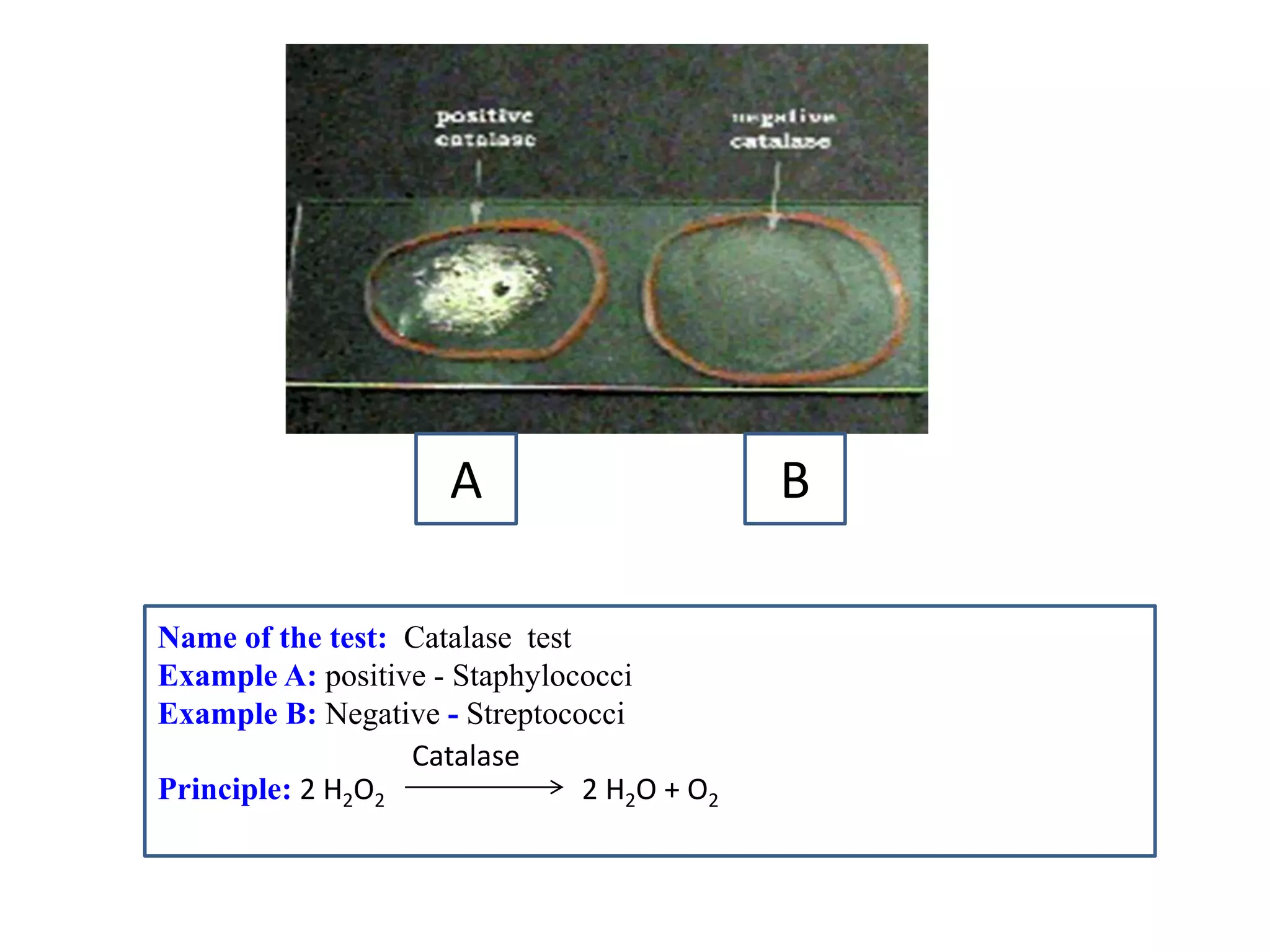
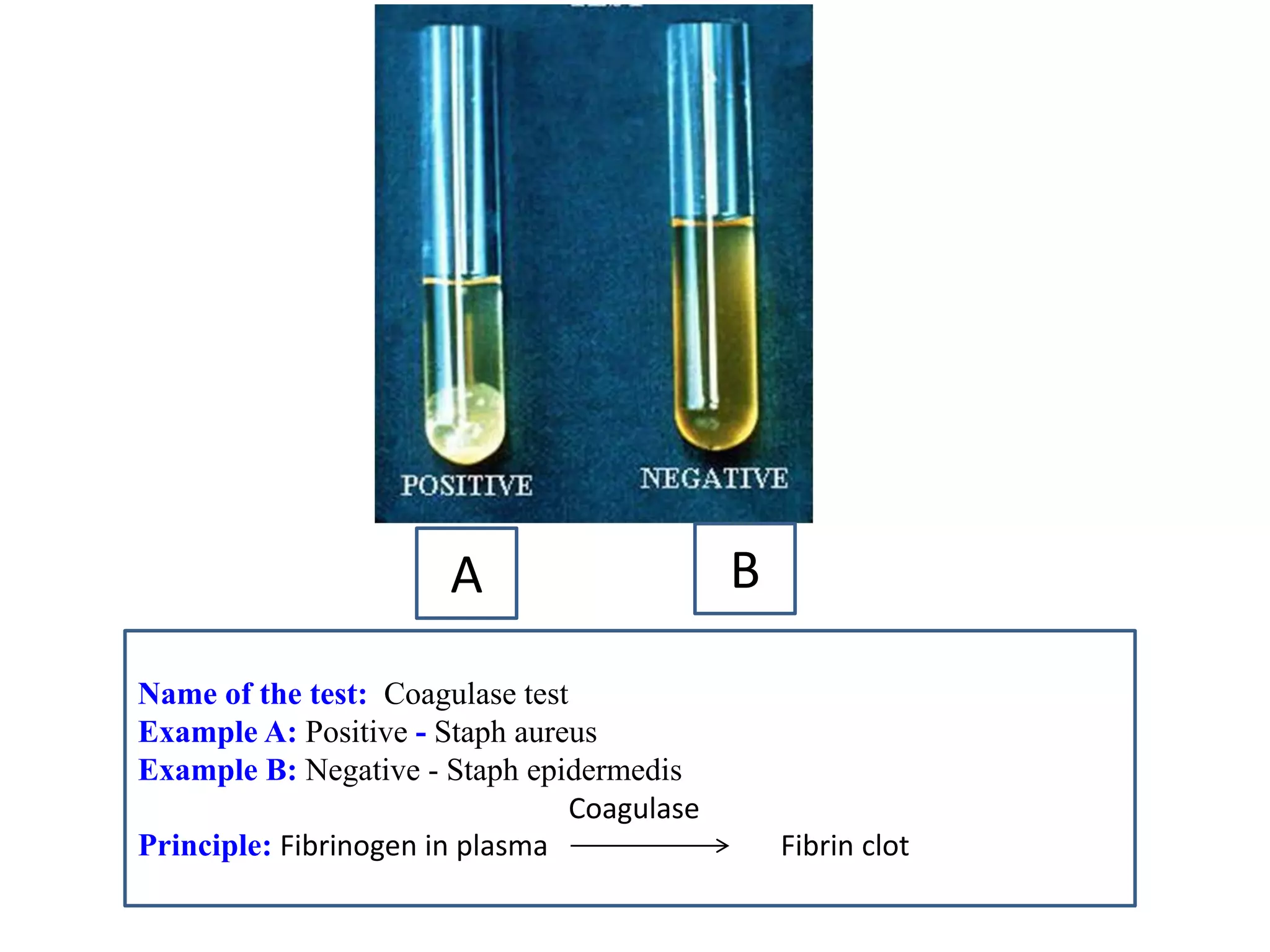
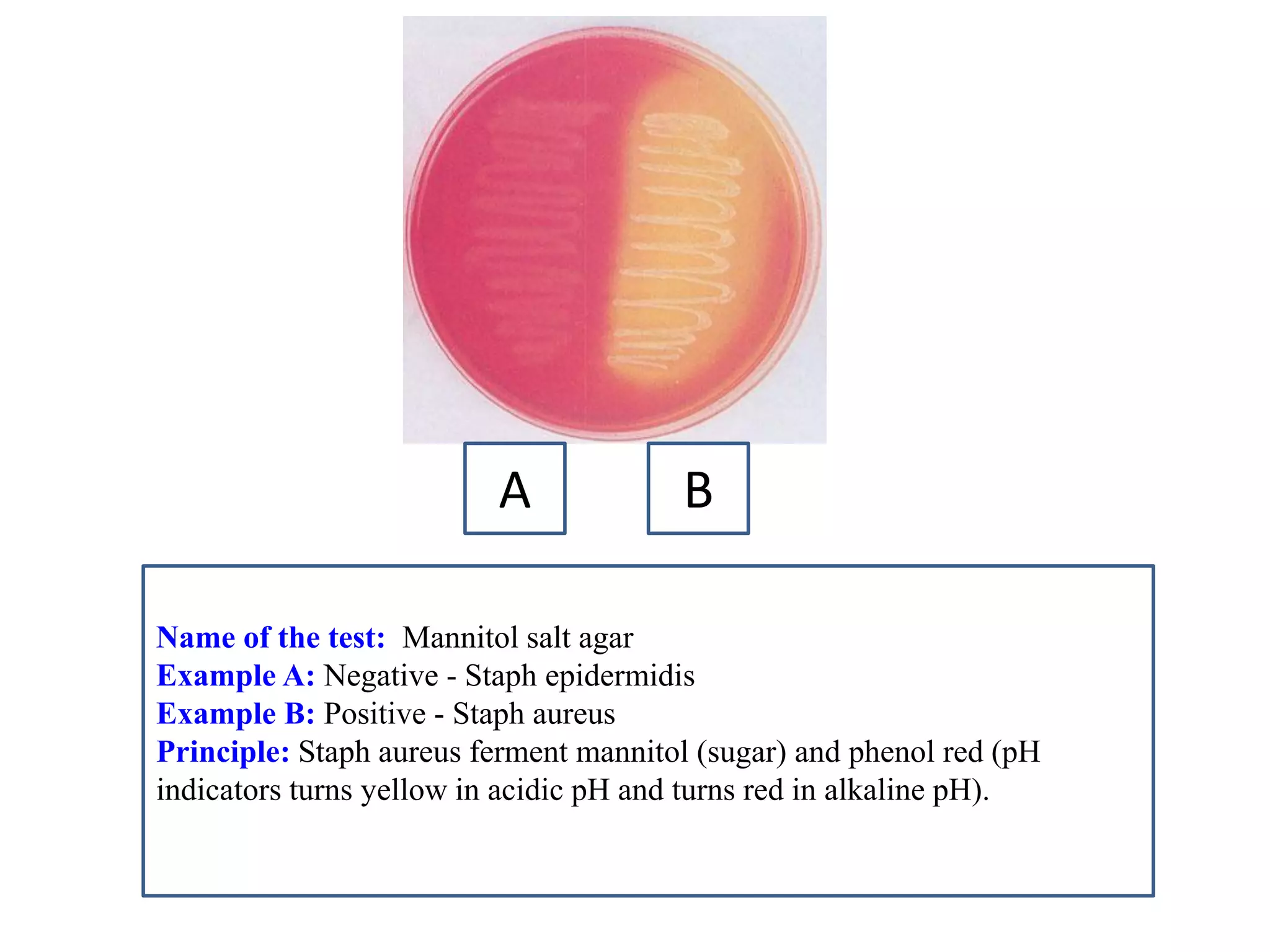
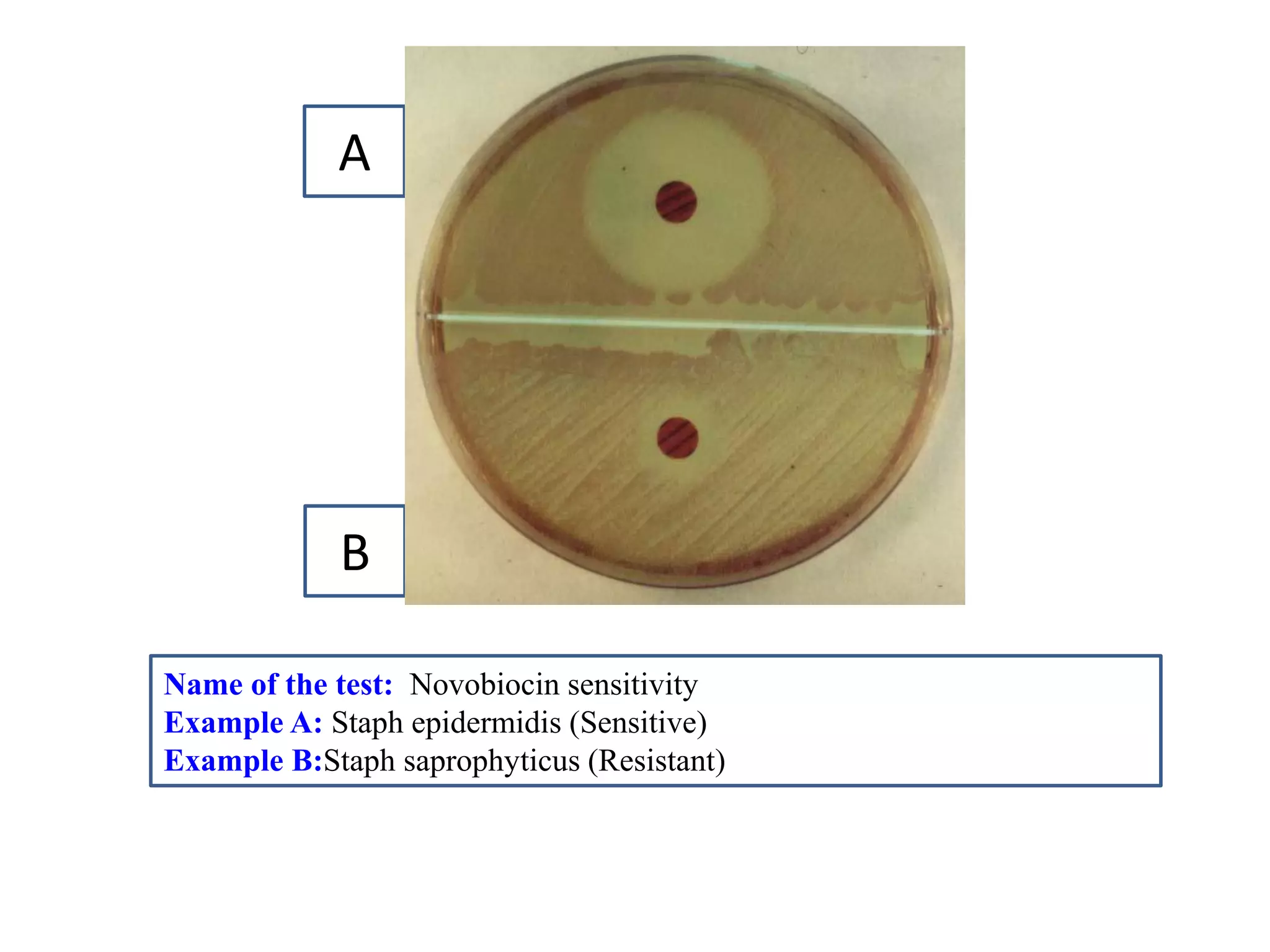
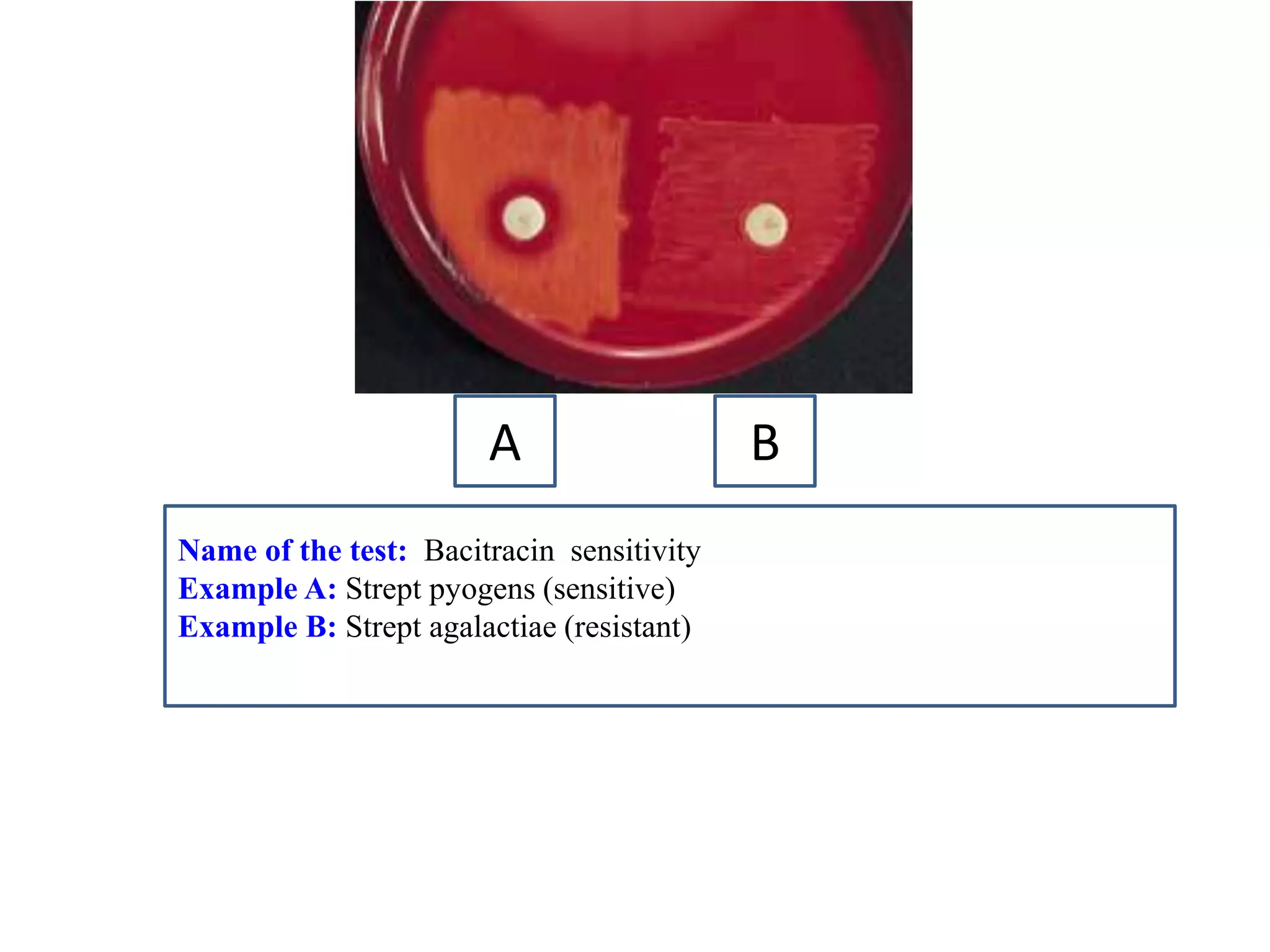
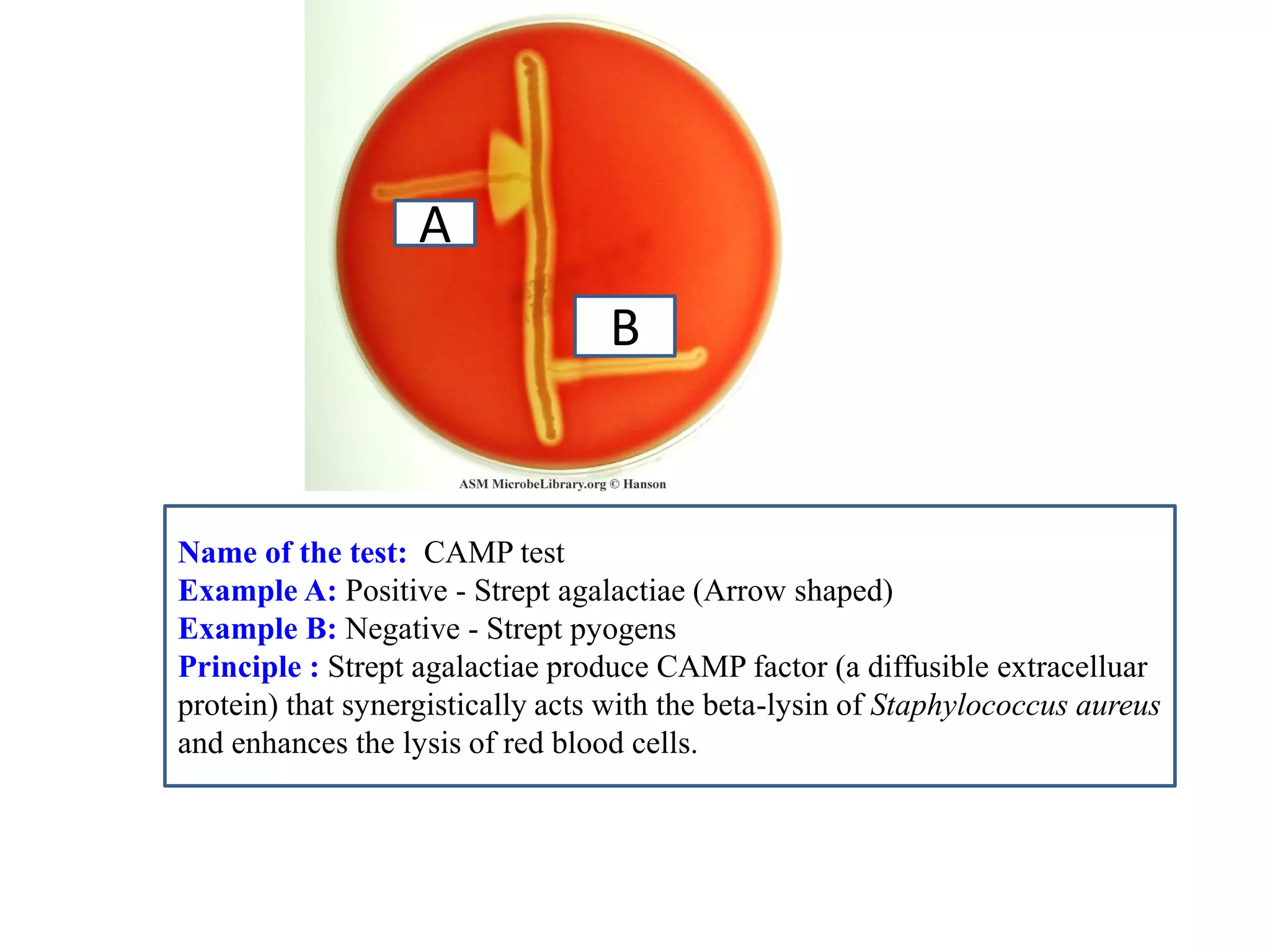
