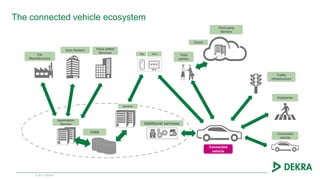
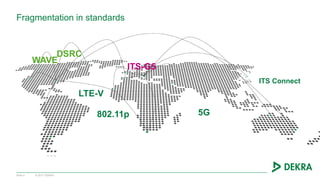
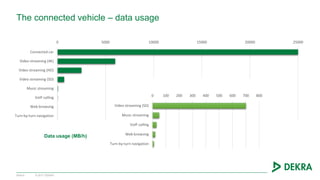
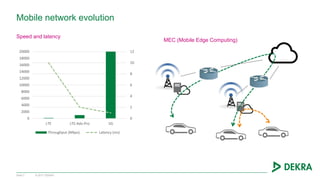
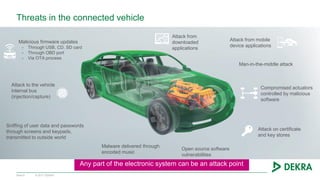
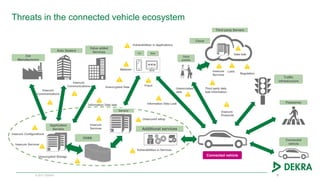
The document discusses the challenges and opportunities presented by connected vehicles, focusing on standards, data usage, and cybersecurity. It highlights the fragmentation in communication standards and the significant data usage associated with various connected vehicle applications. Additionally, the document identifies security threats that could affect vehicle systems and emphasizes the importance of secure communications to mitigate vulnerabilities.