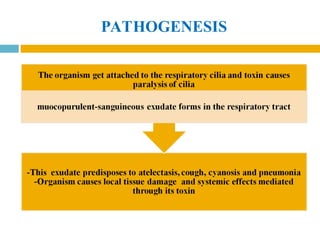
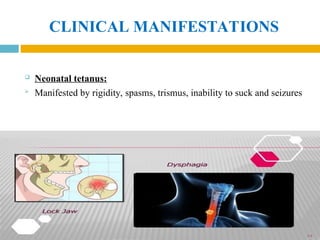
The document provides a comprehensive overview of diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus, including their causative agents, transmission dynamics, clinical manifestations, and treatment protocols. Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, pertussis by Bordetella pertussis, and tetanus by Clostridium tetani, with their respective epidemiological profiles emphasizing the importance of vaccination and antimicrobial therapy for prevention and management. The clinical descriptions detail symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and complications associated with each disease, highlighting the need for timely medical intervention.














![TREATMENT
1. Antitoxin:
Mainstay of therapy
Neutralizes only free toxin, efficacy diminishes with elapsed time
Antitoxin is administered as a single empirical dose of 20,000-
120,000 U based on the degree of toxicity, site and size of the
membrane, and duration of illness
2. Antimicrobial therapy
Halt toxin production, treat localized infection and prevent transmission
of the organism to contacts
erythromycin (40-50 mg/kg/day 6 hrly [PO] or [IV]), aqueous
crystalline penicillin G (100,000-150,000 U/kg/day 6 hrly IV or [IM]),
or procaine penicillin (25,000-50,000 U/kg/day 12 hrly IM) for 14 days](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diphtheriapertussistetanus2-250111044436-82c765b4/85/Diphtheria_Pertussis_tetanus-2-pptMMMMMMMMMM-18-320.jpg)