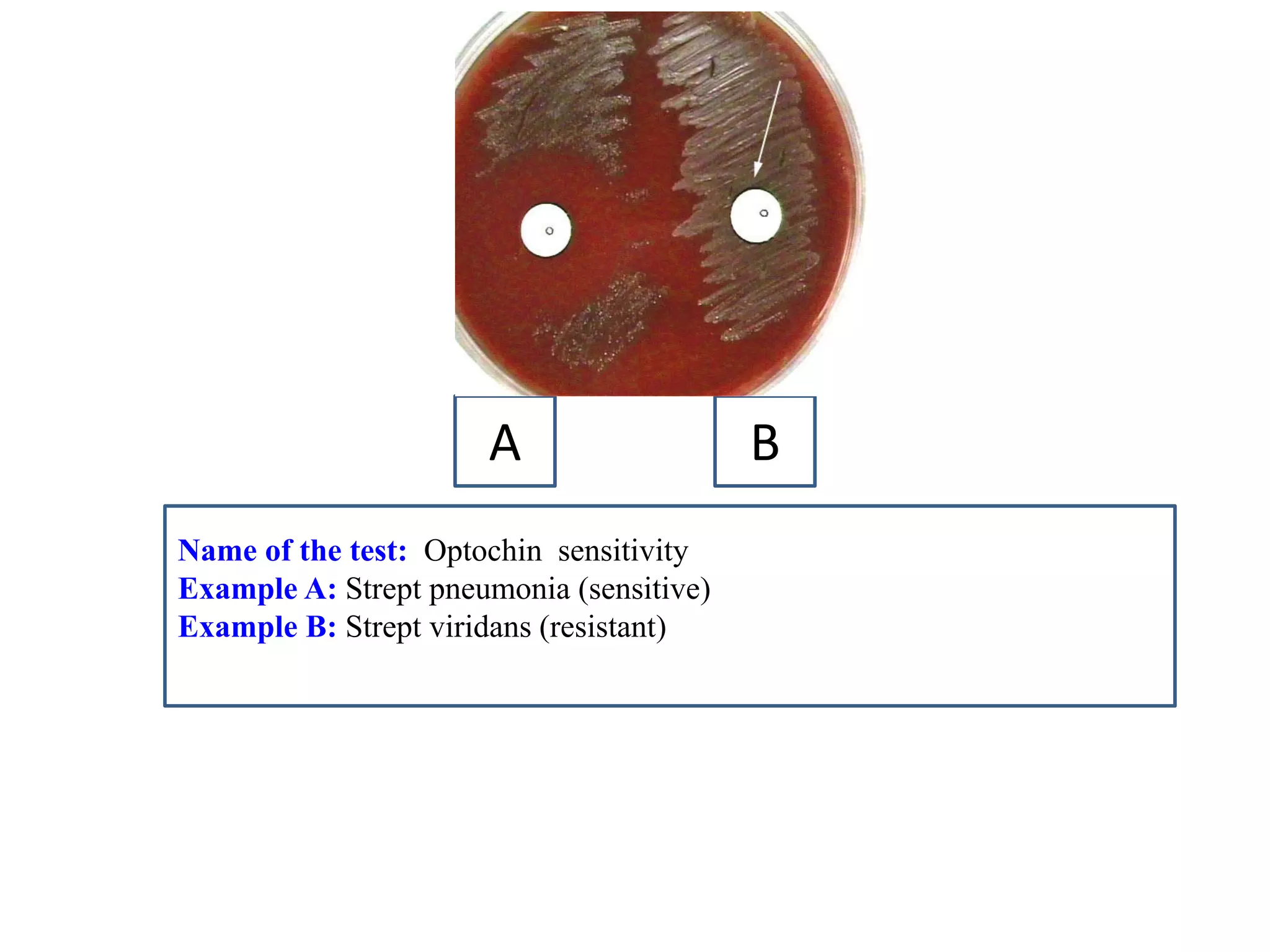
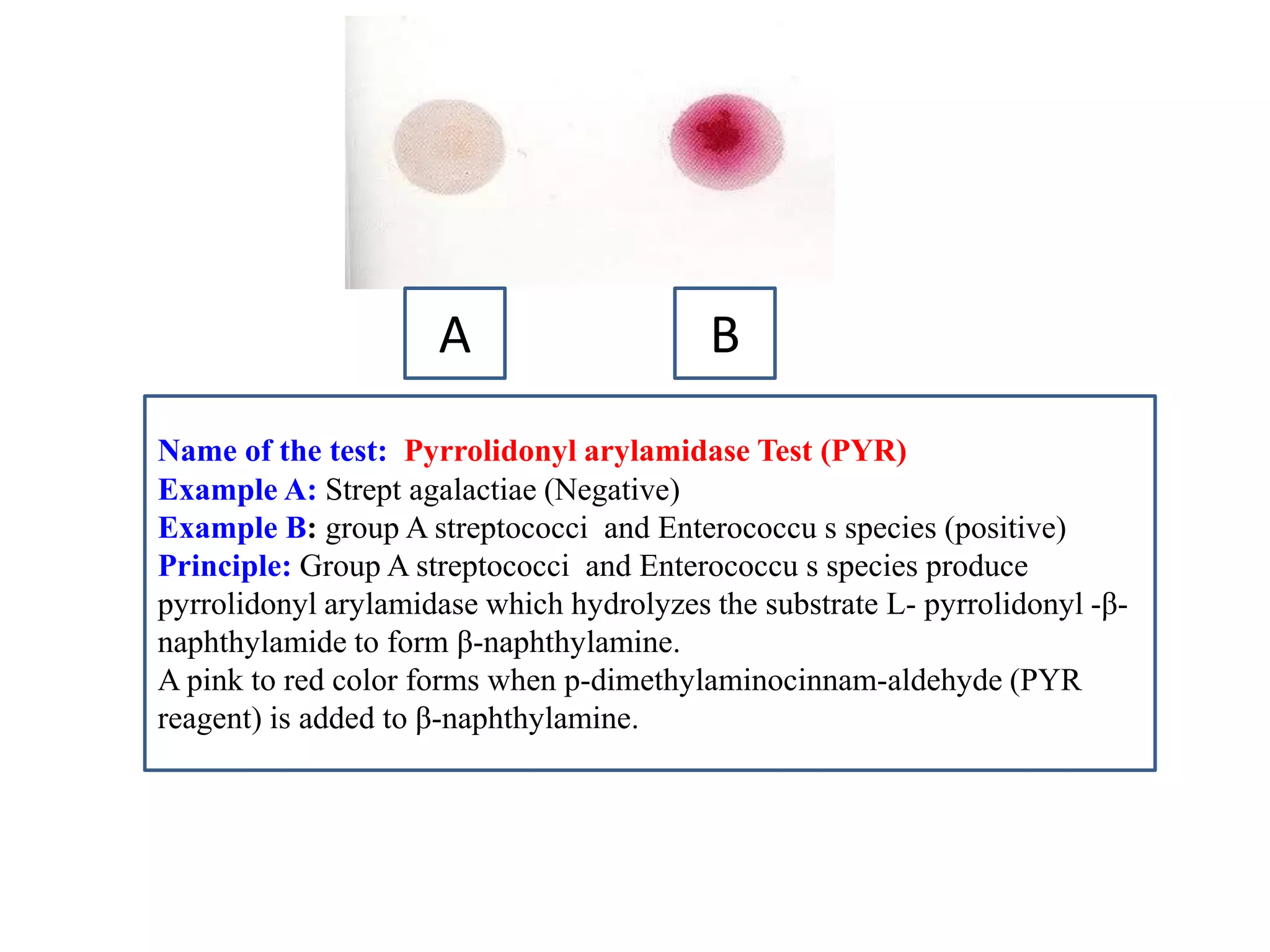
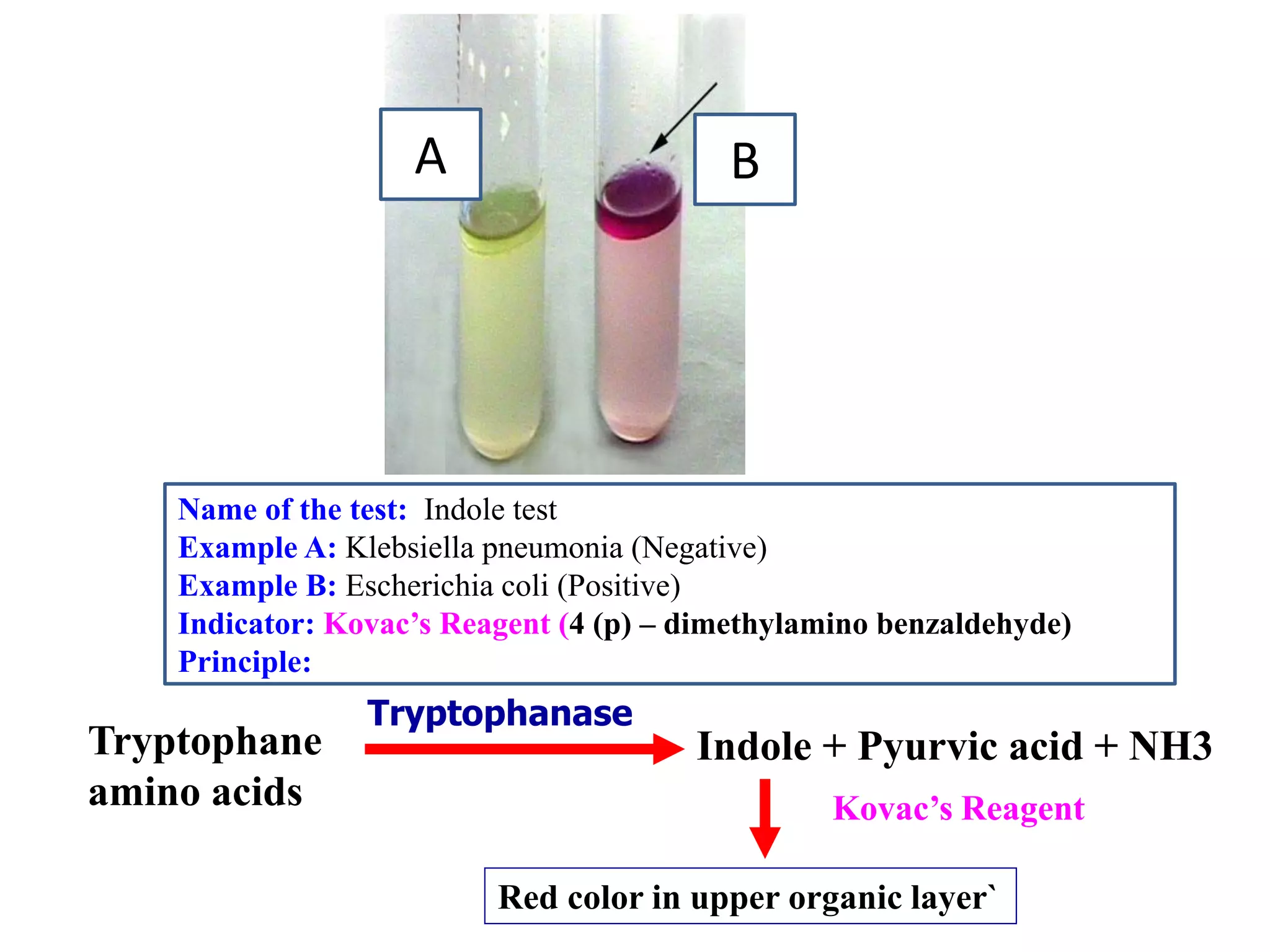
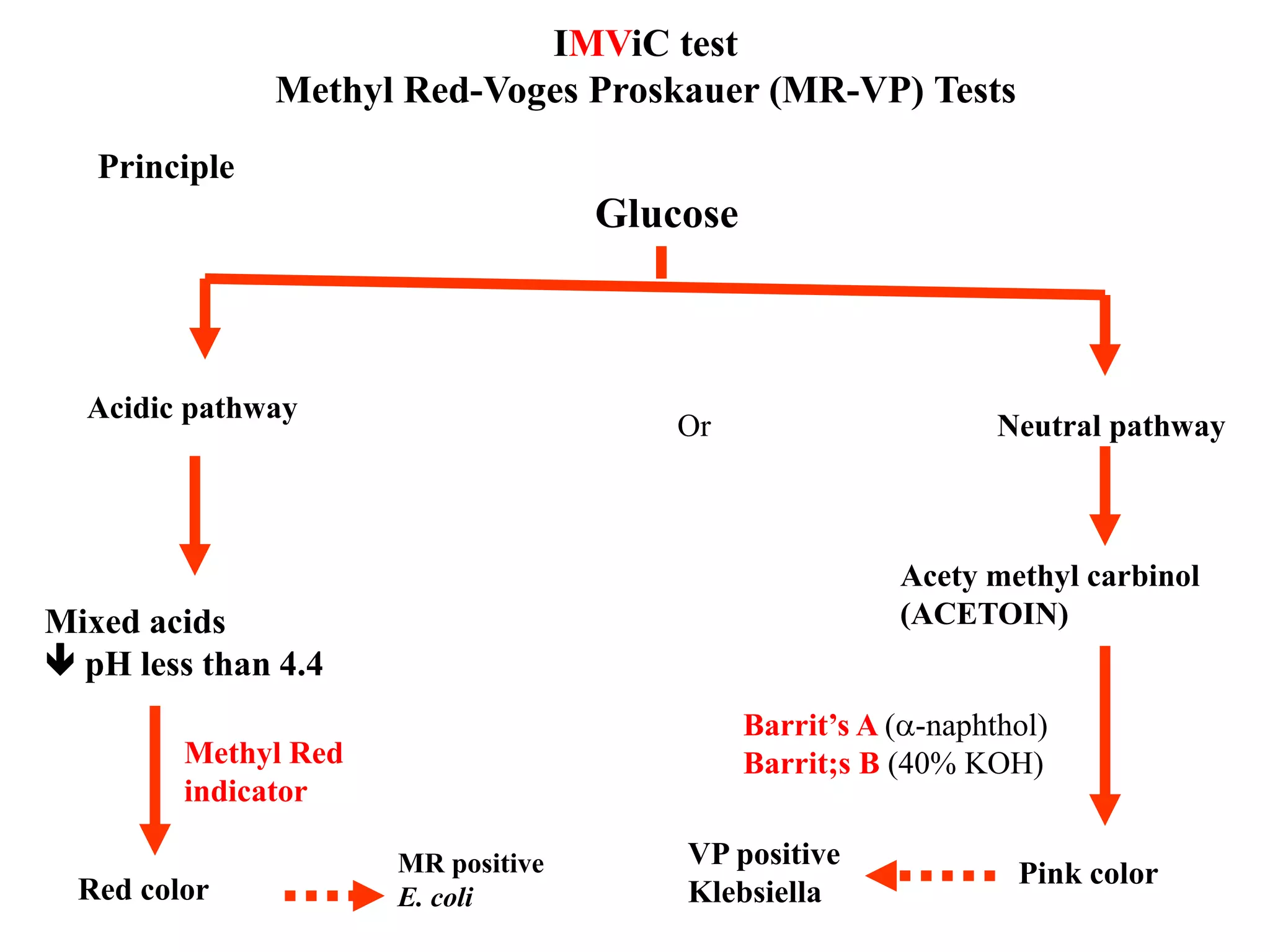
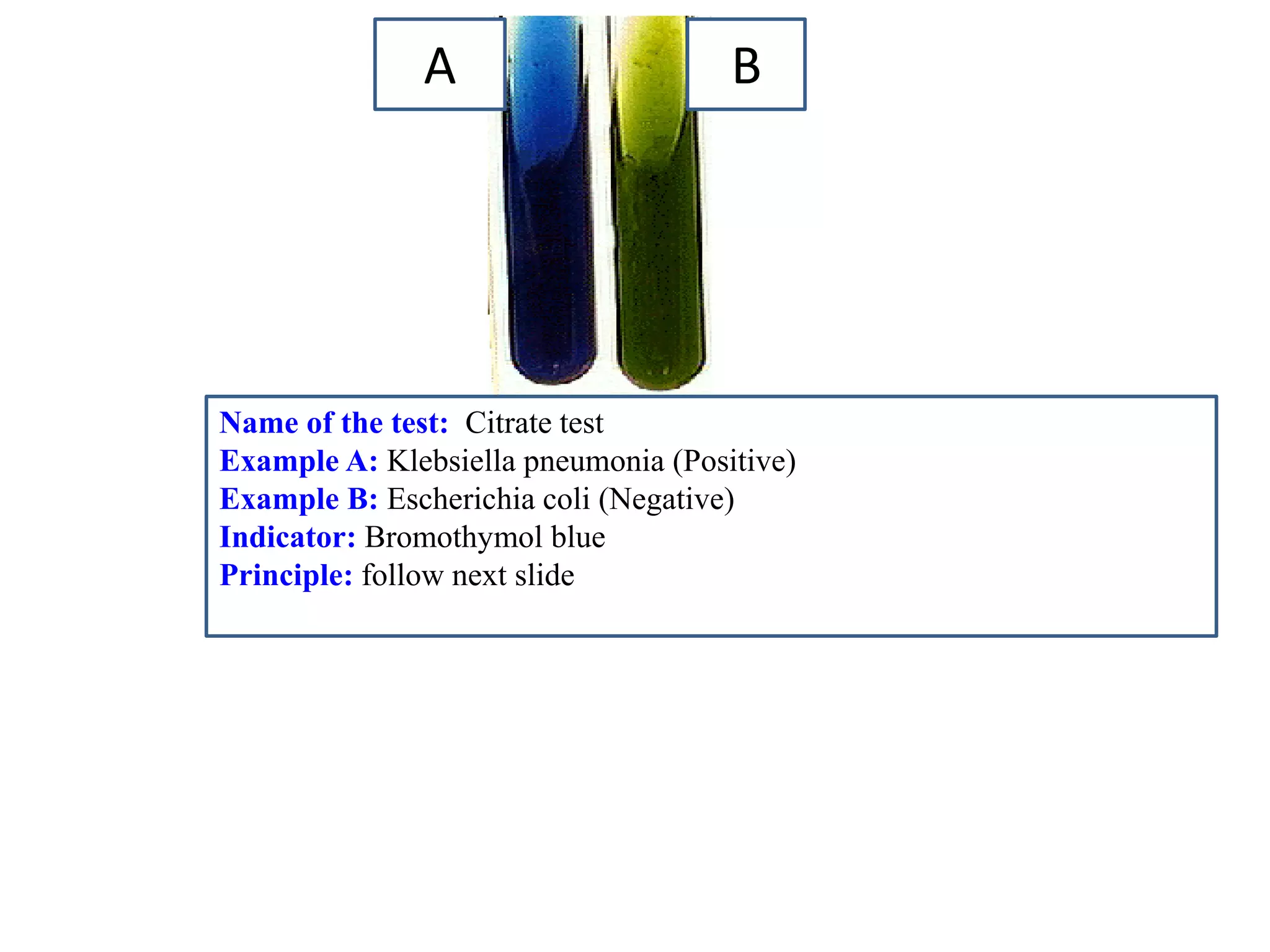
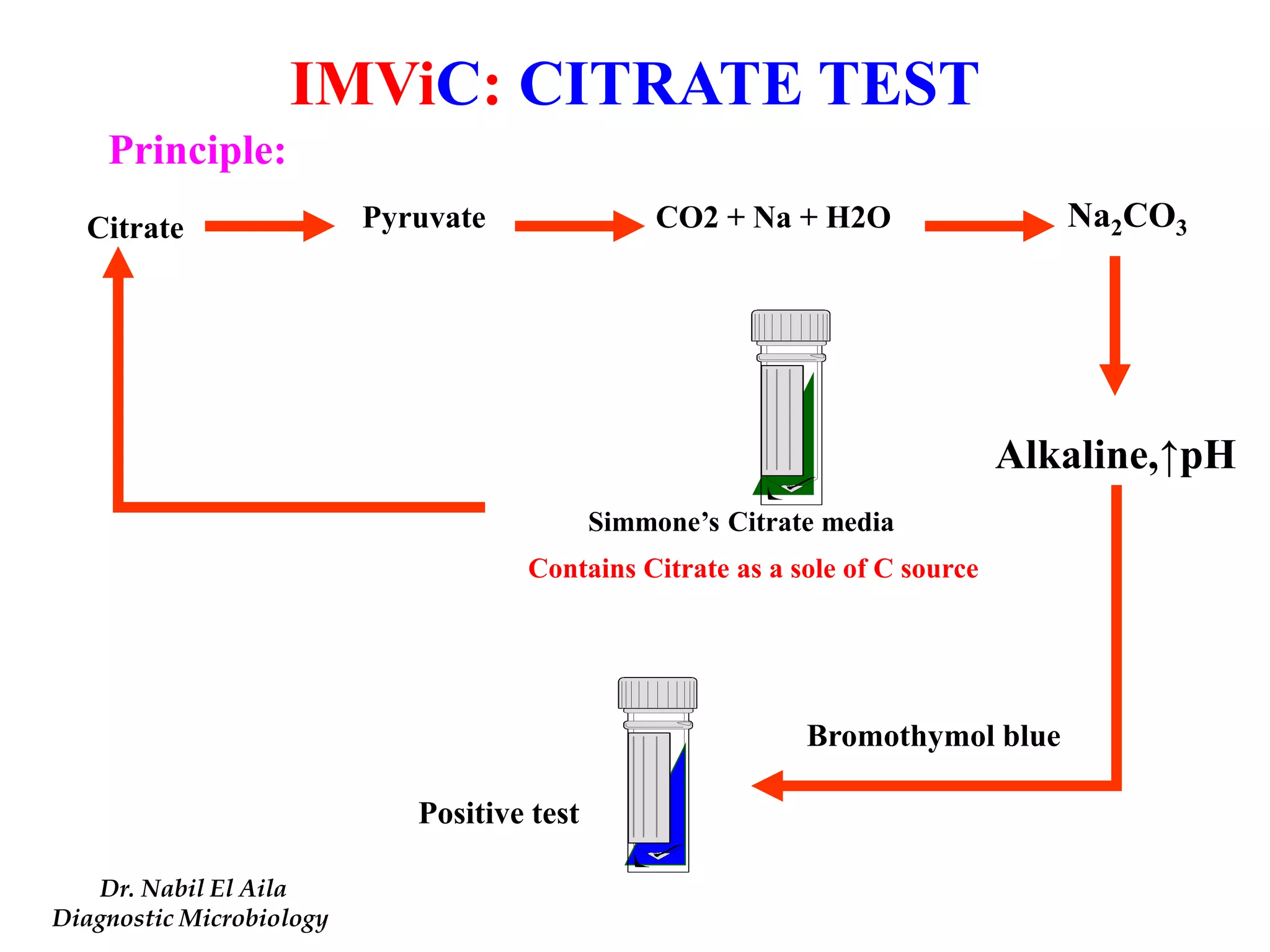
