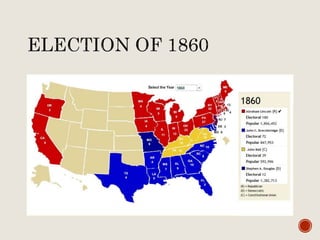
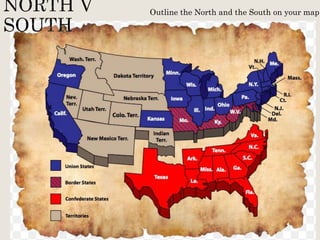
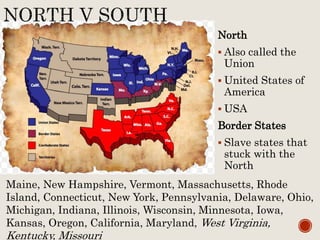
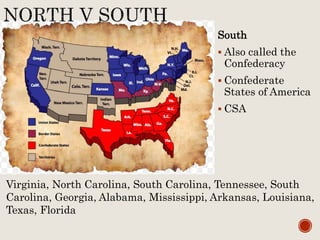
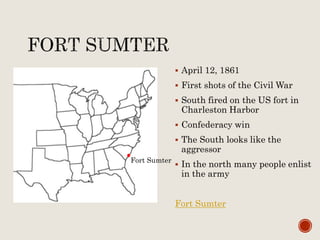
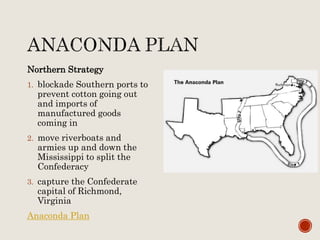
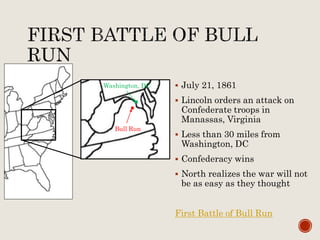
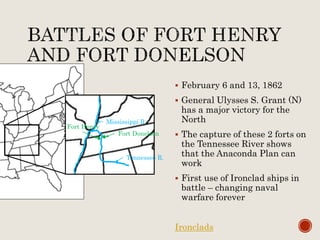
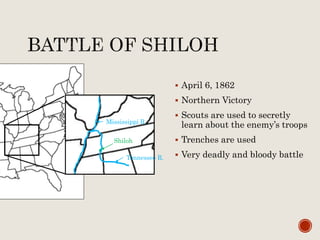
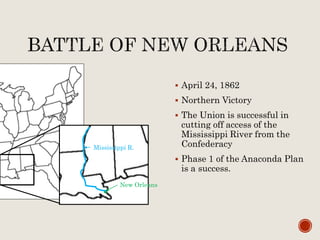
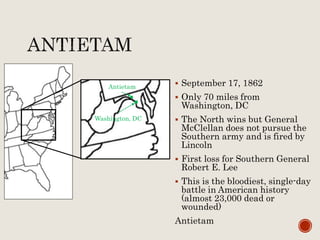
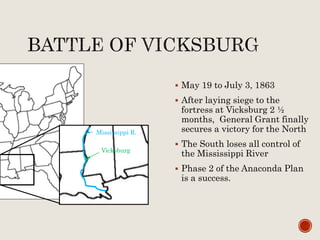
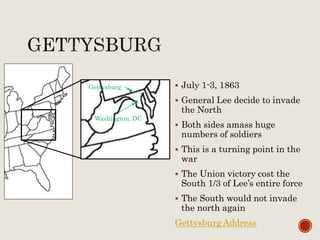
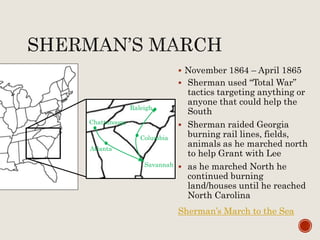
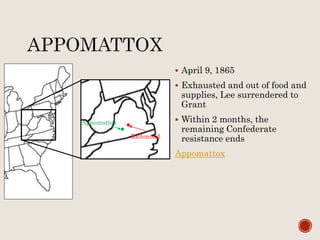
Abraham Lincoln was elected President in 1860. In response, South Carolina seceded from the Union in December 1860 and formed the Confederate States of America in February 1861. The Civil War began in April 1861 when Confederate forces fired on Fort Sumter in South Carolina. Over the next four years, there were many major battles between Union and Confederate forces across rivers, coastlines, and states as the Union tried to regain control and split the Confederacy through its Anaconda Plan blockade. Key battles and events shifted momentum between the North and South until General Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Court House in April 1865, effectively ending the Civil War.