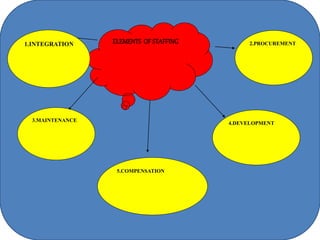
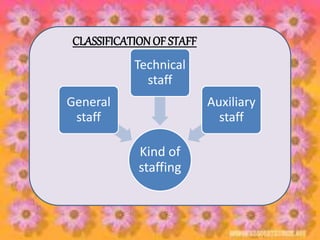
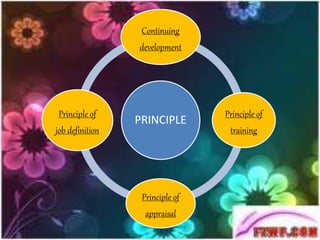
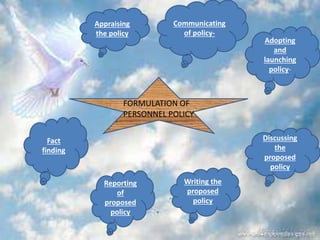
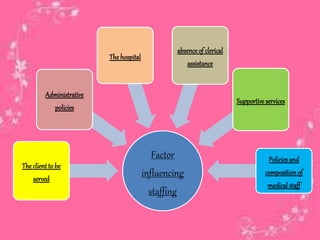
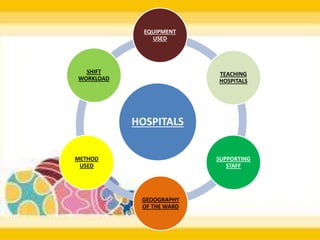
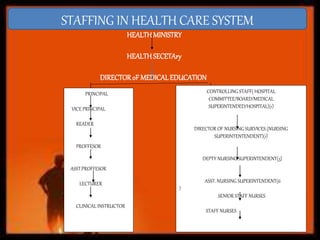
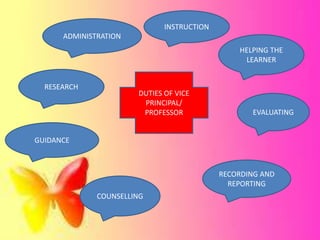
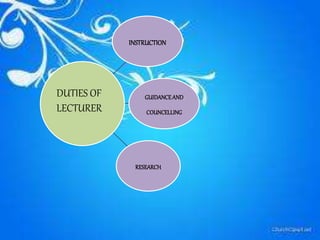
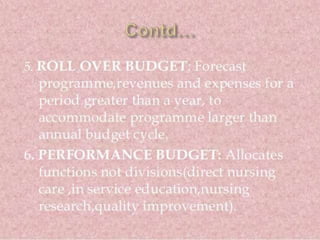
Staffing involves selecting, training, motivating and retaining personnel in an organization. Nurse staffing presents constant challenges for healthcare facilities. The staffing process includes human resource planning, recruitment, selection, placement, training, development, promotion and compensation. Effective staffing requires determining the appropriate number and mix of nursing staff needed to meet patient care needs. Factors like patient volume and acuity, unit layout, budget and professional standards influence staffing decisions. The goal of nurse staffing is to match employee skills with patient needs to optimize job satisfaction and care quality.