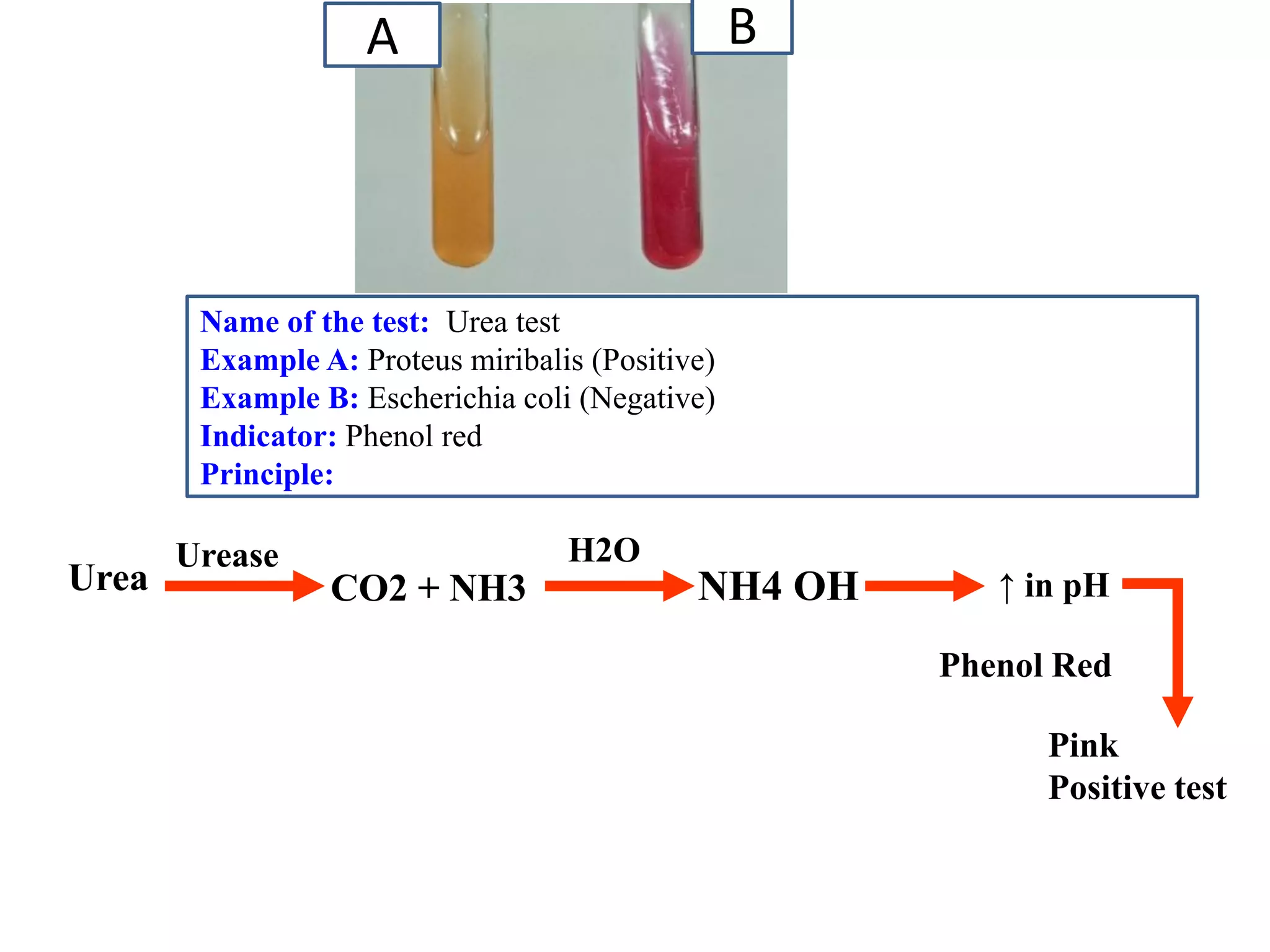
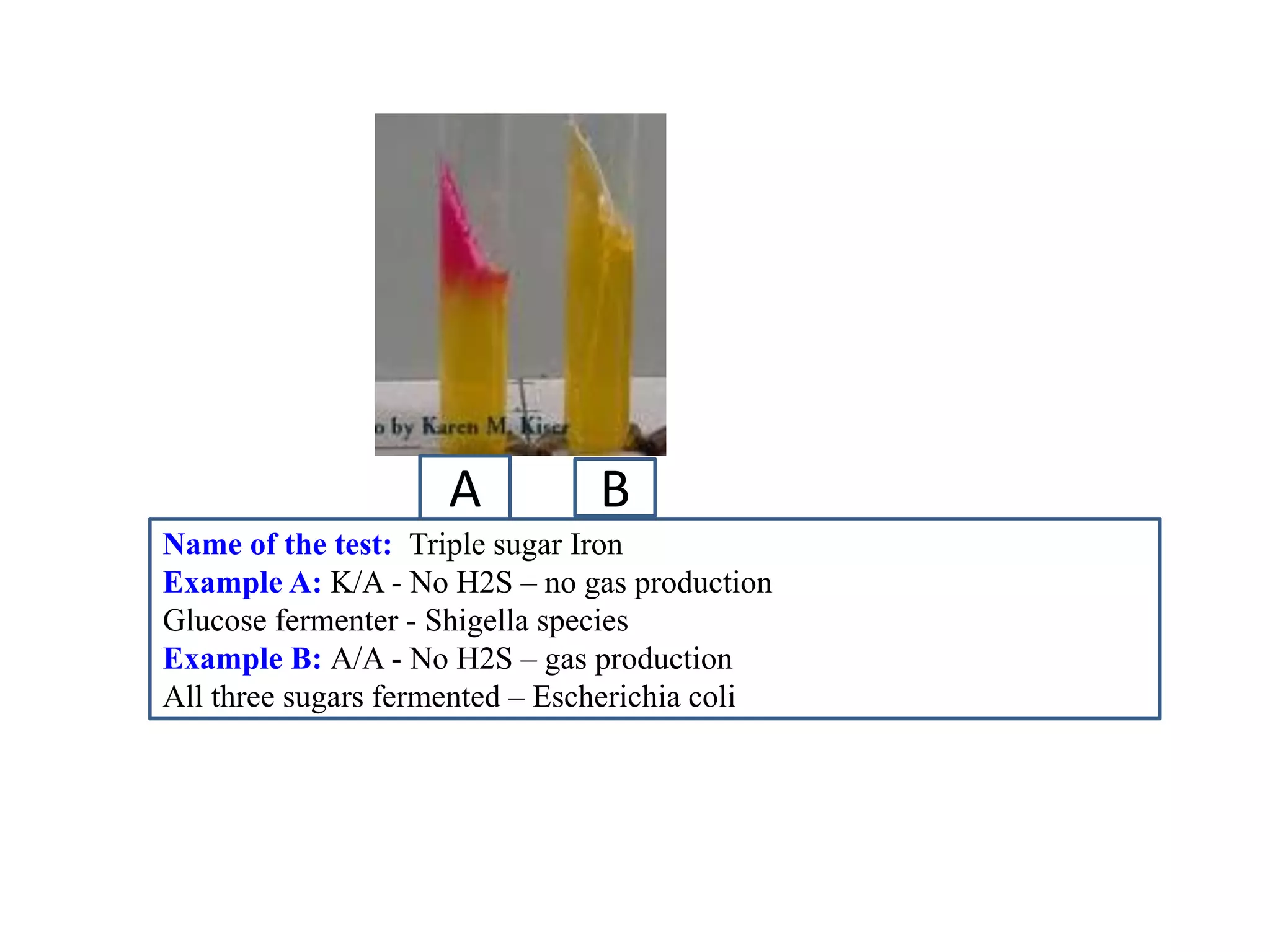
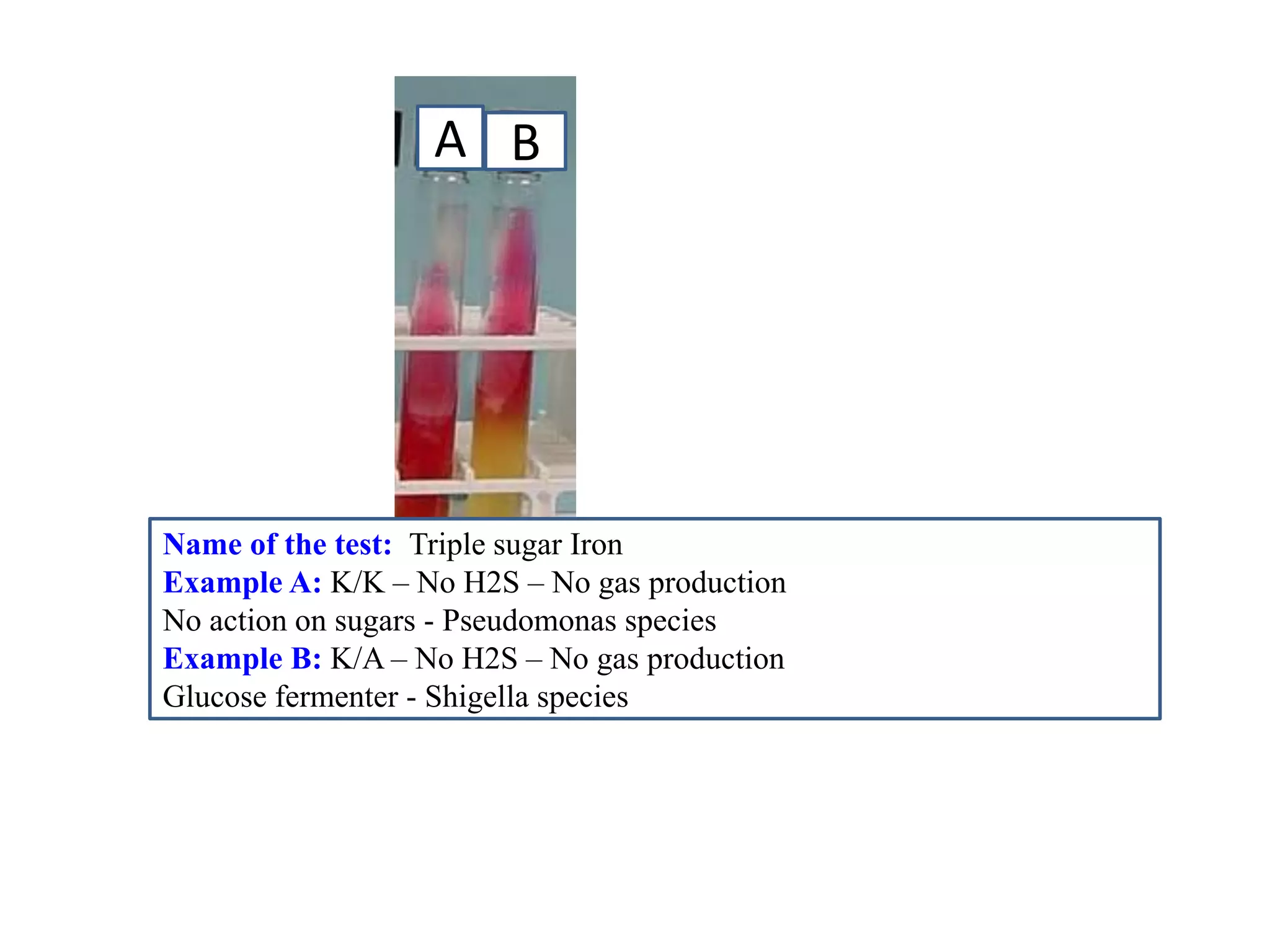
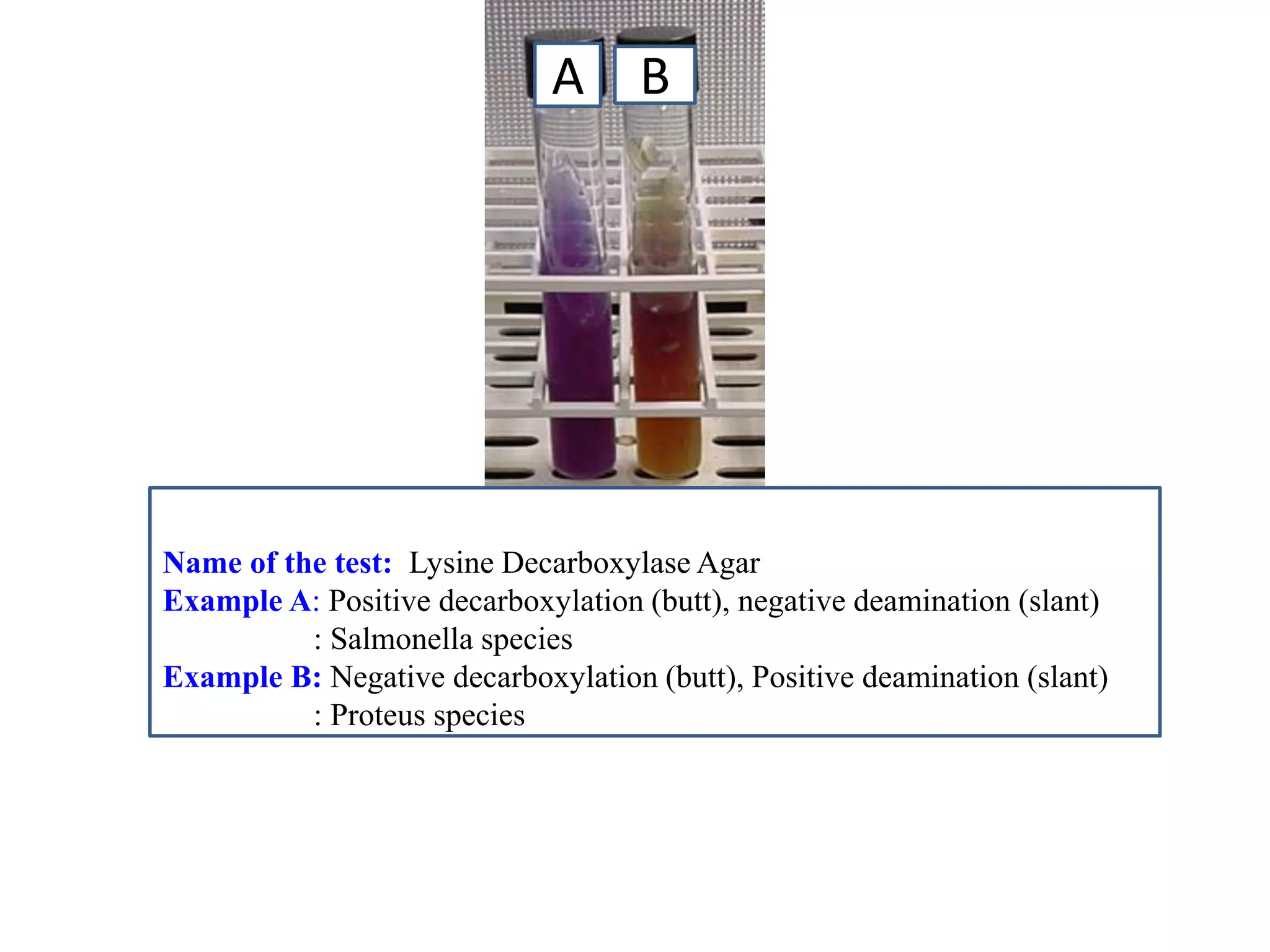
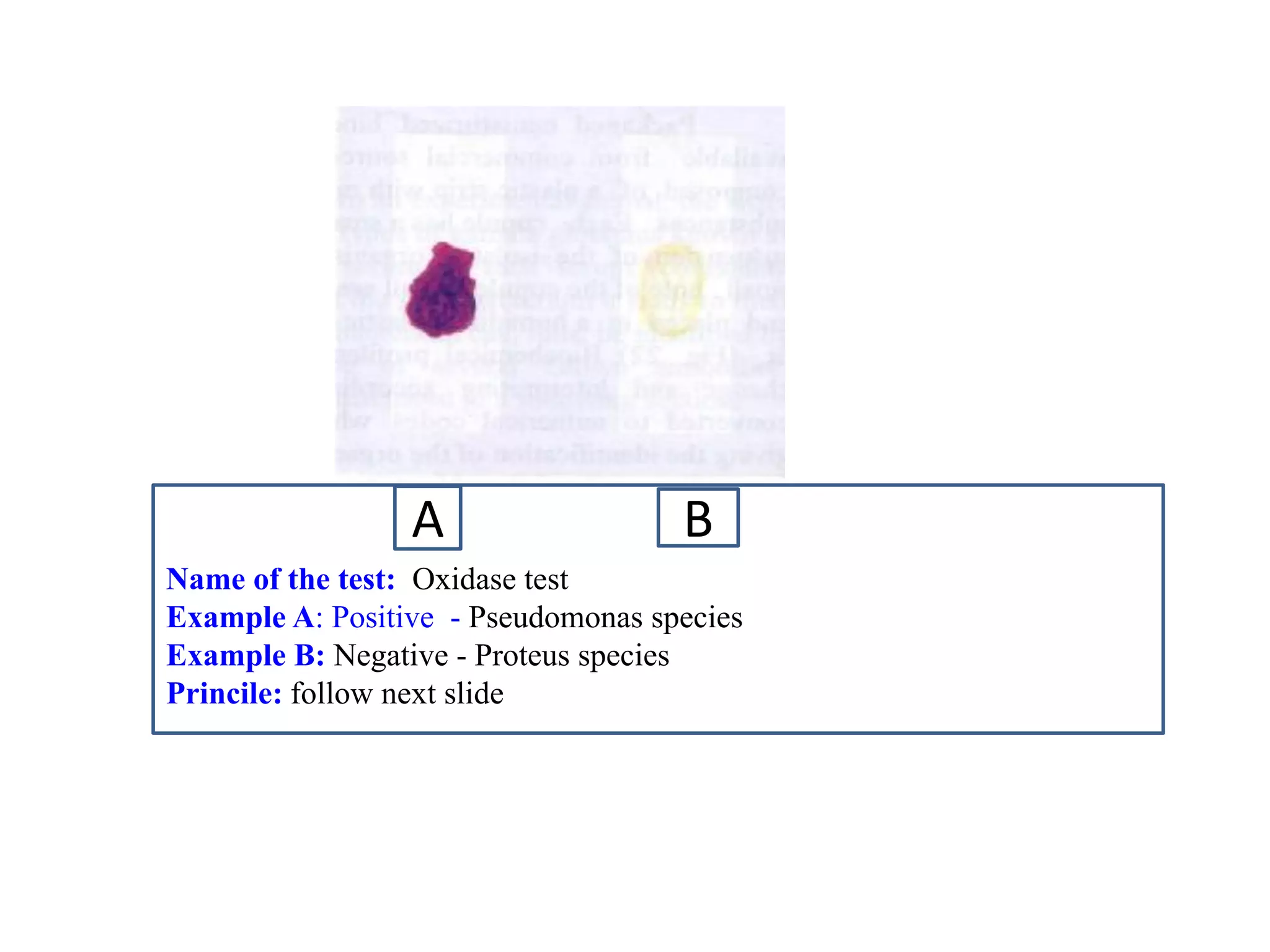
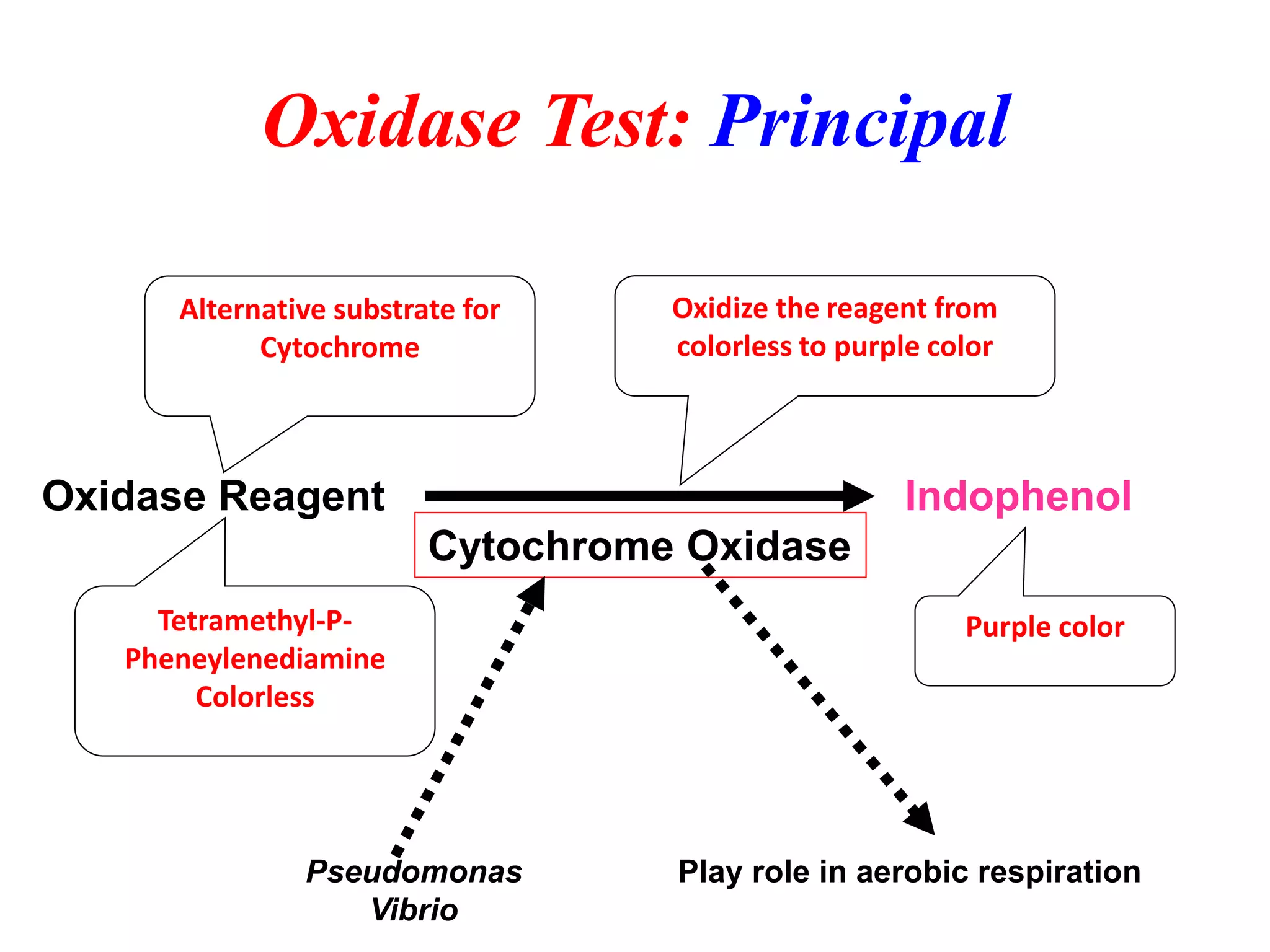
