established the Treaty of Versailles, which punished Germany with reparations and territorial losses. Canada emerged from the war with greater autonomy on the world stage.