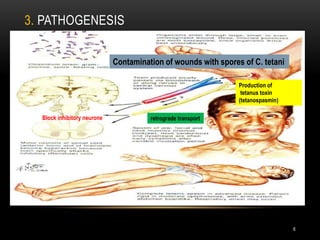
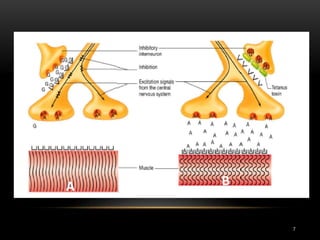
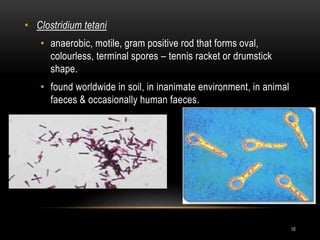
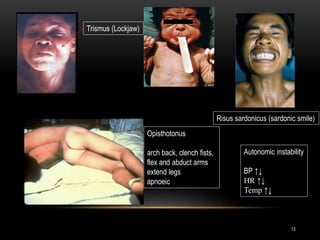
1. Tetanus is caused by Clostridium tetani bacteria and is characterized by painful muscle spasms. It remains endemic in developing countries where immunization rates are low.
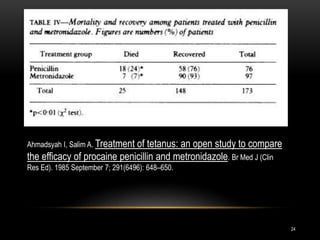
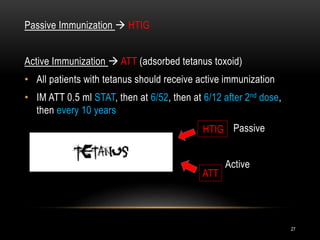
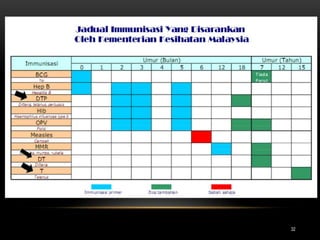
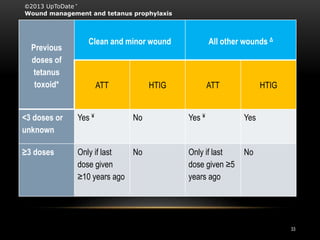
2. Treatment involves supportive care, eliminating ongoing toxin production through wound debridement and antibiotics, neutralizing unbound toxin with tetanus immune globulin, and immunizing against tetanus with toxoid vaccine.
3. Muscle spasms are controlled through sedation, usually with benzodiazepines, while autonomic dysfunction is treated with medications like magnesium sulfate or labetolol. Proper wound management and vaccination are crucial to prevent tetanus.