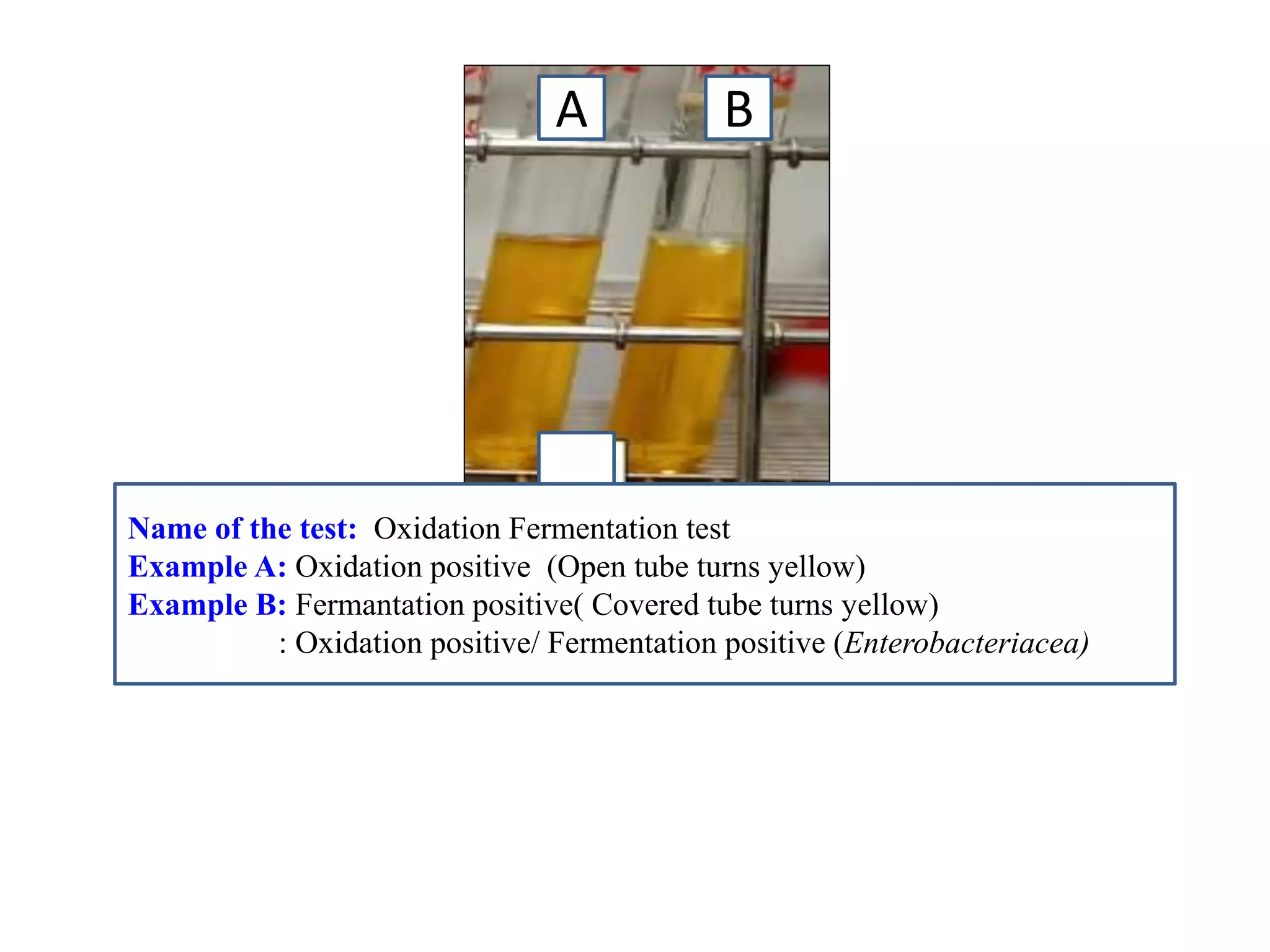
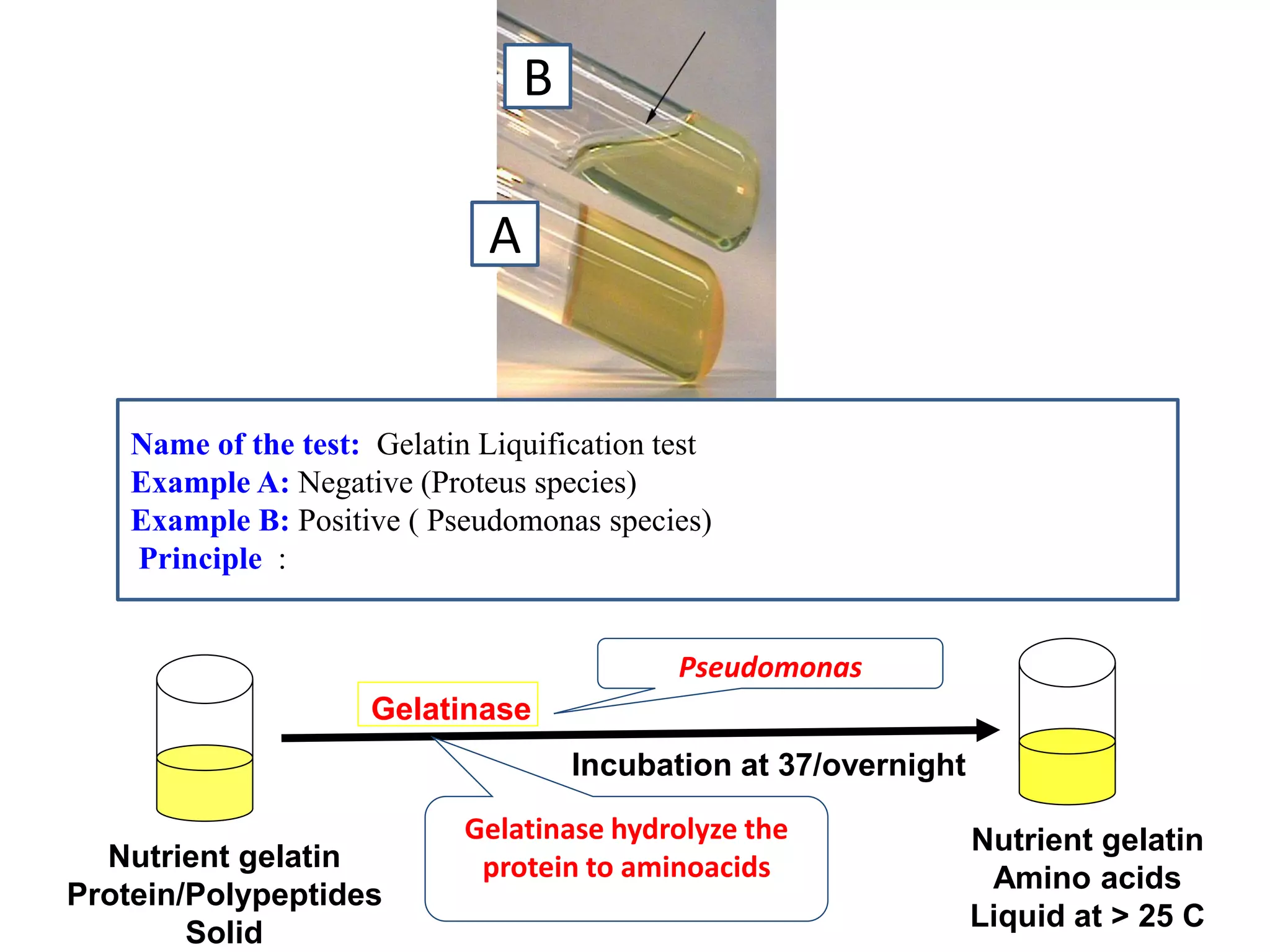
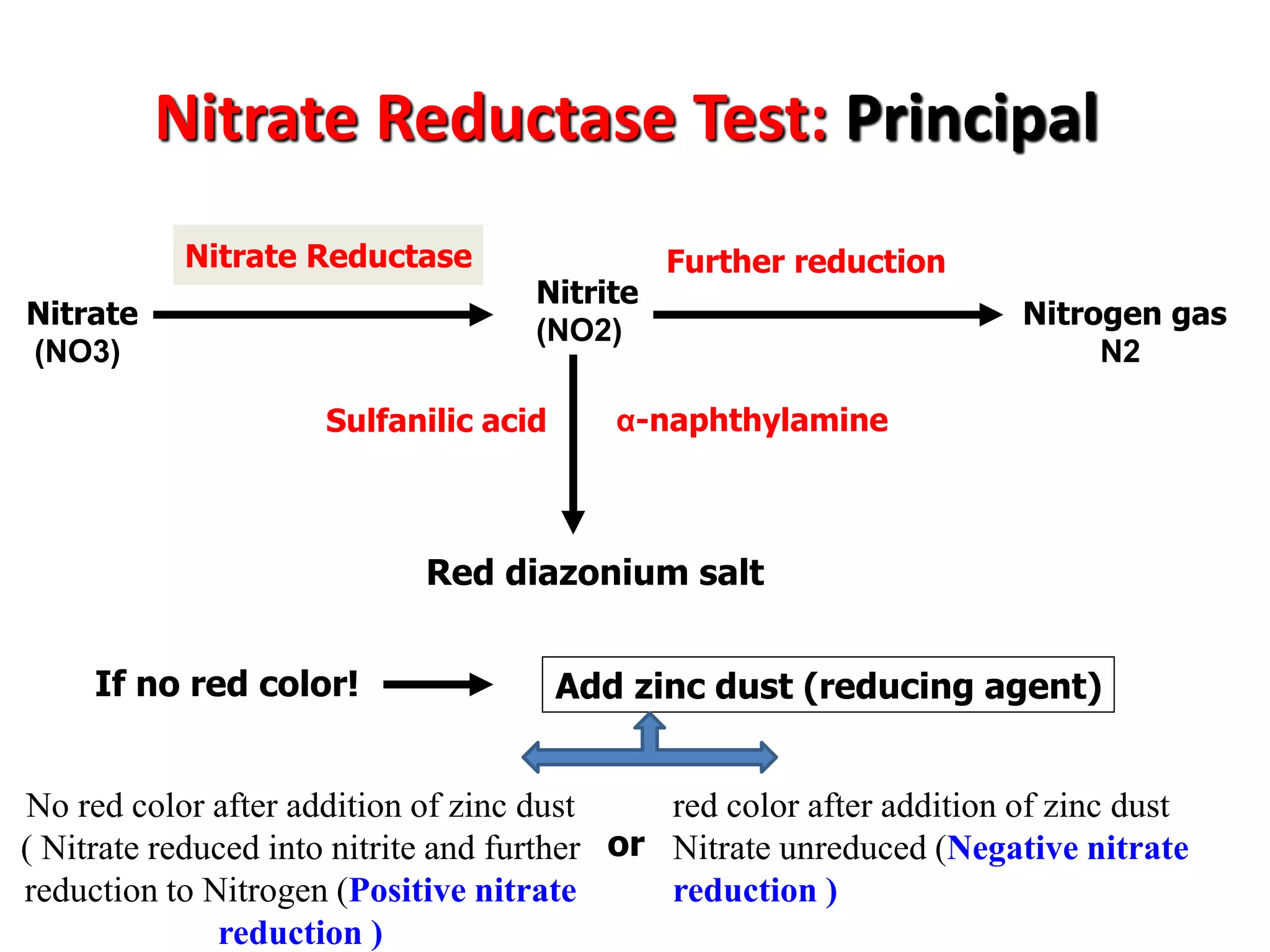
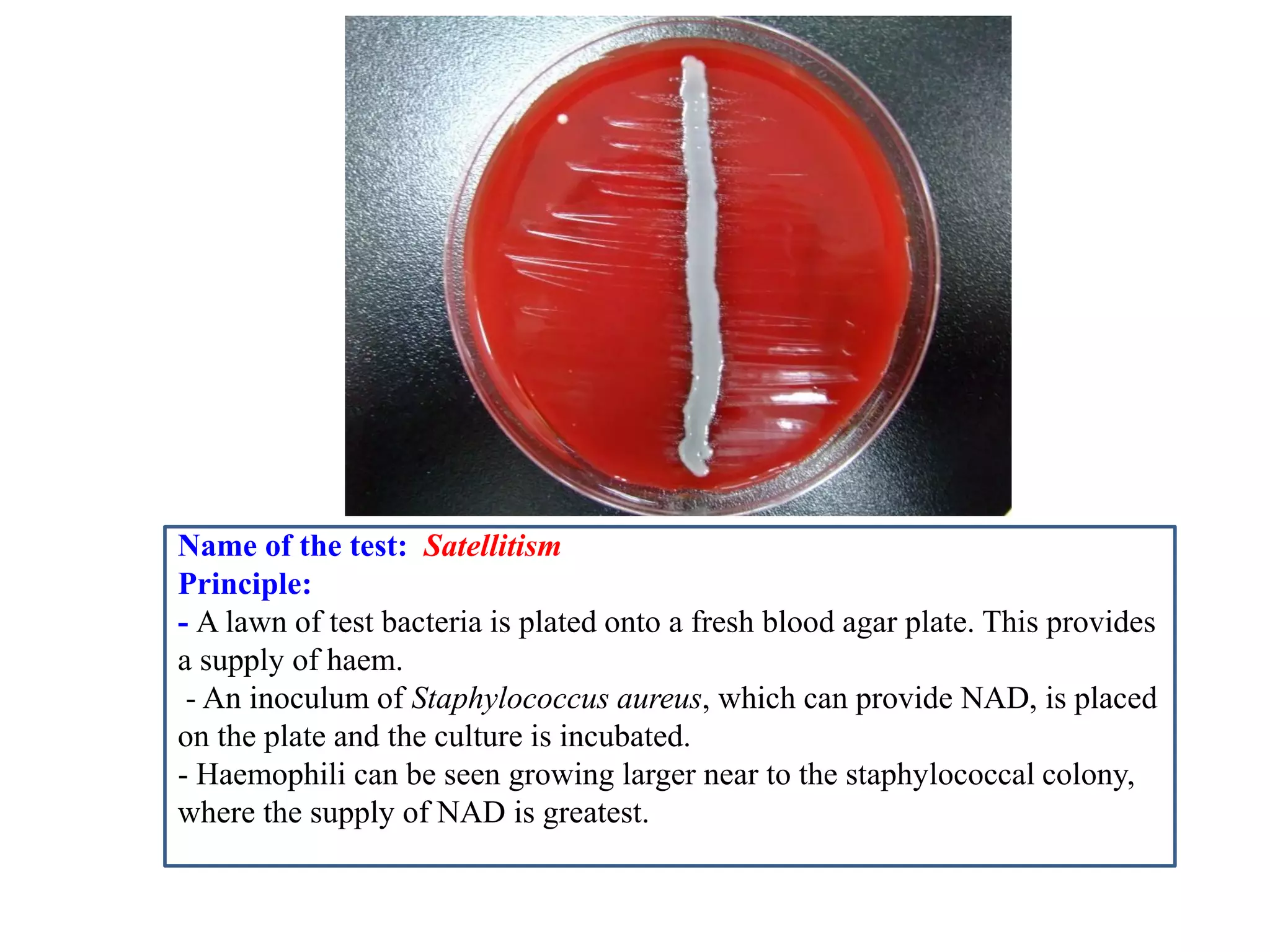
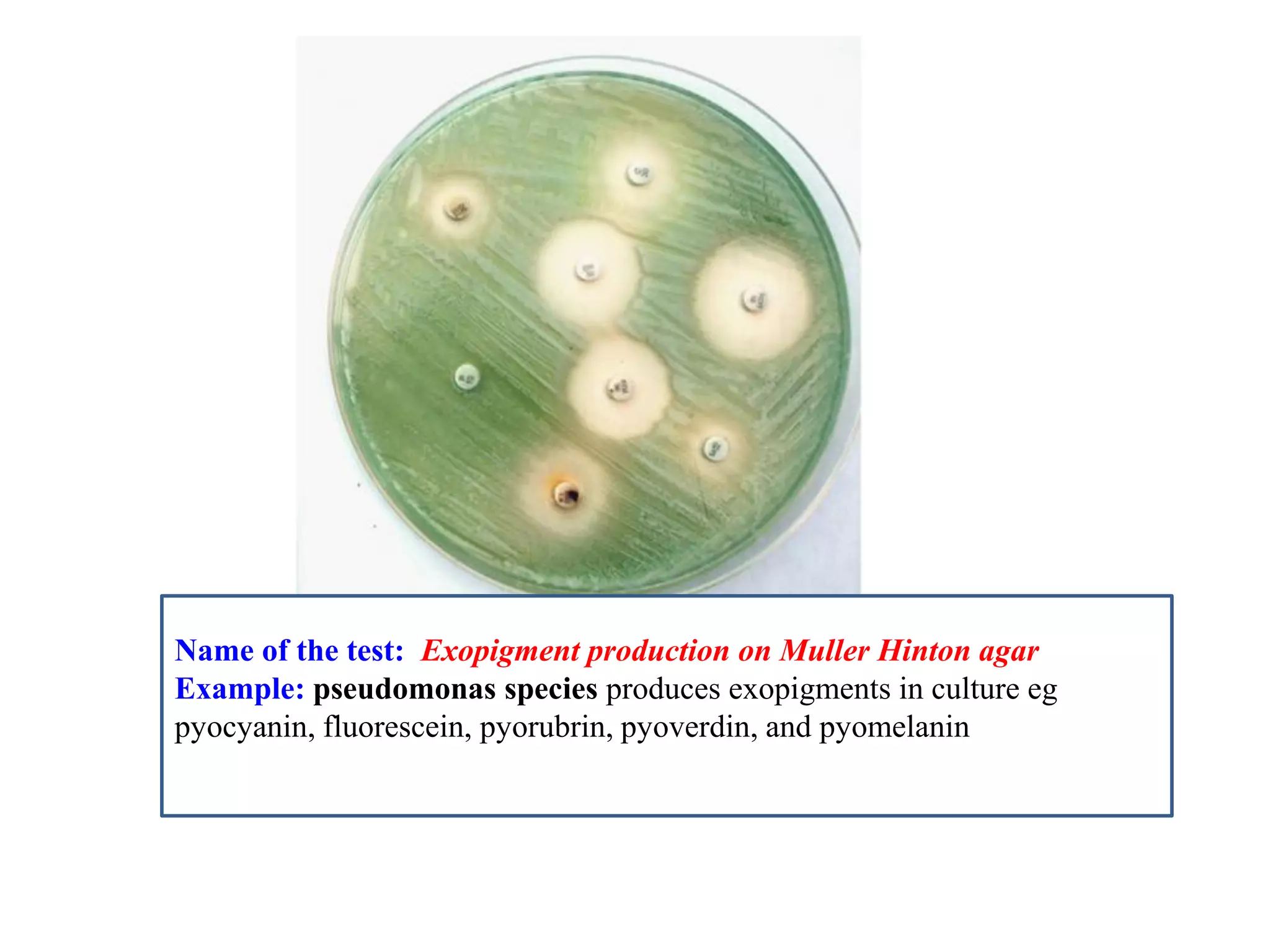
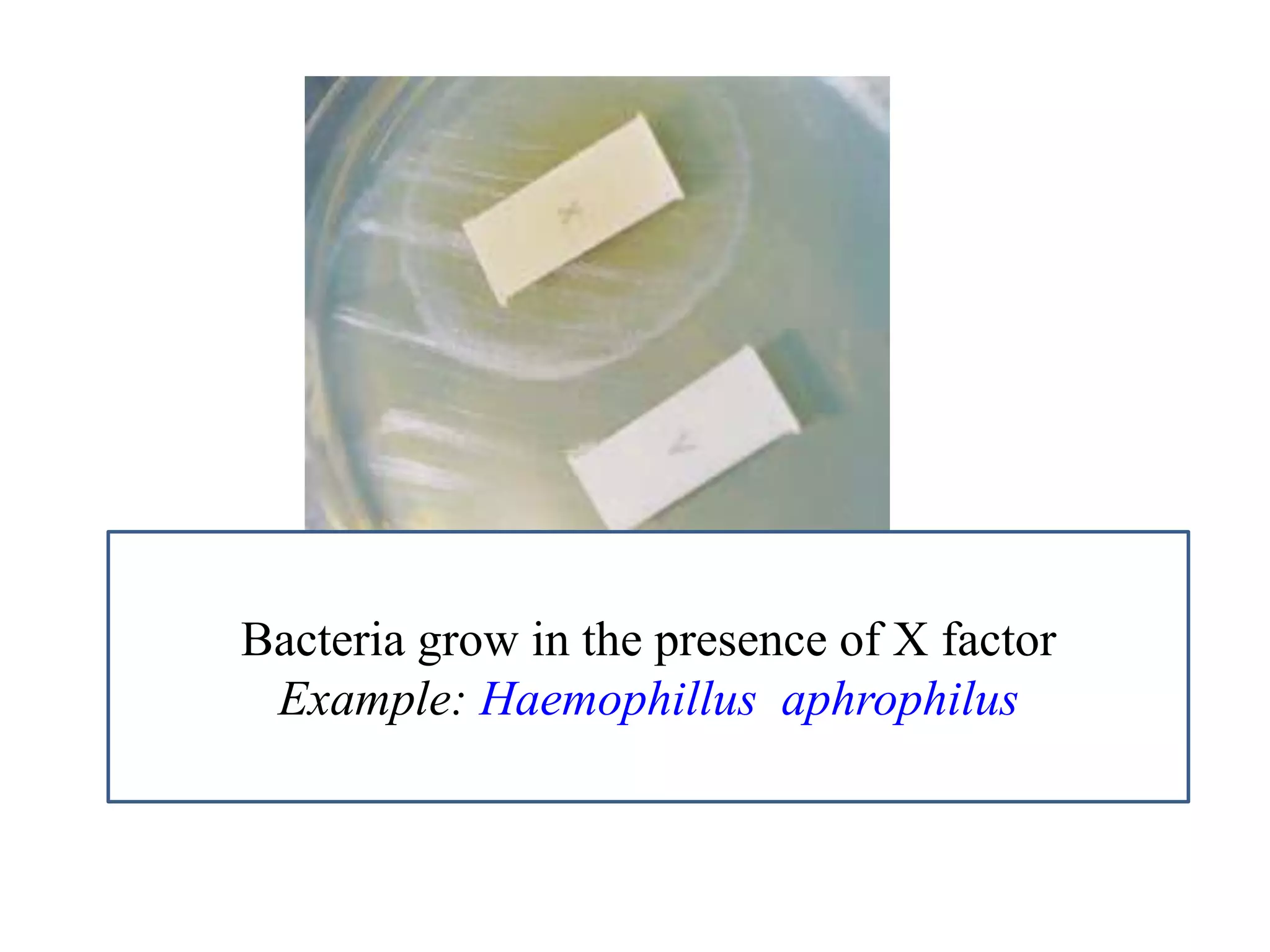
