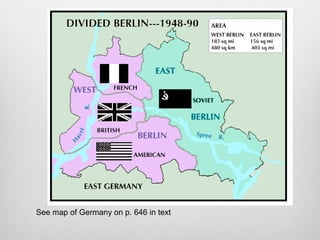
The document summarizes key events in the escalation of the Cold War in the late 1940s. It describes the Marshall Plan to rebuild Western Europe, the Berlin Airlift when the Soviets blocked access to West Berlin, and the formation of NATO as a military alliance between Western nations. It also discusses growing fears of communist influence in the US government and Hollywood during this period, fueled by investigations into suspected Soviet spies.