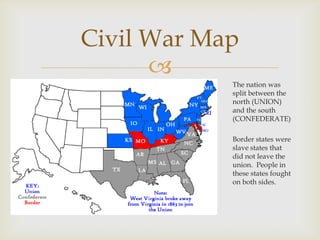
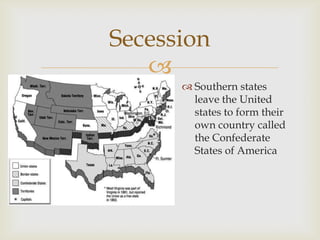
This document provides information to help students select a topic for a research project on a person or event from the Civil War era. It instructs students to choose a topic that genuinely interests them, as they will spend a significant amount of time studying it. The document lists numerous potential topics, including important figures from both the Union and Confederacy, to help students identify three topics they are most interested in researching further. Students are then asked to defend their topic choices to their teacher.