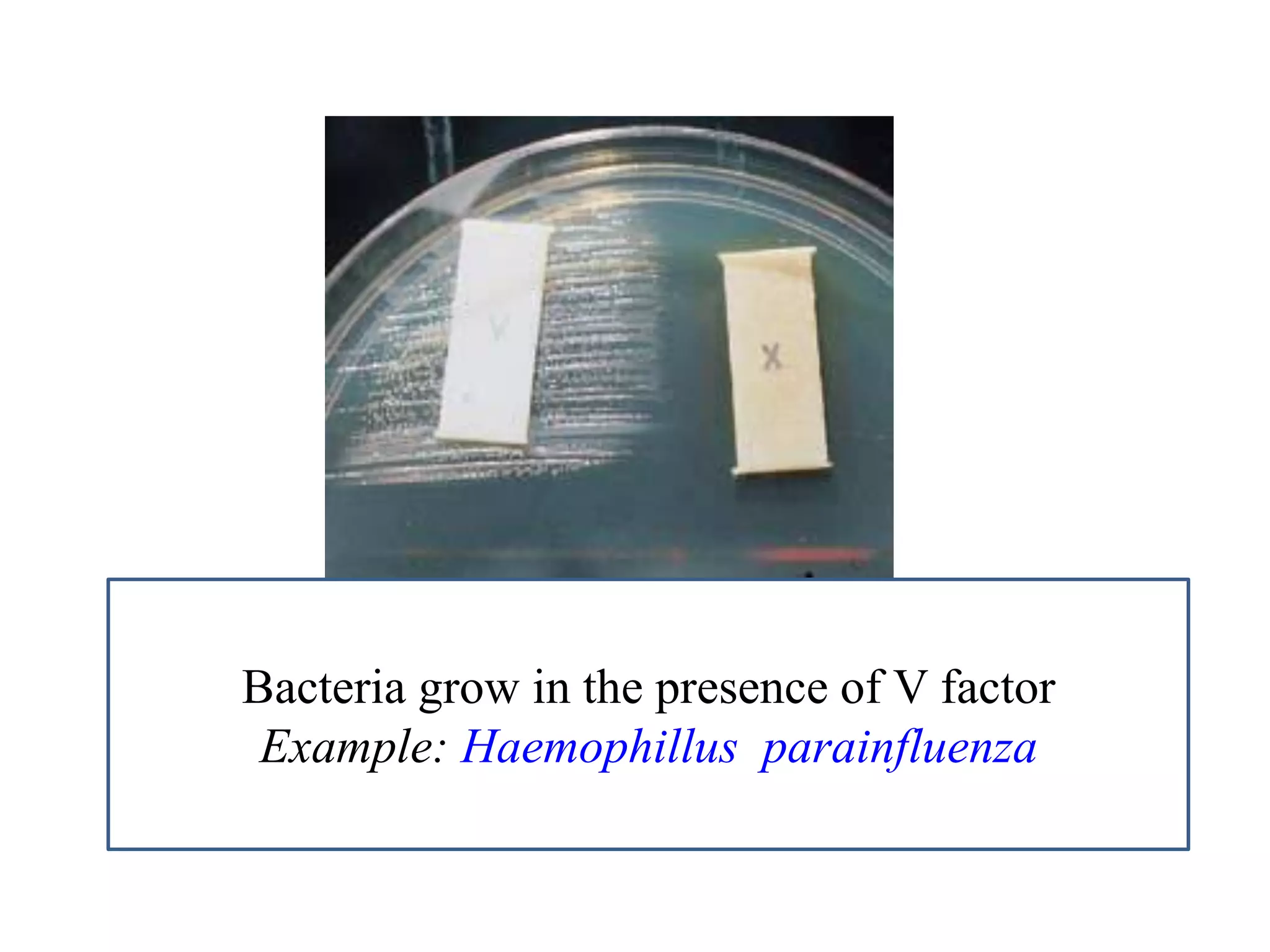
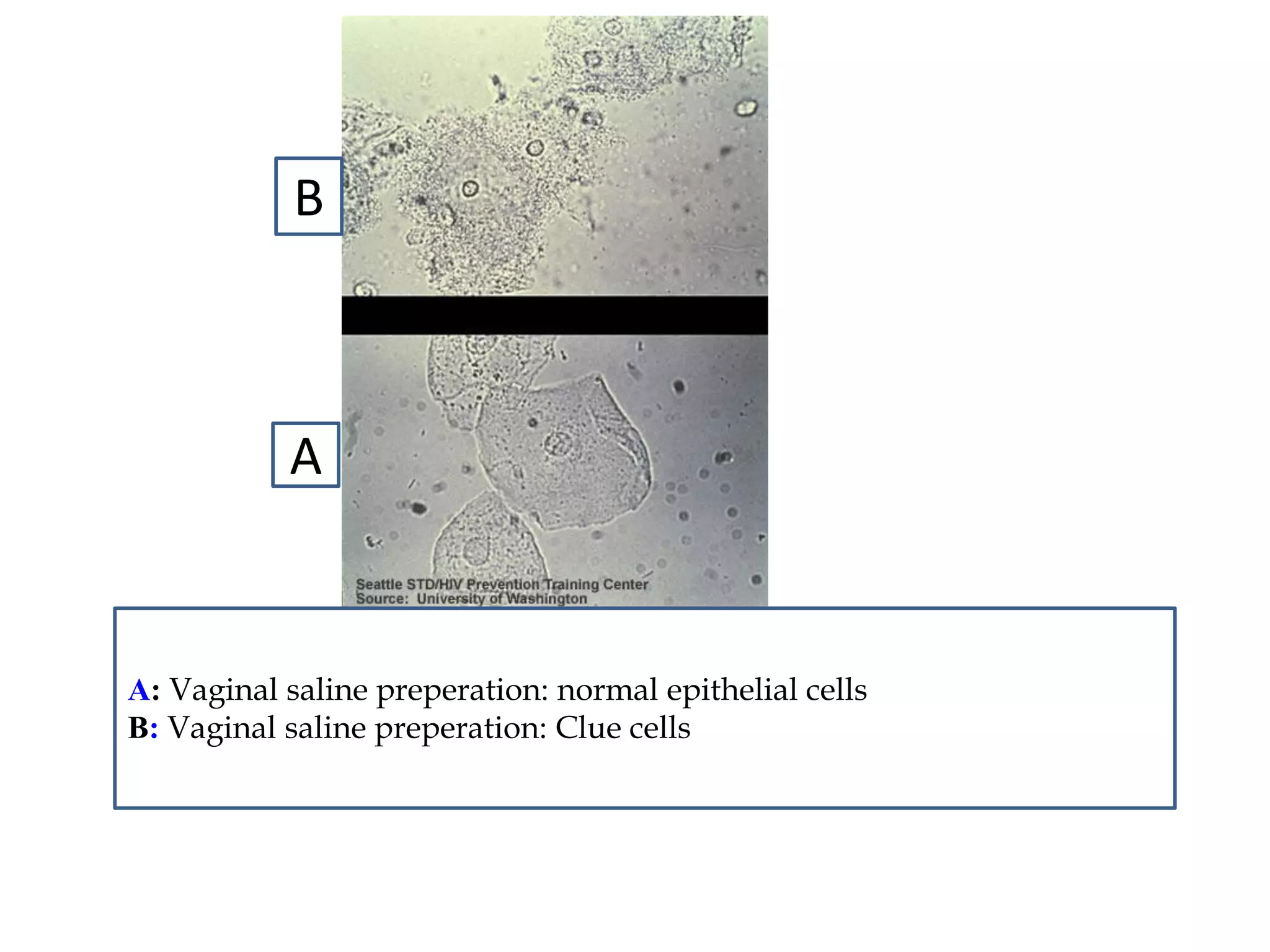
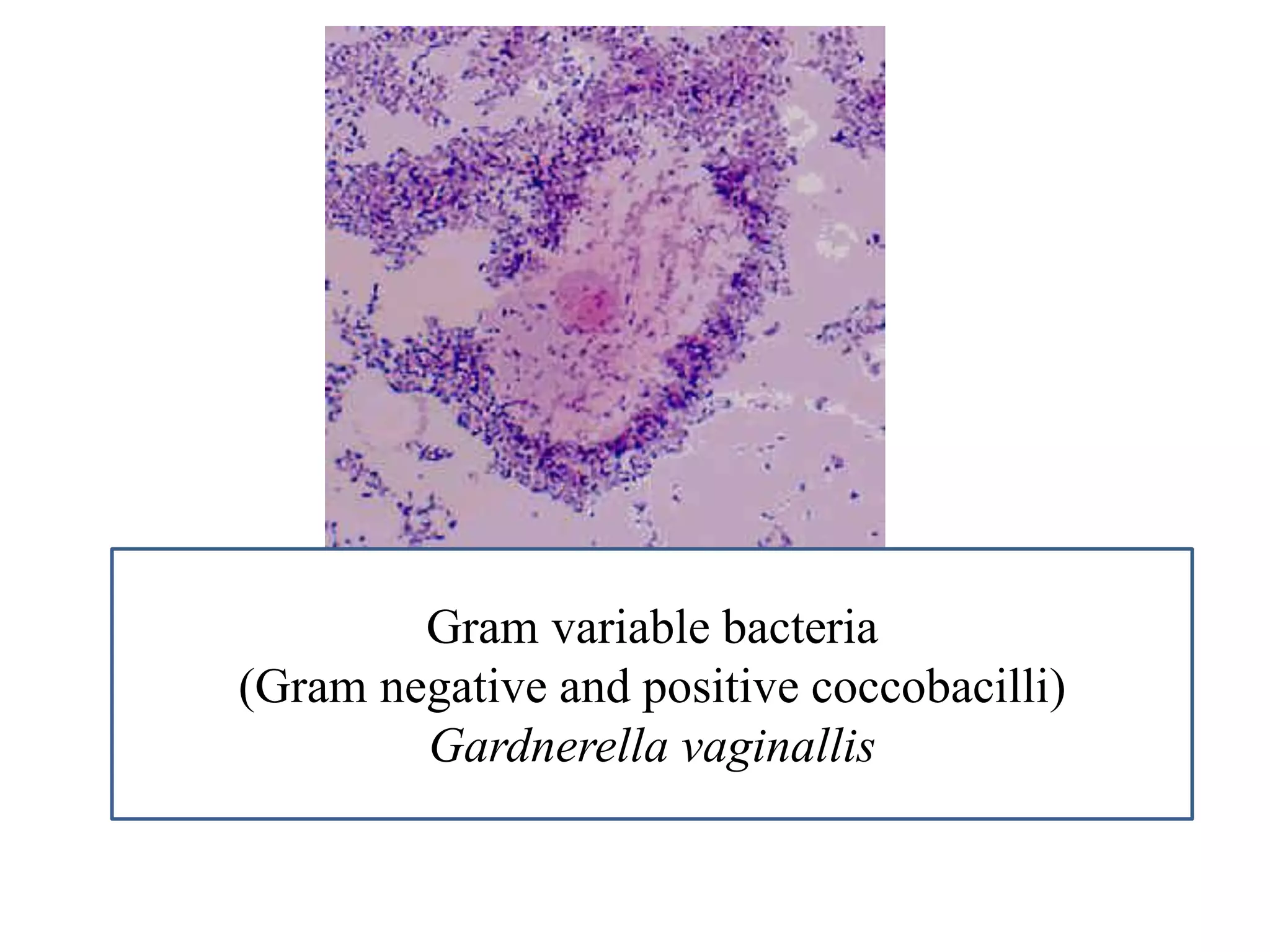
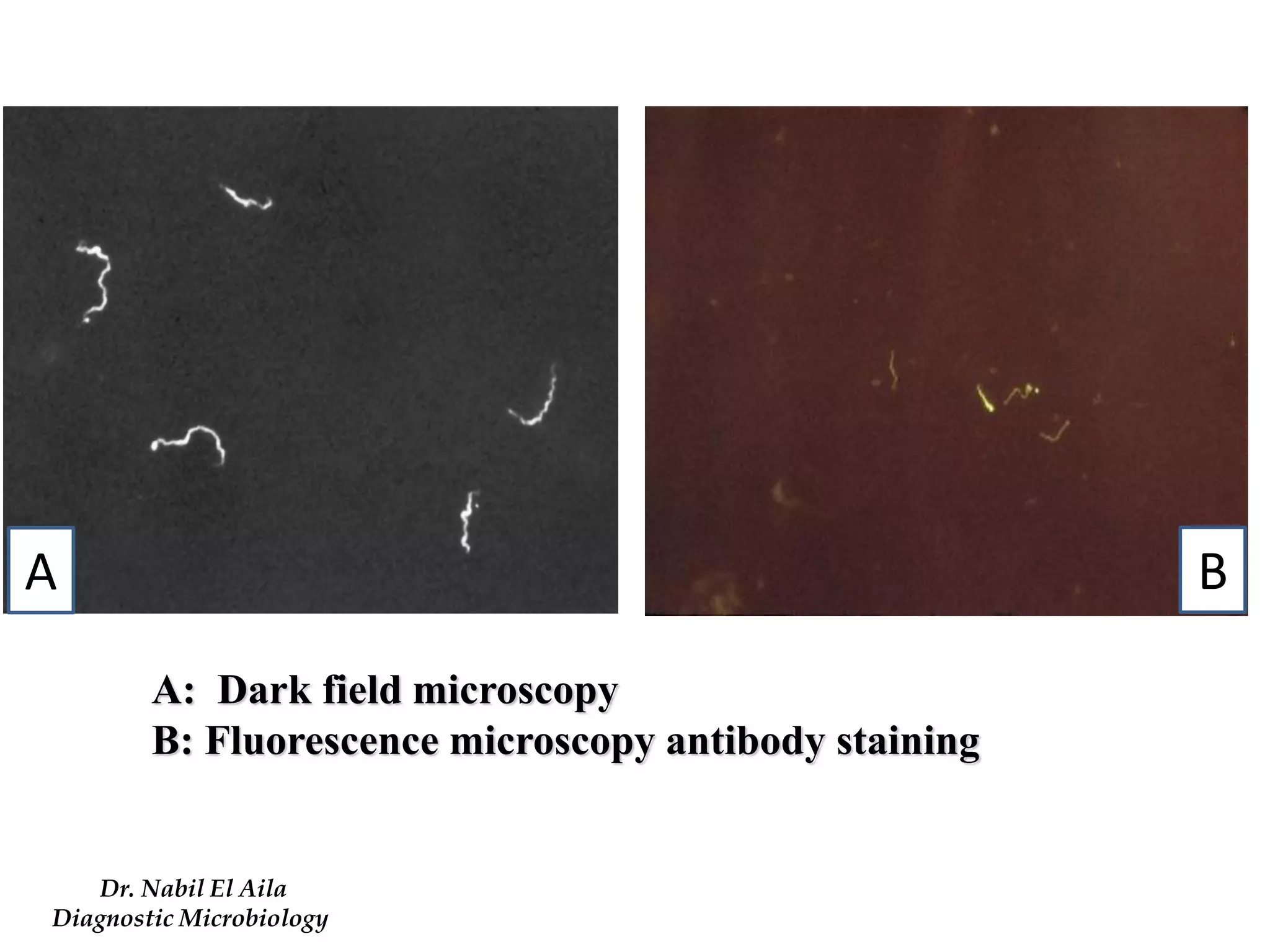
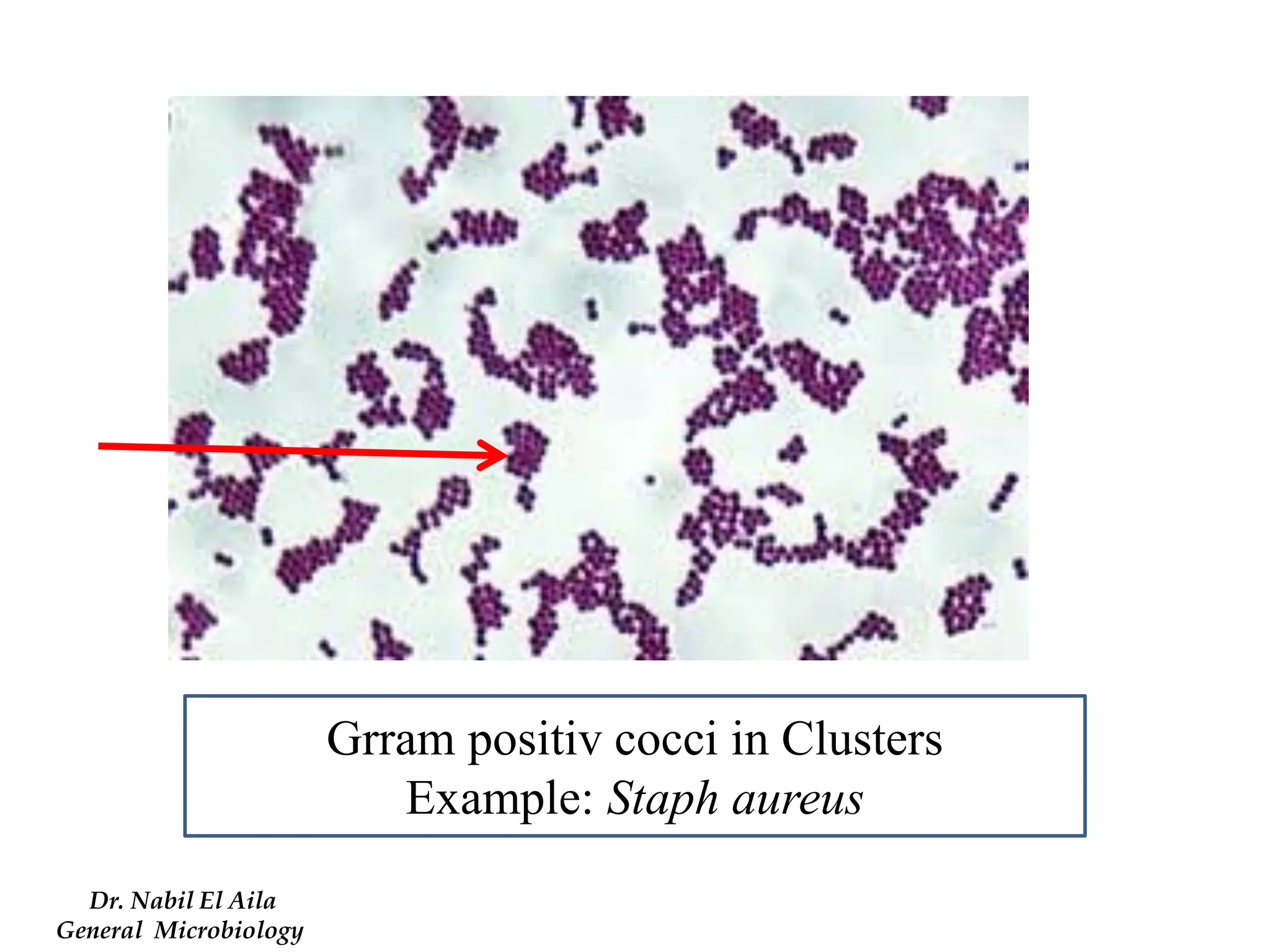
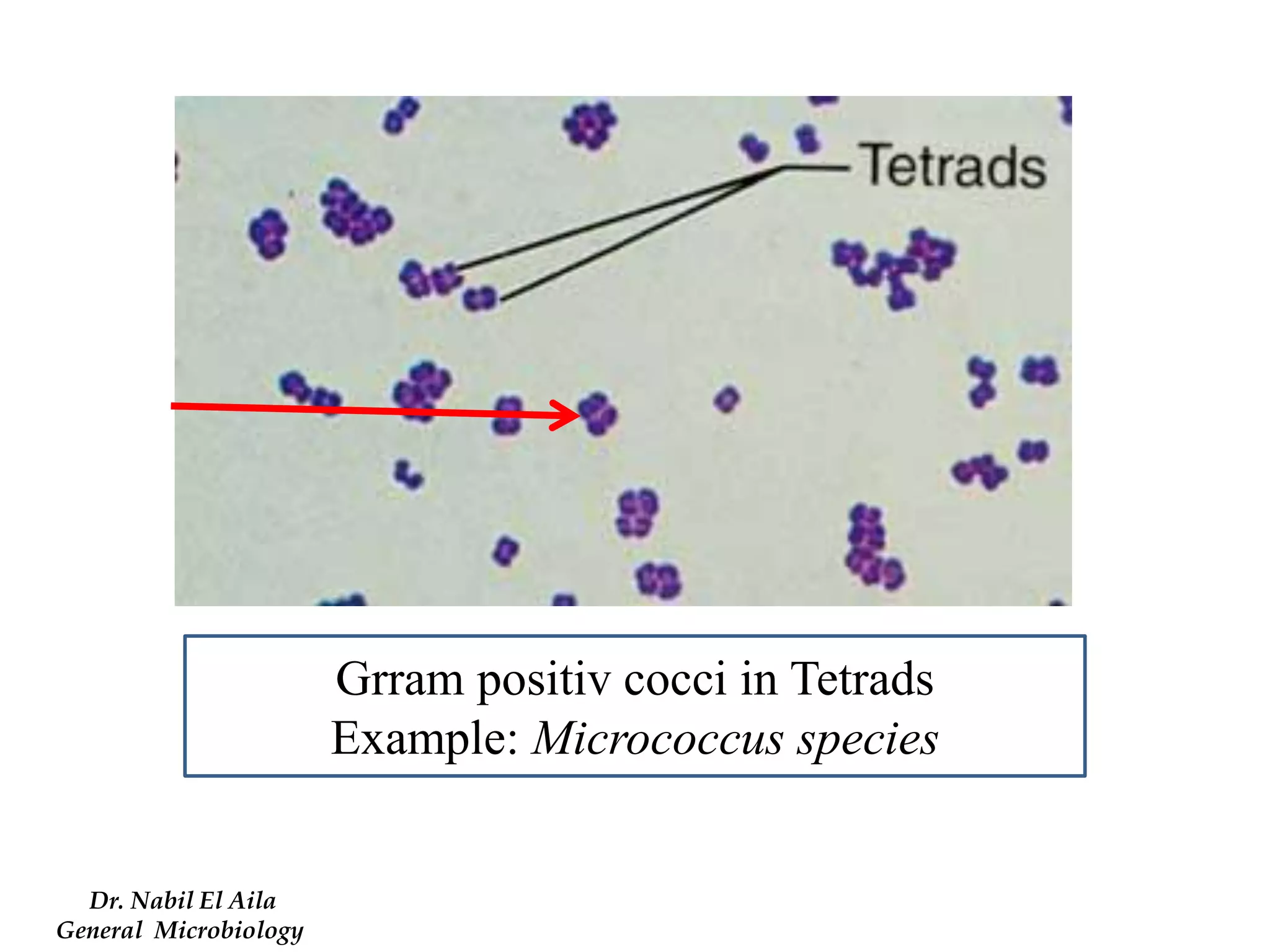
