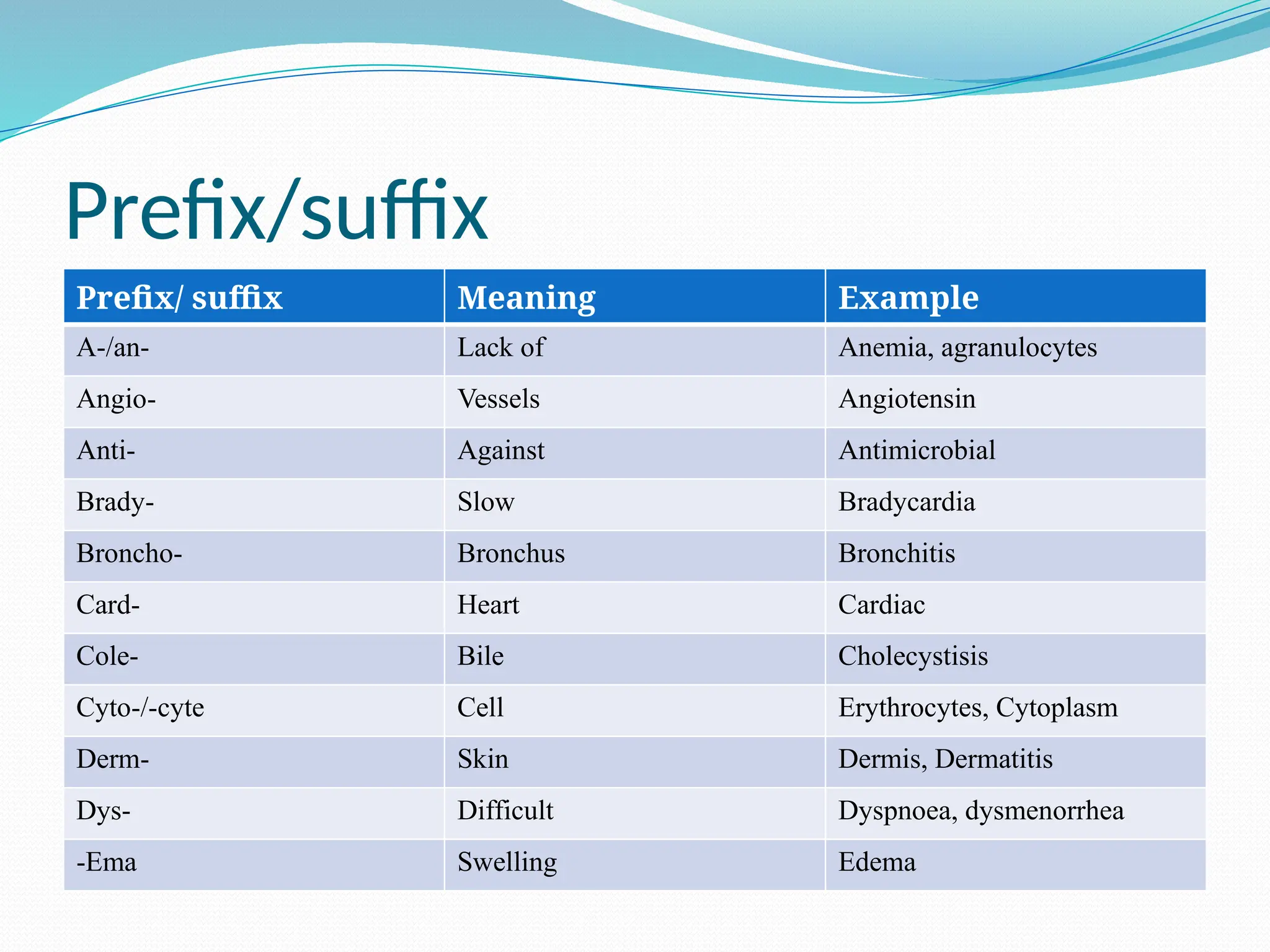
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to anatomy and physiology, detailing essential anatomical terms, body planes, and body cavities. It also covers the nine abdominal regions along with their corresponding organs and includes information on prefixes and suffixes commonly used in medical terminology. Lastly, it discusses concepts of movement and homeostasis, including negative and positive feedback mechanisms.