Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times




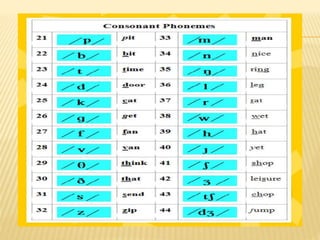
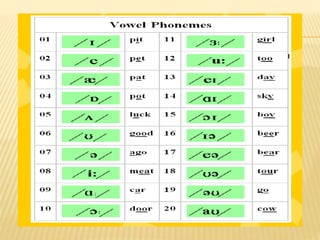









![DENTALS
In a dental consonant, the tip or blade of the tongue
approaches or touches the upper teeth. English [θ] and
[ð] are dental fricatives. There are actually a couple of
different ways of forming these sounds:
The tongue tip can approach the back of the upper
teeth, but not press against them so hard that the
airflow is completely blocked.
The blade of the tongue can touch the bottom of the
upper teeth, with the tongue tip protruding between the
teeth -- still leaving enough space for a turbulent
airstream to escape. This kind of [θ] and [ð] is often
called interdental.
The diagram to the right shows a typical interdental [θ]
or [ð].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconsonantsoundspowerpointno2-141002090735-phpapp01/85/The-consonant-sounds-17-320.jpg)

![GLOTTAL
The glottis is the opening between the vocal
folds. In an [h], this opening is narrow
enough to create some turbulence in the
airstream flowing past the vocal folds. For
this reason, [h] is often classified as a glottal
fricative.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconsonantsoundspowerpointno2-141002090735-phpapp01/85/The-consonant-sounds-19-320.jpg)


This document discusses different types of consonant sounds in English pronunciation: - Dental consonants involve the tongue touching or approaching the upper teeth, such as the sounds in "thin" and "then". - Alveopalatal consonants involve the tongue blocking air between the hard palate and alveolar ridge, including the sounds in "chip", "gym", "shore", and "azure". - Glottal consonants involve a narrow opening of the glottis, or space between vocal folds, creating turbulence in the airstream, such as the sound in "hi".
















![DENTALS
In a dental consonant, the tip or blade of the tongue
approaches or touches the upper teeth. English [θ] and
[ð] are dental fricatives. There are actually a couple of
different ways of forming these sounds:
The tongue tip can approach the back of the upper
teeth, but not press against them so hard that the
airflow is completely blocked.
The blade of the tongue can touch the bottom of the
upper teeth, with the tongue tip protruding between the
teeth -- still leaving enough space for a turbulent
airstream to escape. This kind of [θ] and [ð] is often
called interdental.
The diagram to the right shows a typical interdental [θ]
or [ð].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconsonantsoundspowerpointno2-141002090735-phpapp01/85/The-consonant-sounds-17-320.jpg)

![GLOTTAL
The glottis is the opening between the vocal
folds. In an [h], this opening is narrow
enough to create some turbulence in the
airstream flowing past the vocal folds. For
this reason, [h] is often classified as a glottal
fricative.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconsonantsoundspowerpointno2-141002090735-phpapp01/85/The-consonant-sounds-19-320.jpg)