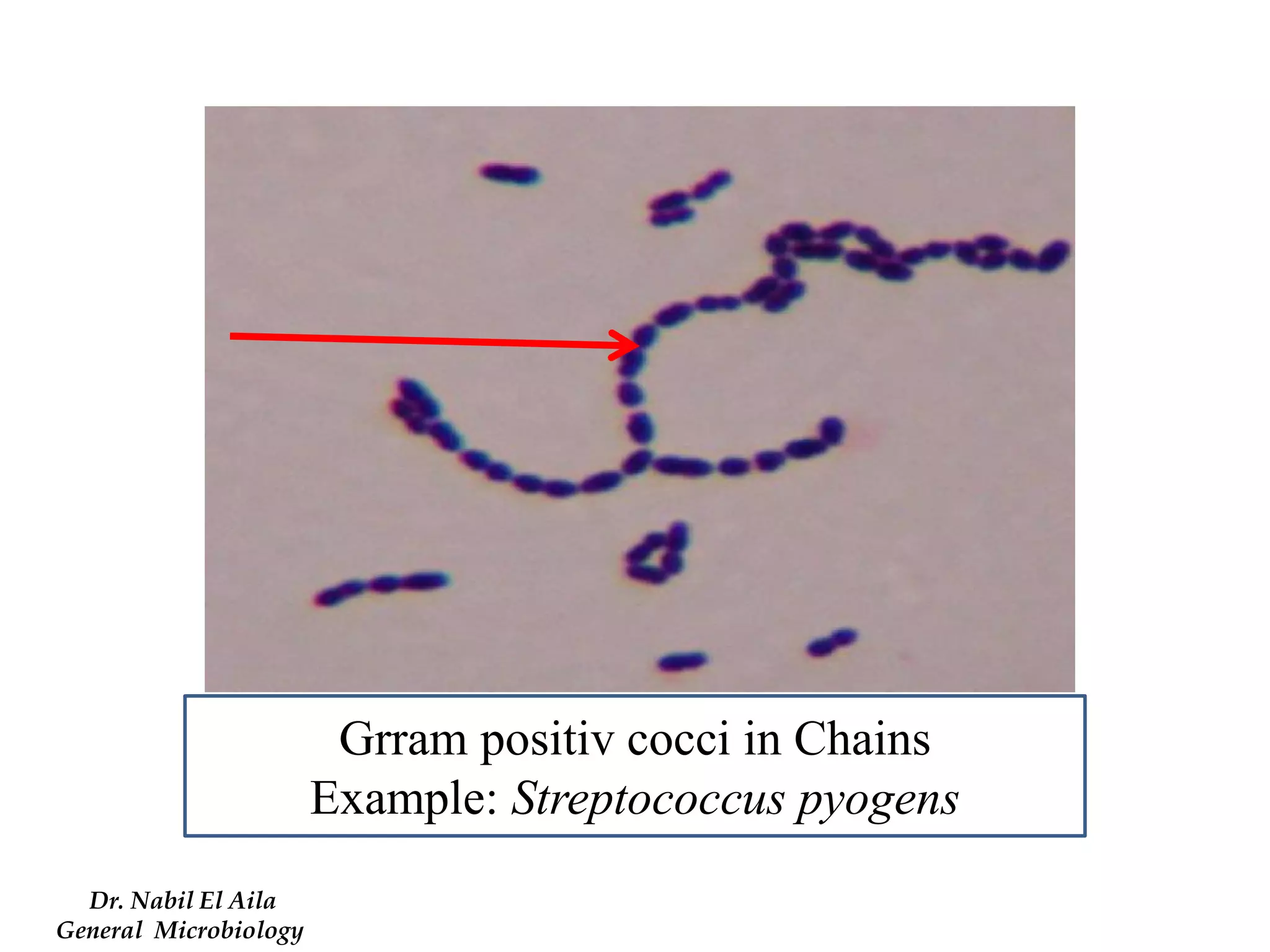
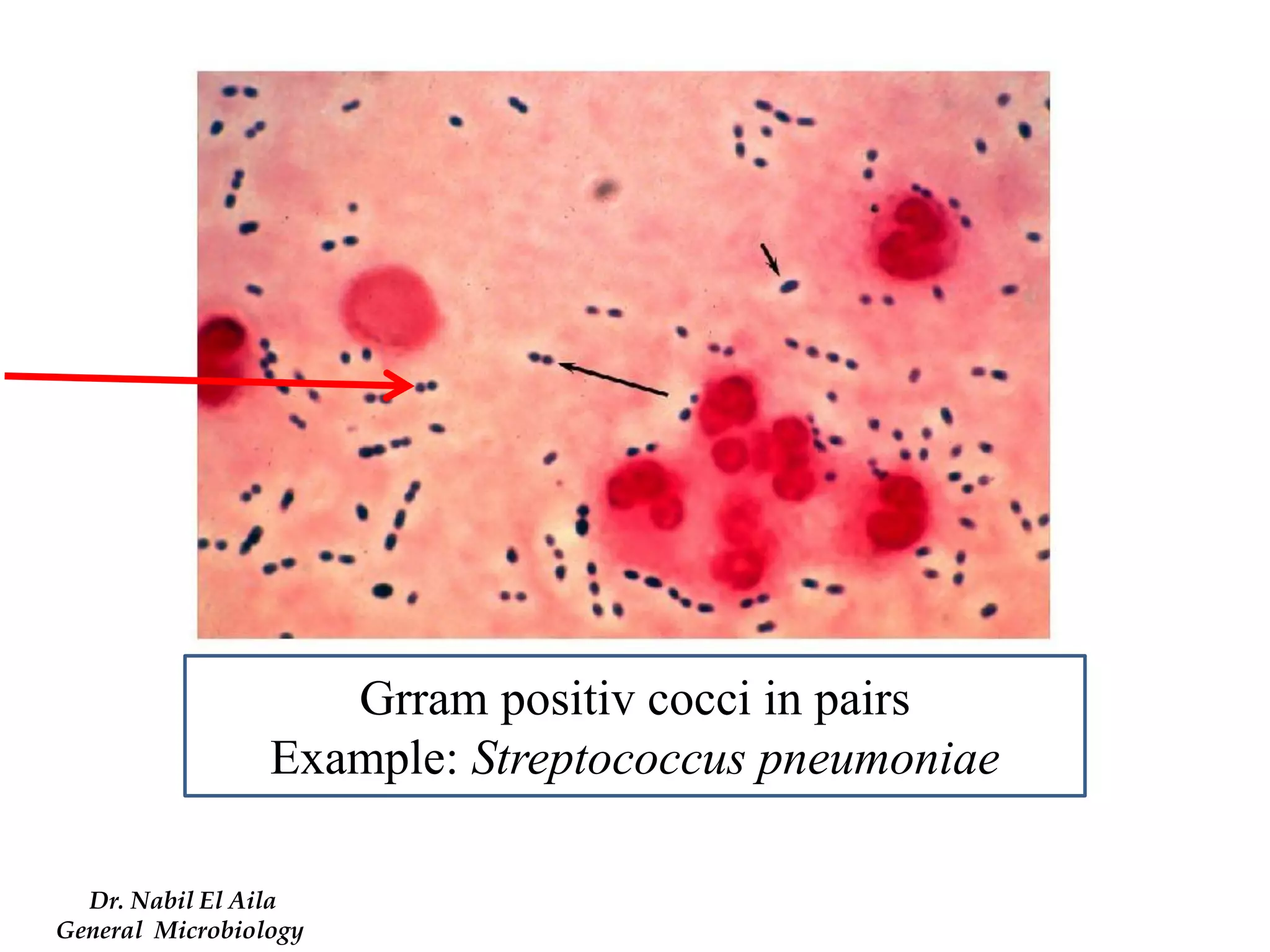
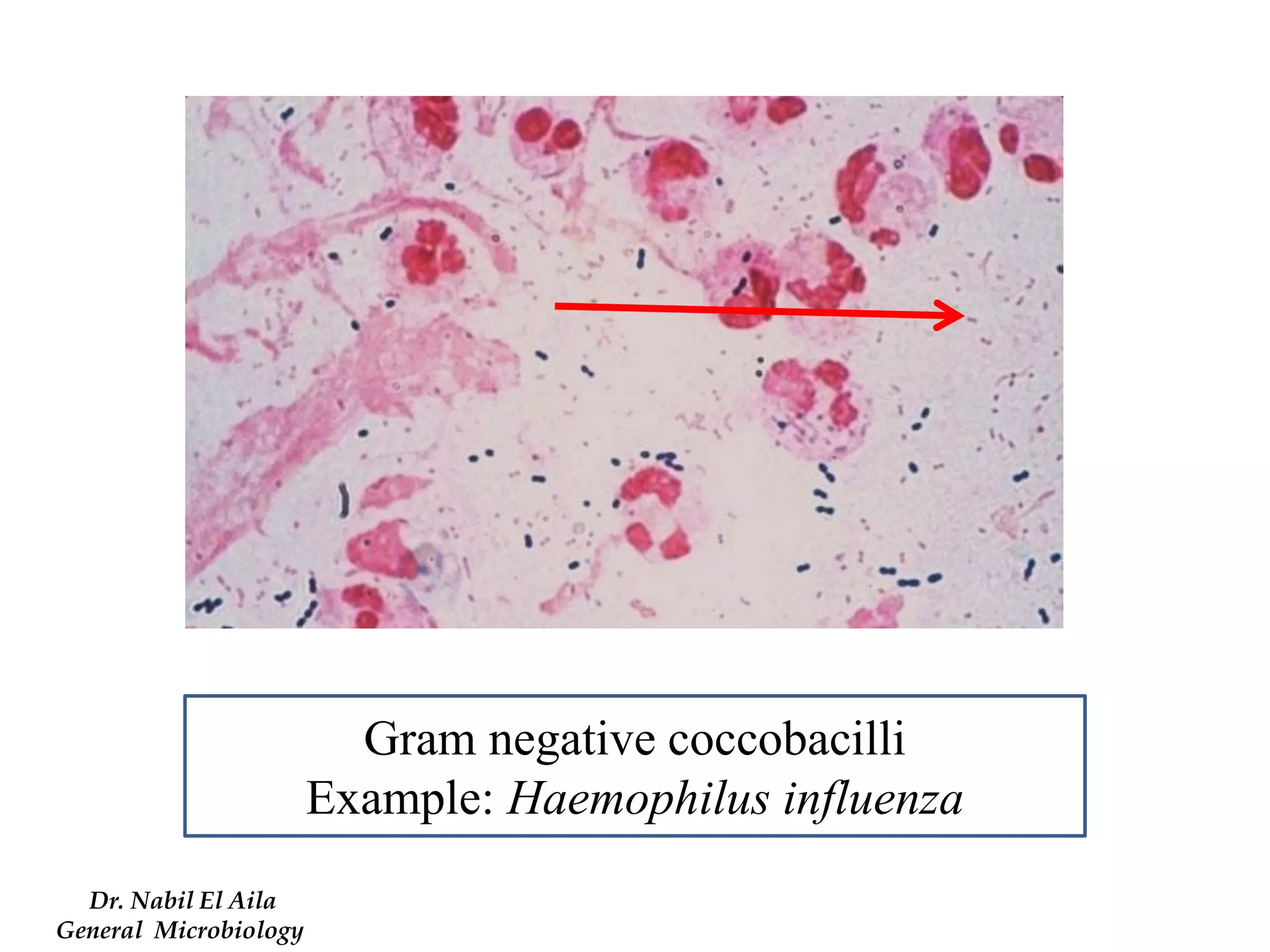
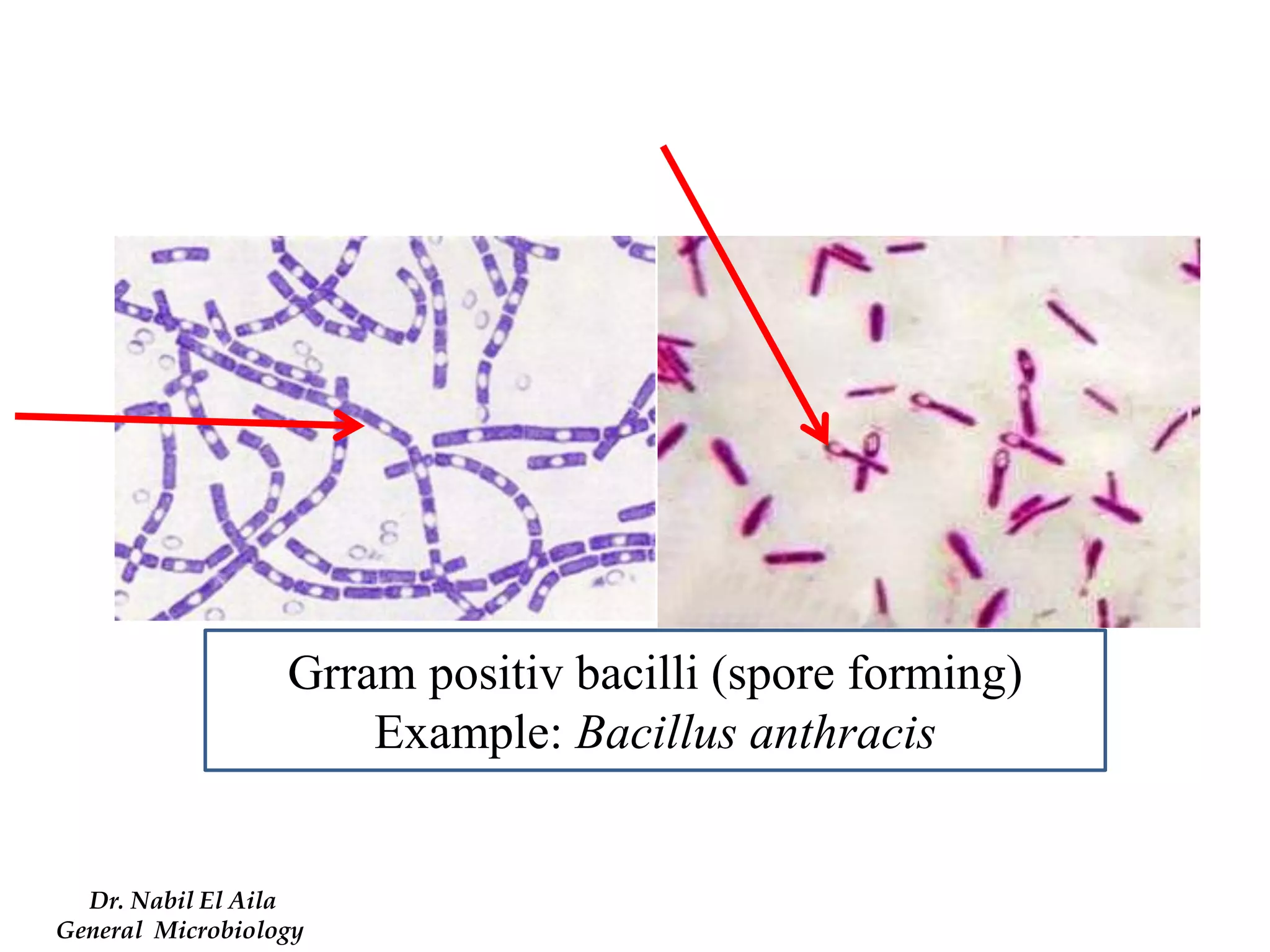
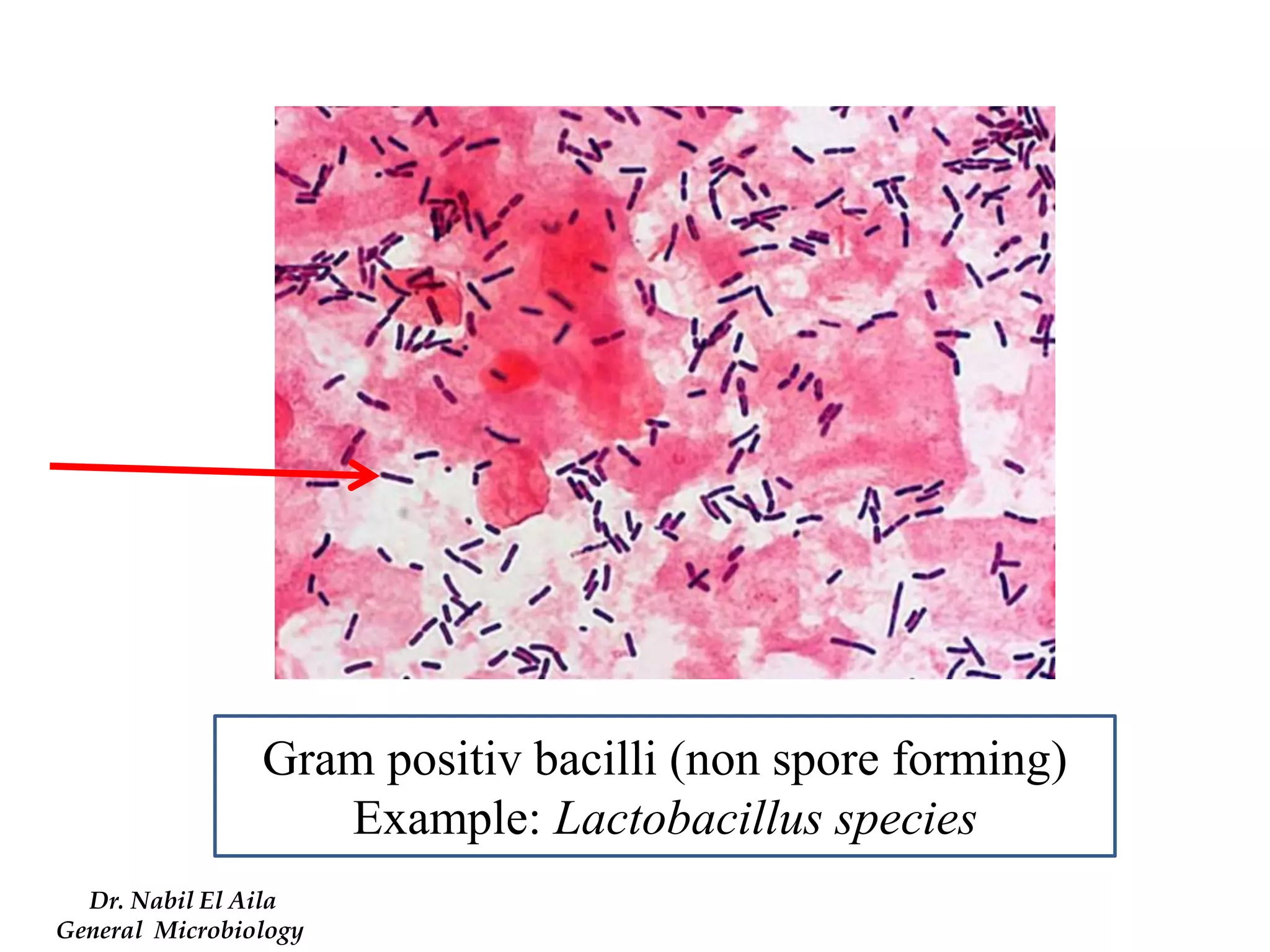
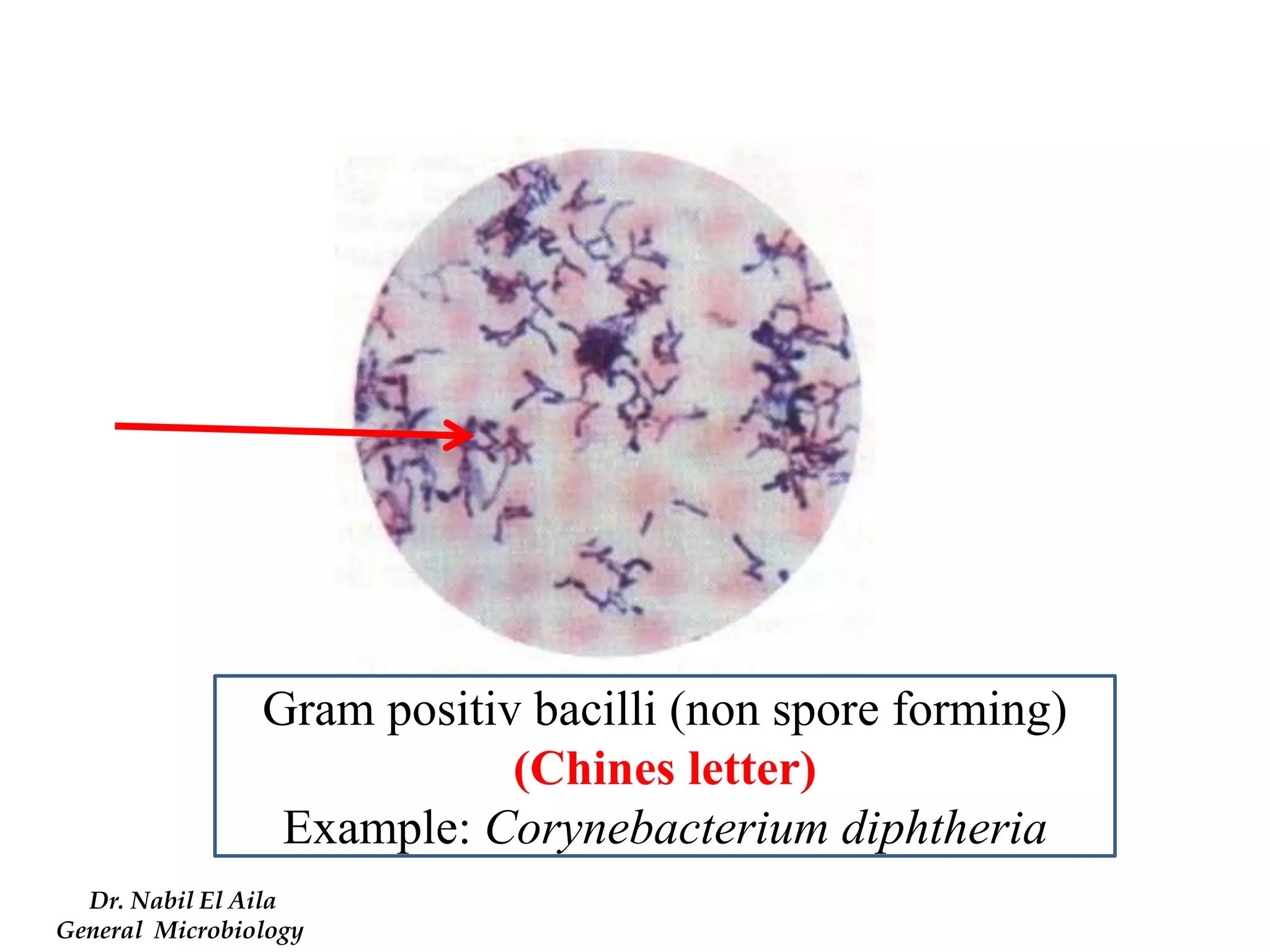
