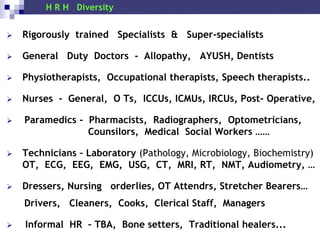
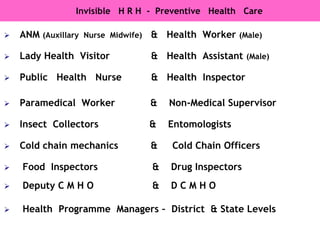
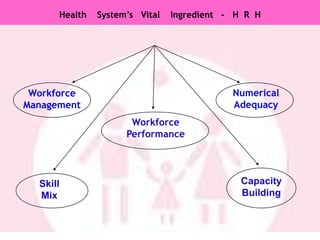
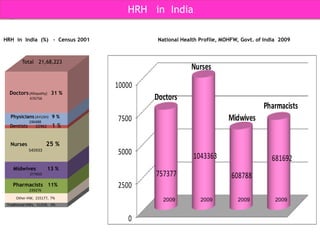
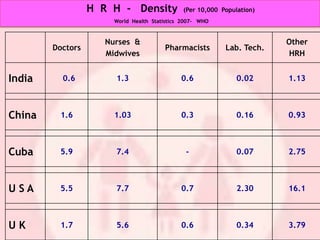
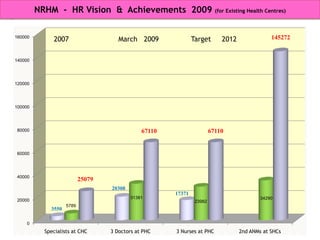
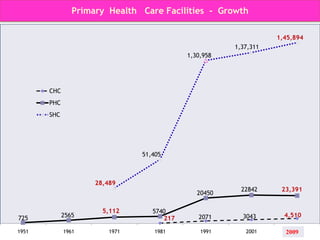
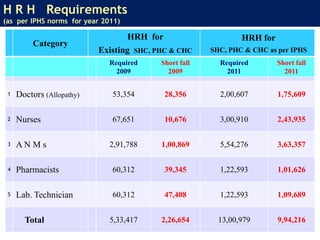
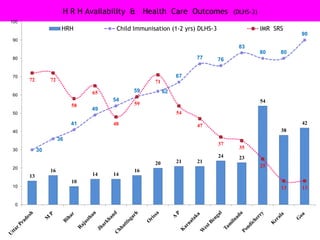
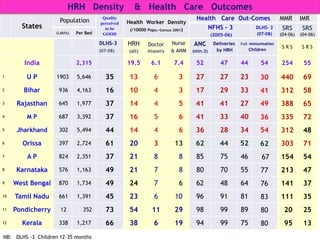
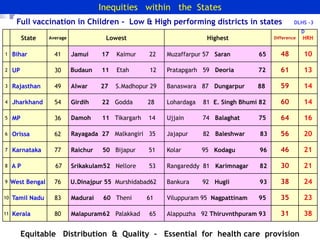
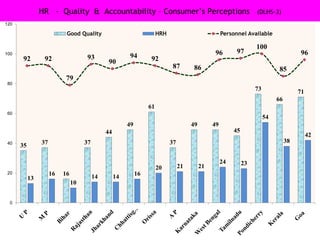
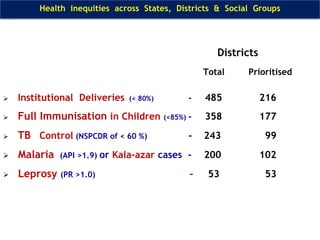
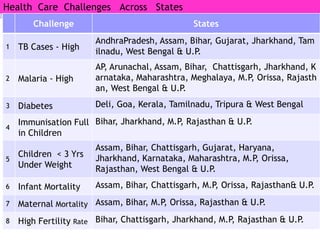
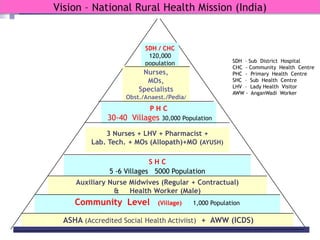
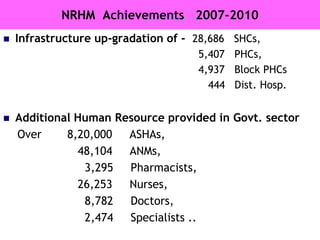
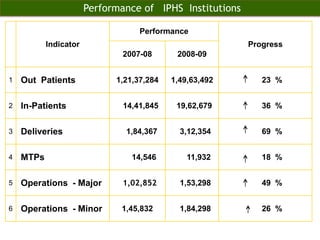
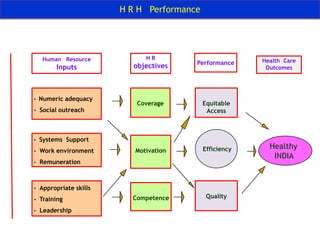
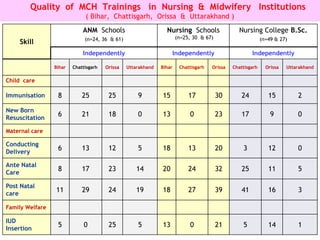
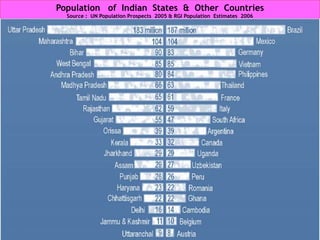
The document discusses human resources for health (HRH) in India. It notes that HRH is critical for ensuring health care accessibility, equity and quality. It provides a brief history of health sector planning and HRH development in India since 1946. It discusses the diversity of HRH in India, including various types of providers, managers and support staff. It highlights challenges in maintaining adequate numbers, distribution and quality of HRH to meet changing health needs. It also summarizes NRHM's achievements and goals in addressing HRH issues like shortages, inequitable distribution and skills upgradation in order to improve health outcomes in India.