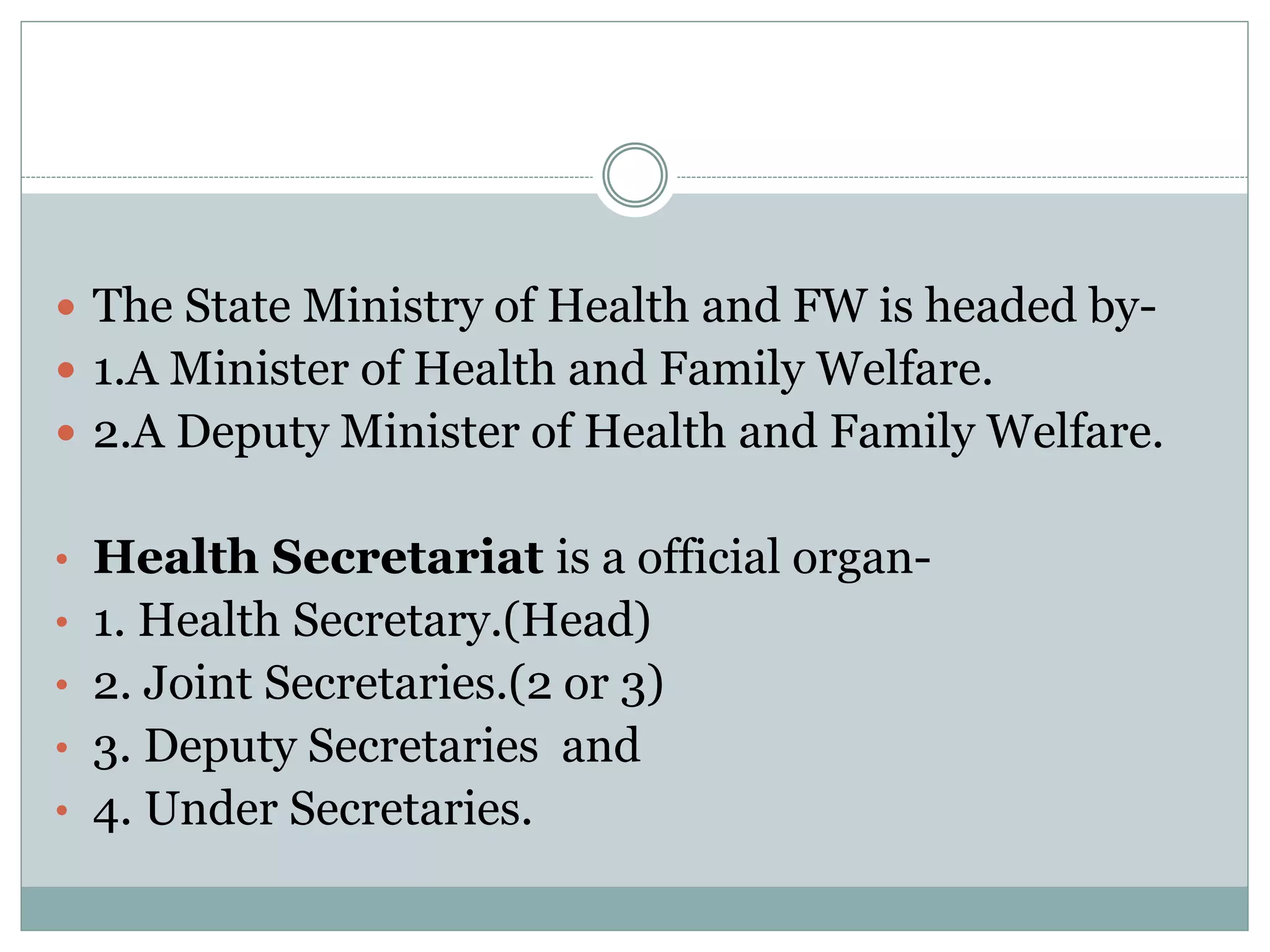
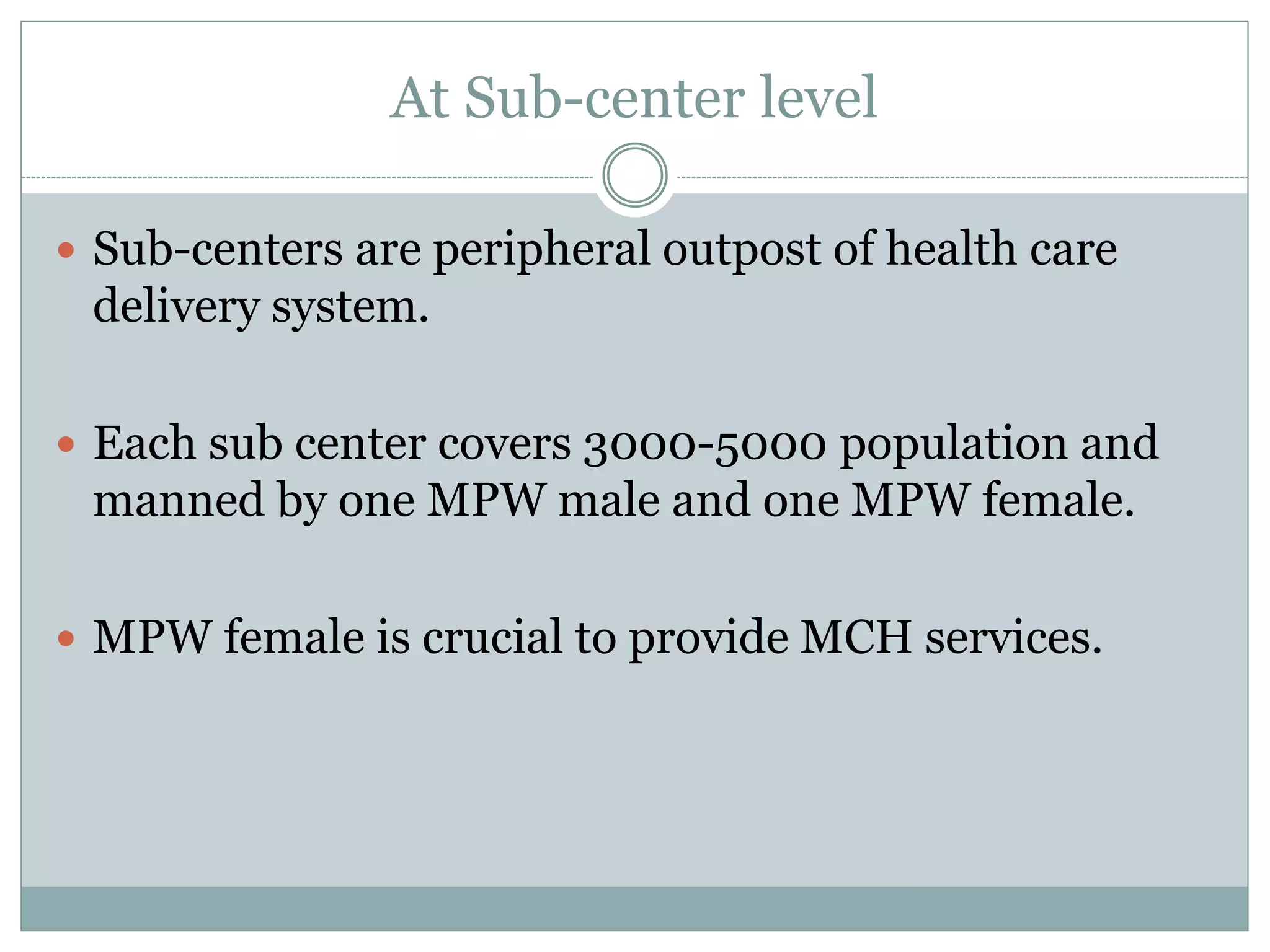
This document provides an overview of the health care delivery system in India. It describes the organizational structure at the central, state, district, block, primary health center, and village levels. The key shortcomings are discussed as inverse care, impoverishing care, fragmented care, unsafe care, and misdirected care. Reforms proposed by the WHO are also outlined, including universal coverage, service delivery, public policy, and leadership reforms. The objectives and importance of establishing Indian Public Health Standards are also presented. In conclusion, it acknowledges advances but notes the system remains ineffective and discusses needed reforms and decentralization to improve healthcare quality and delivery.