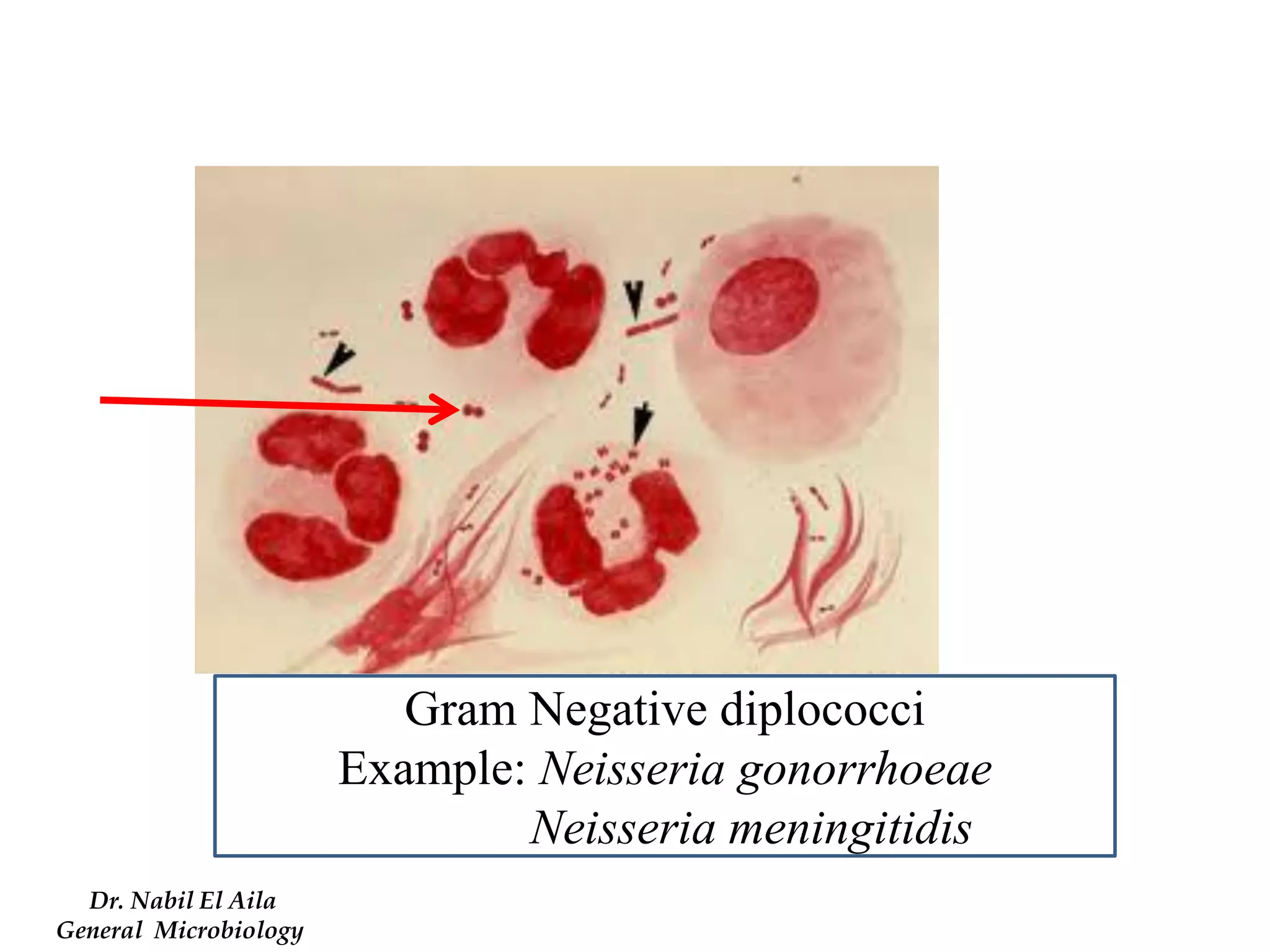
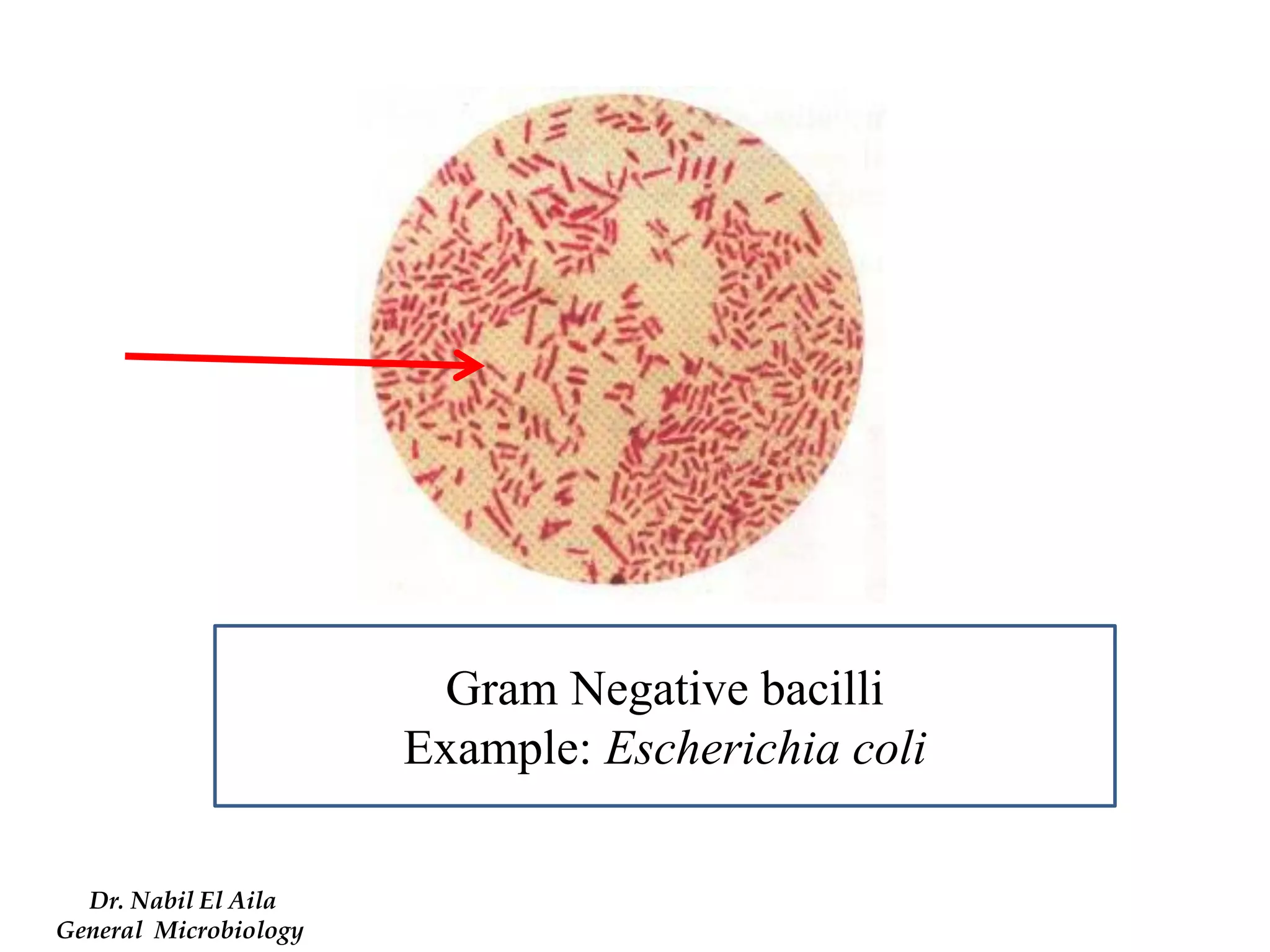
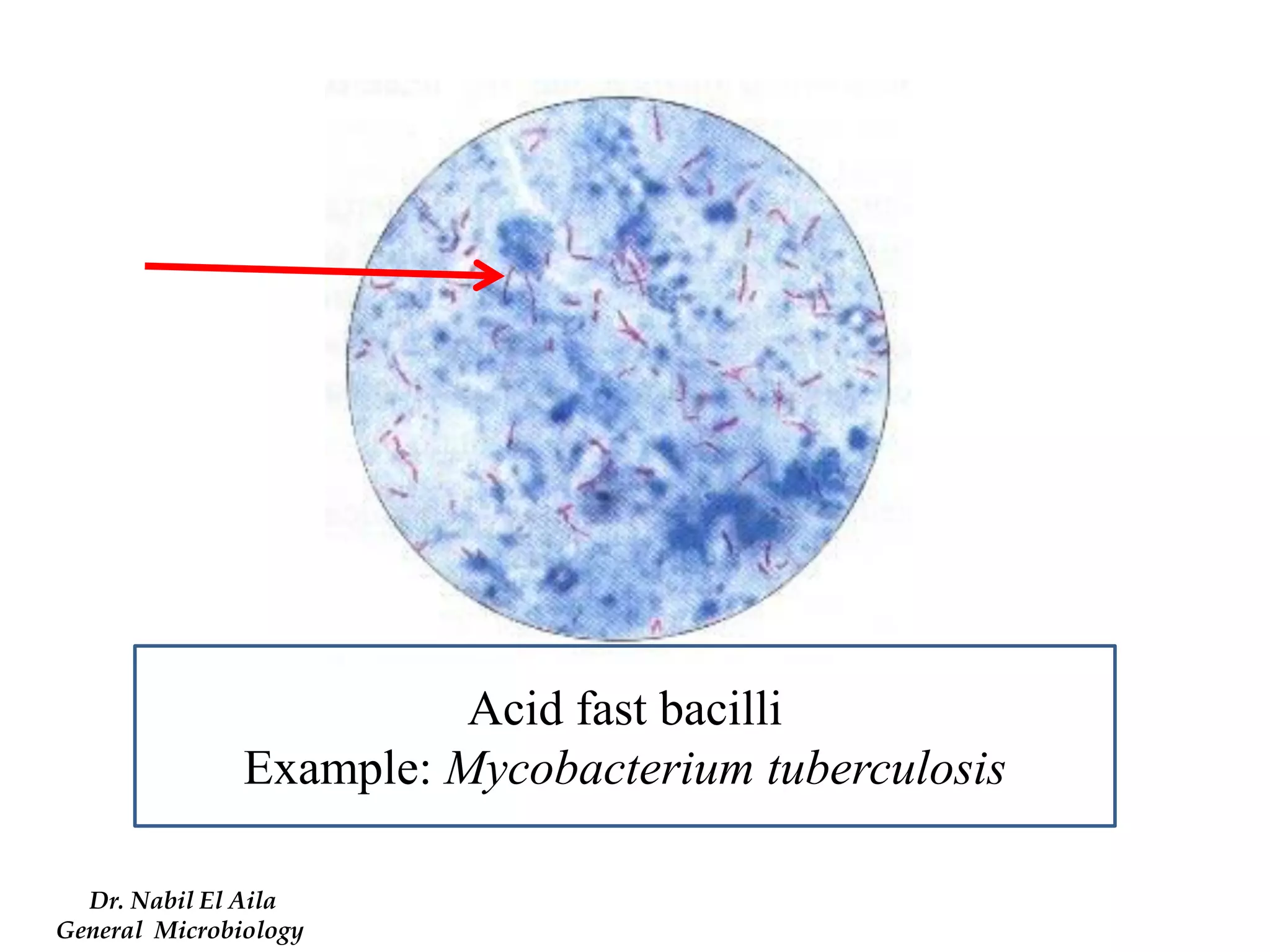
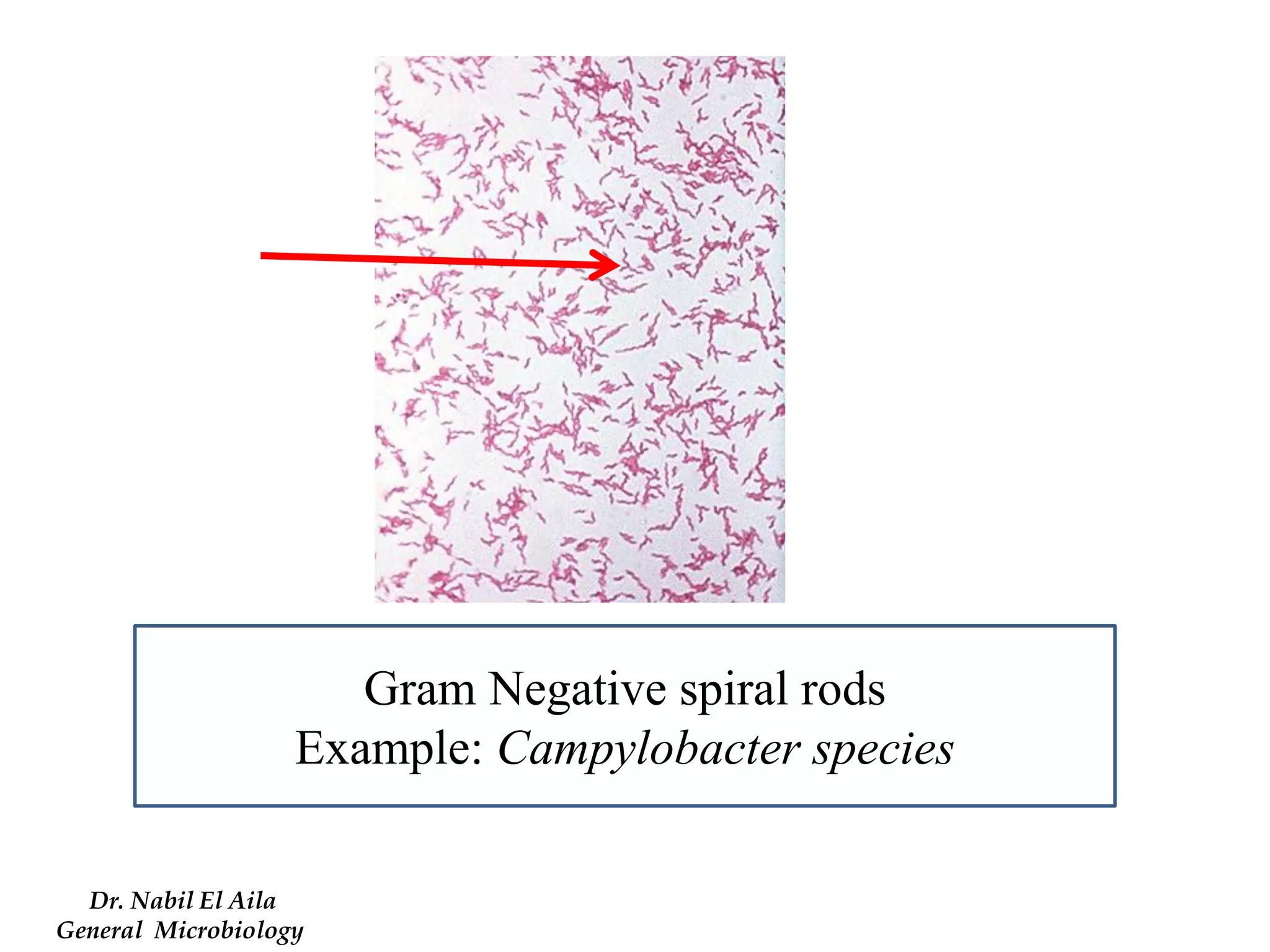
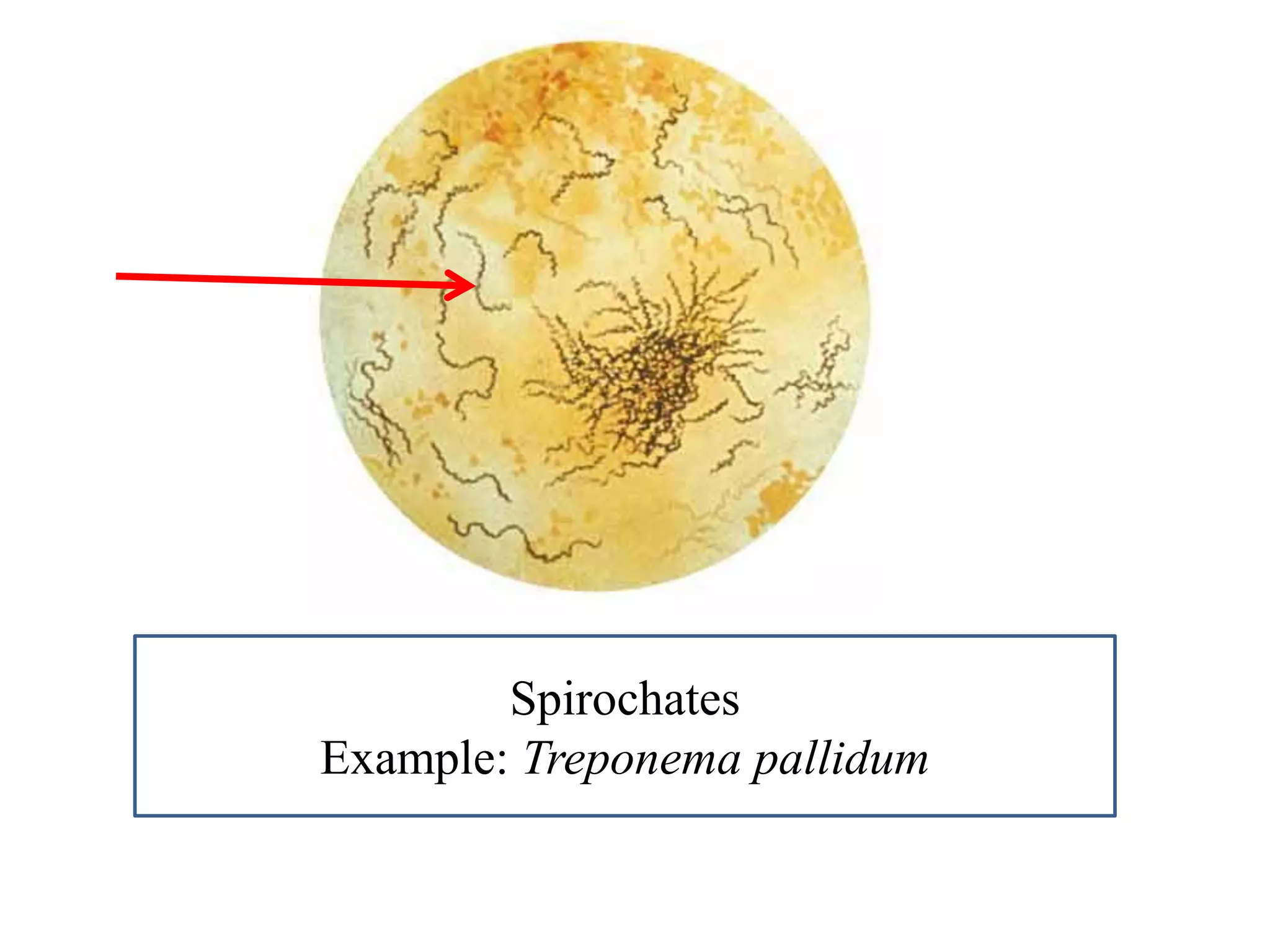
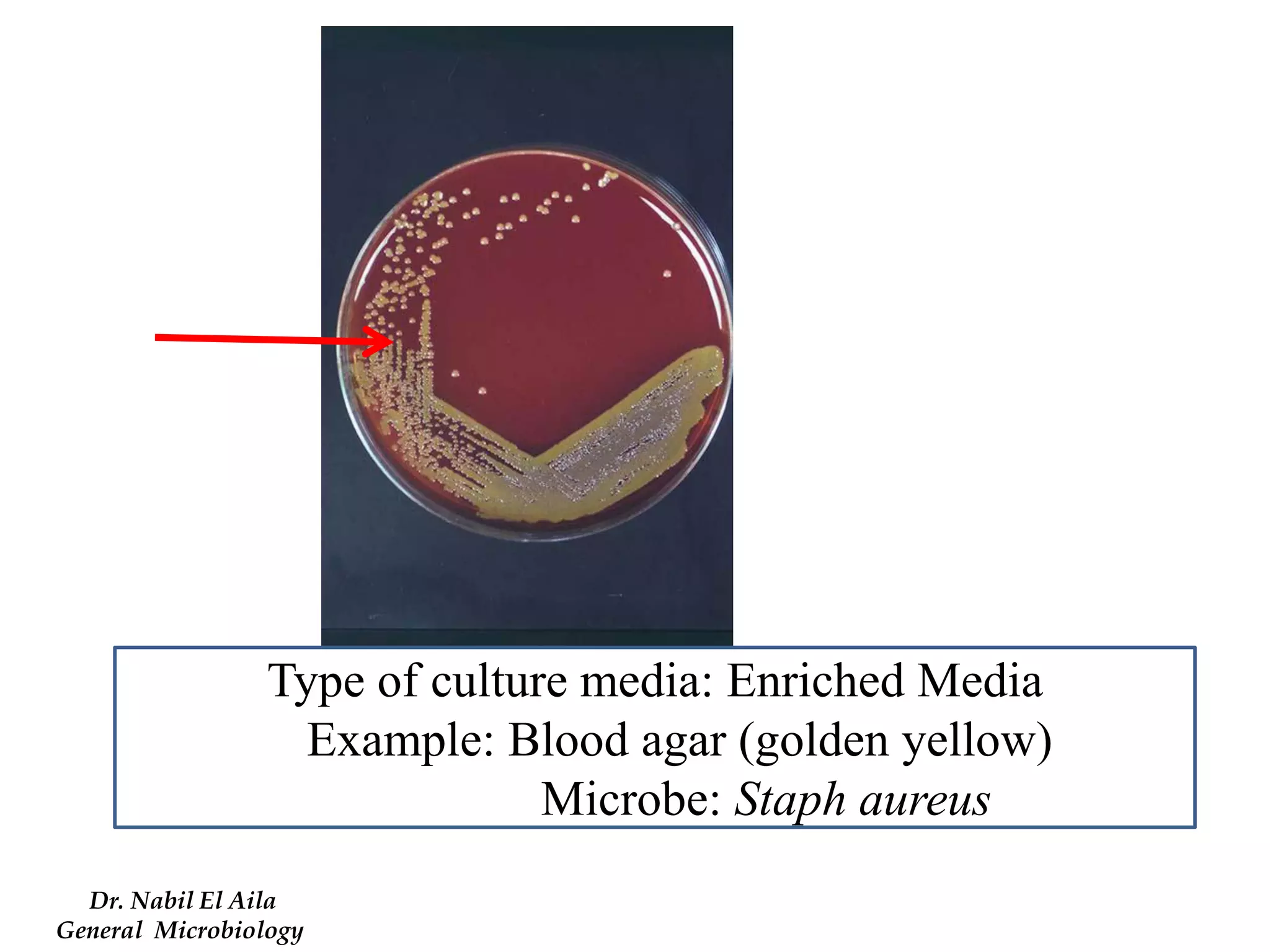
