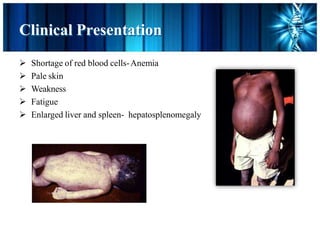
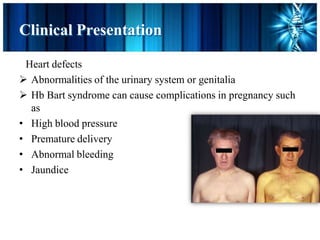
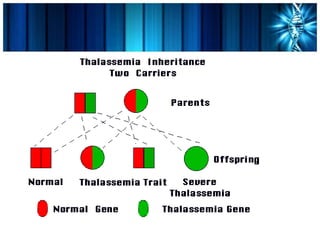
This document discusses thalassemia, an inherited blood disorder. It provides details on alpha thalassemia, including that it results from mutations in the genes responsible for the alpha globin component of hemoglobin. Symptoms include anemia, enlargement of the liver and spleen, and heart defects. Treatment involves regular blood transfusions, folate supplements, and chelation therapy to remove excess iron from transfused blood. Key medications discussed are folic acid, used to treat folate deficiency, and deferoxamine, an iron-chelating drug administered via injection to remove excess iron from the body.






















































![References
• American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Hemoglobinopathies in Pregnancy.
ACOG Practice Bulletin, number 78, January 2007.
• Beta Thalassemia. (Sept 2, 2011). Retrieved from http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/206490-overview
• Bleibel, S. et al. Thalassemia,Alpha. Retrieved: 29 September, 2011 from
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/206397-overview#a0104
• Cohen, A.R., et al. Thalassemia. Hematology 2004, American Society of Hematology, pages 14-34.
• Cooley’s Anemia Foundation. About Thalassemia. Updated 2007.
• Cunningham, M.J. Update on Thalassemia: Clinical Care and Complications. Pediatric Clinics of
North America, volume 55, April 2008, pages 447-460.
• Deferoxamine [Pharm GKB]. (n.d.). Retrieved from
http://www.pharmgkb.org/do/serve?objId=PA164746490&objCls=Drug#tabview=tab1
• Di Bartolomeo, P., et al. Long-term Results of Survival in Patients with Thalassemia Major Treated
with Bone Marrow Transplantation. American Journal of Hematology, February 13, 2008 (Epub
ahead of print).
• Exjade (Deferasirox) Drug Information… (Aug 19, 2011). Retrieved from http://www.rxlist.com/exjade-
drug.htm
• Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Approves First Oral Drug for Chronic Iron Overload. FDA
News, November 9, 2005
• Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Approves First Oral Drug for Chronic Iron Overload. FDA
News, November 9, 2005.
• Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies,
University of Washington, School of Medicine; and Yi-Bin Chen, MD, Leukemia/Bone Marrow
Transplant Program, Massachusetts General Hospital; and David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director,
A.D.A.M., Inc., Review Date: 1/31/2010,Thalassemia, retrieved on 2011-09-30,
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001613/
• Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Standford. 2011.Alpha Thalassemia. Retrieved: 29 September, 2011
from http://www.lpch.org/DiseaseHealthInfo/HealthLibrary/hematology/thalapth.htmlth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thalassemiafinal-111212142013-phpapp02-231017062203-b1c61362/85/thalassemiafinal-111212142013-phpapp02-pptx-59-320.jpg)