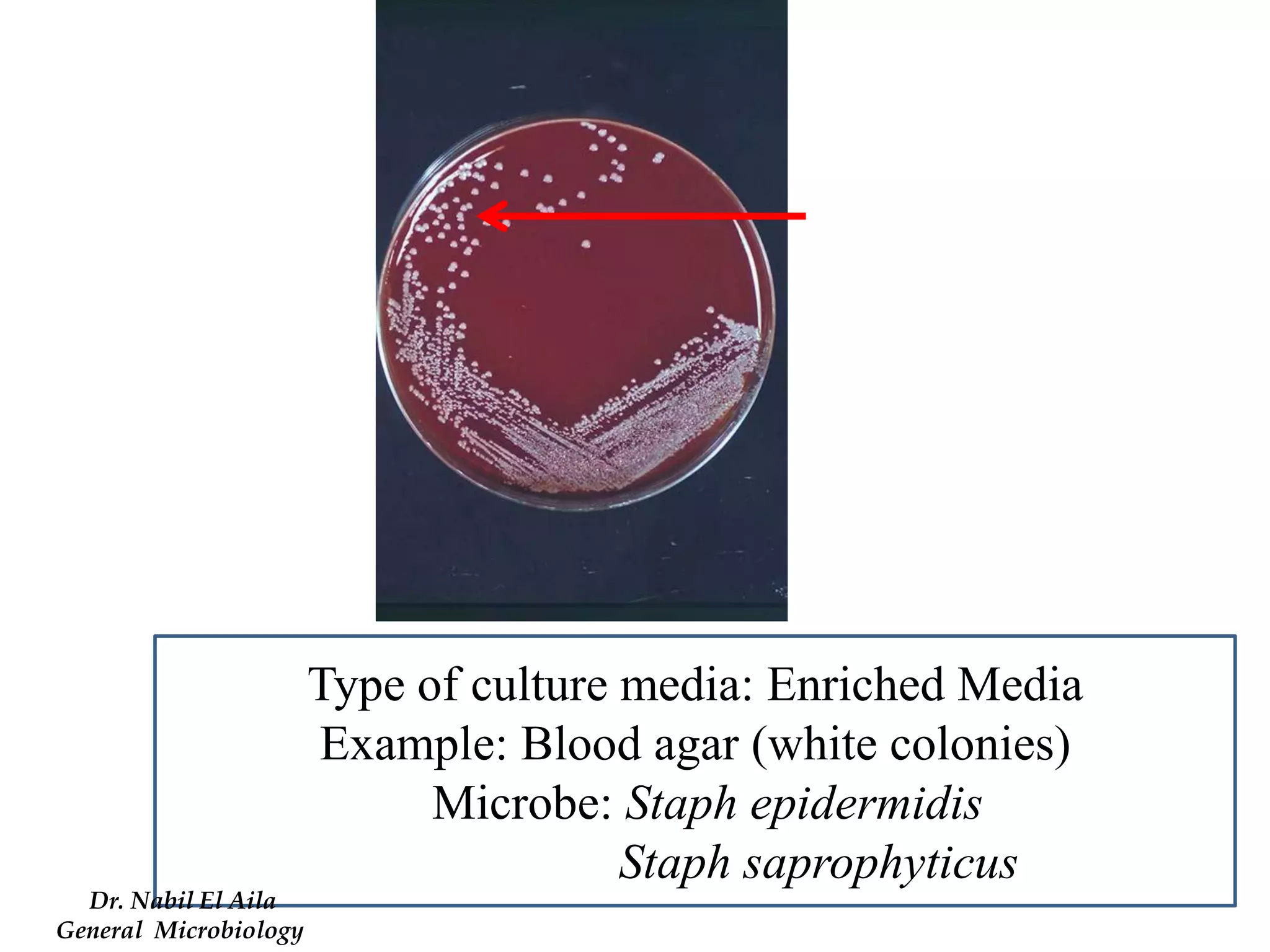
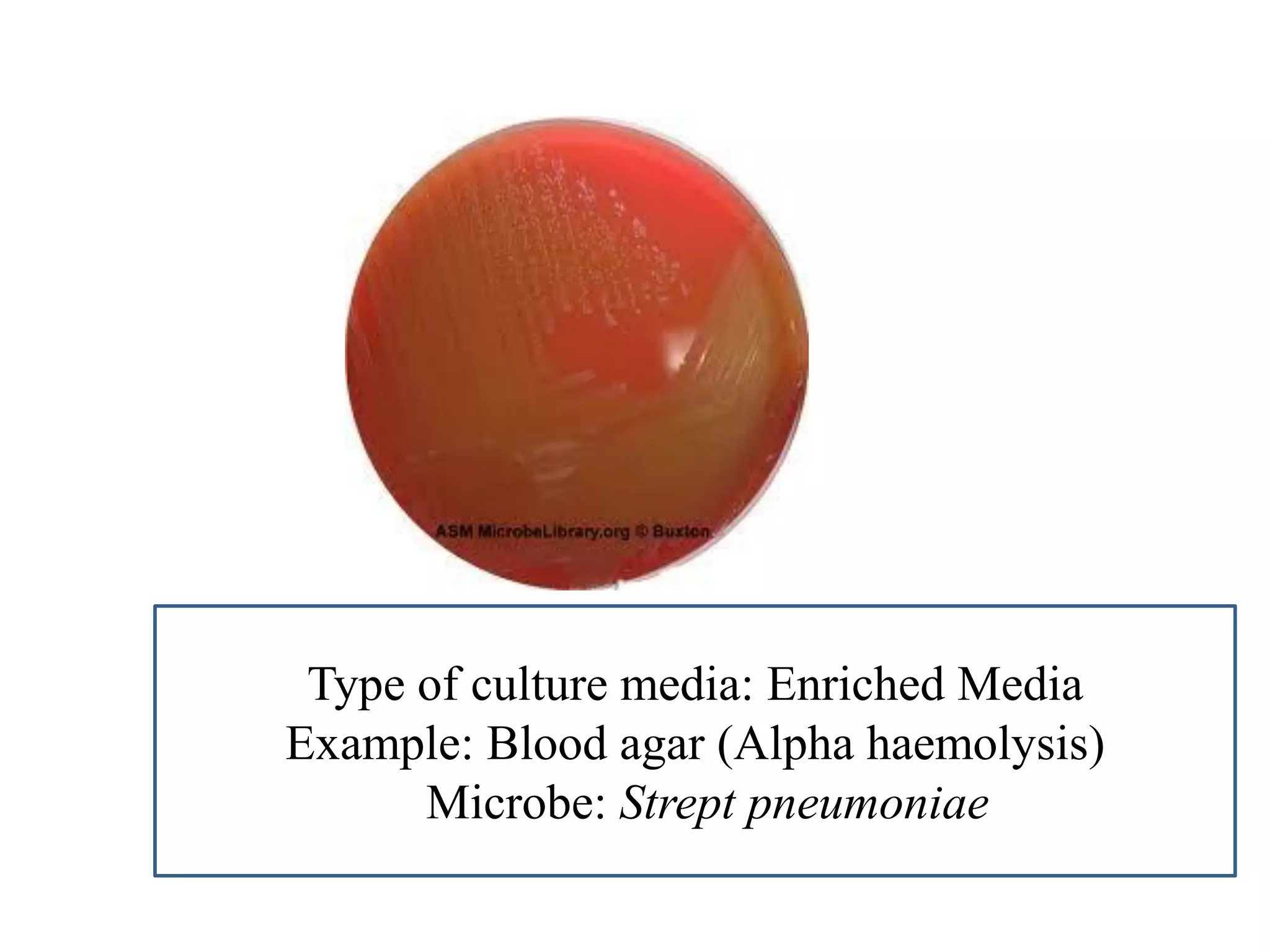
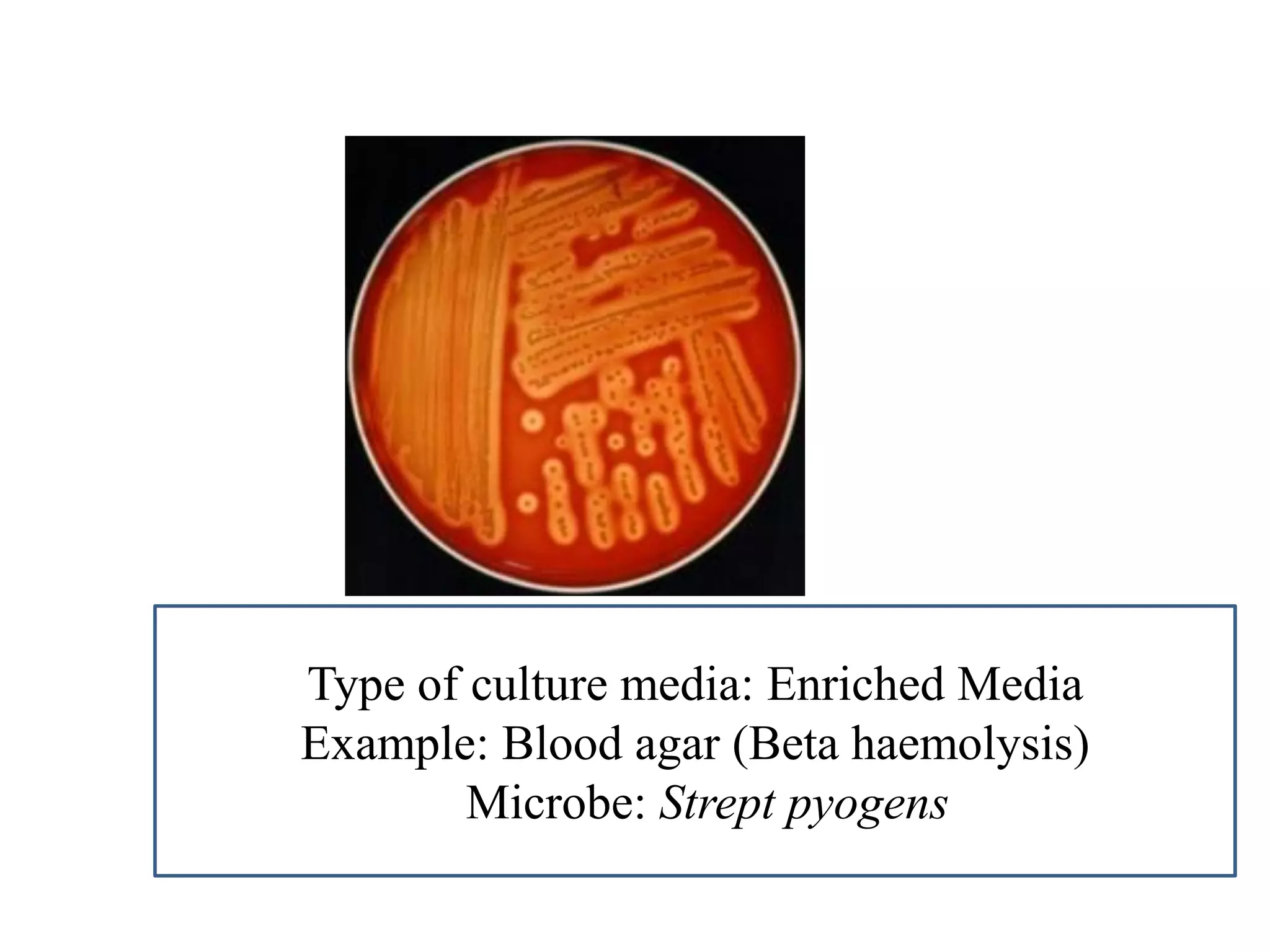
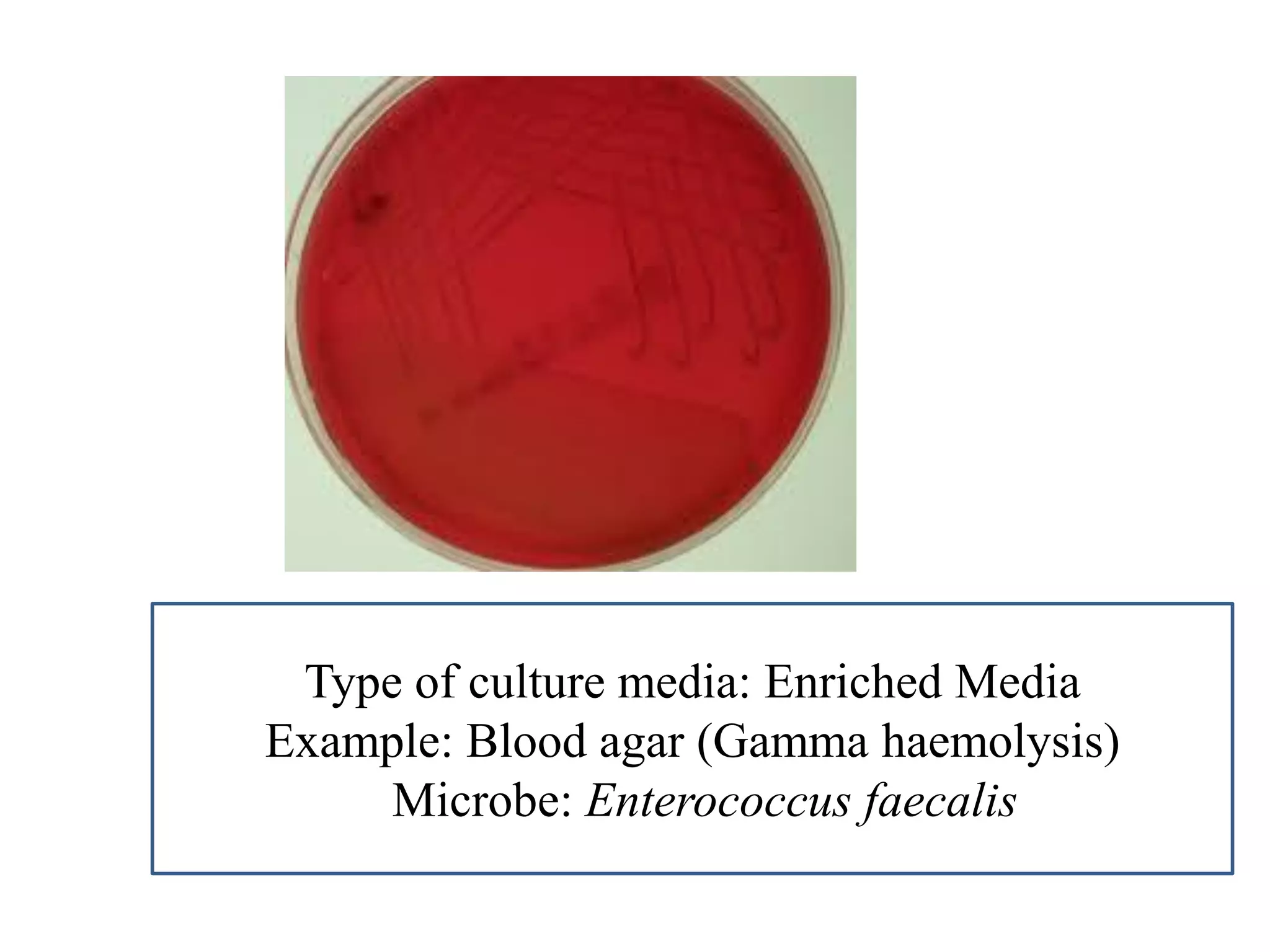
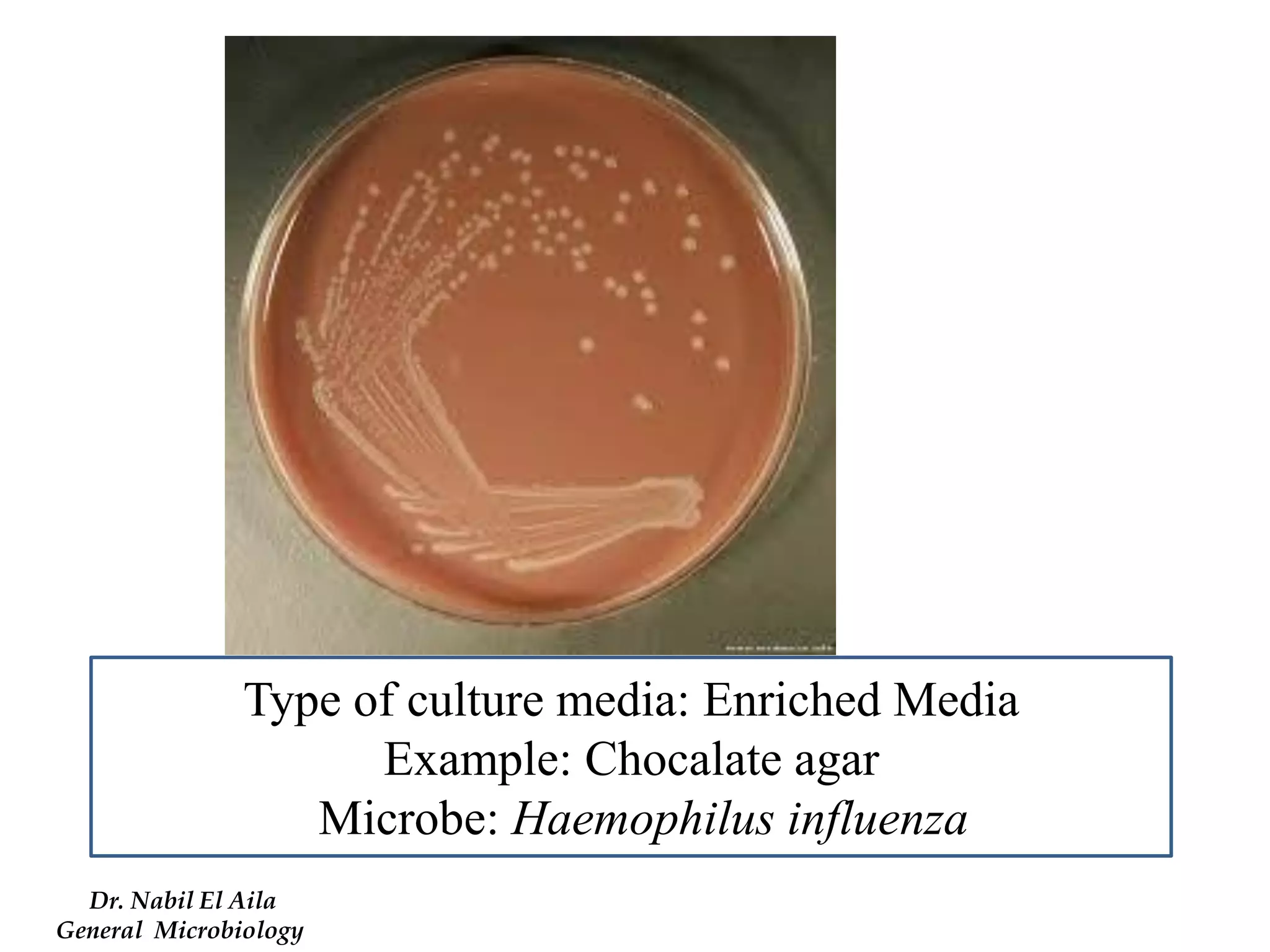
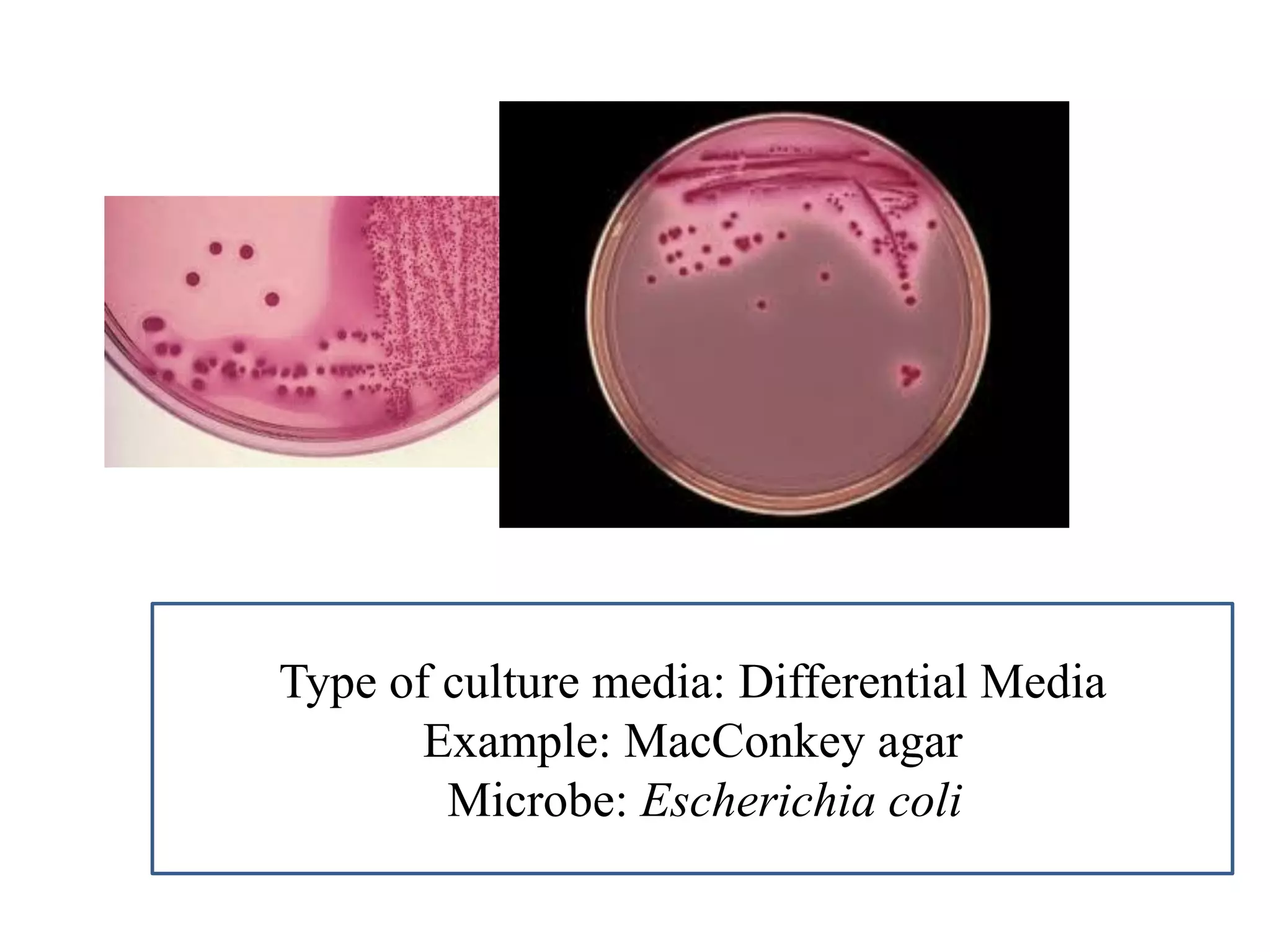
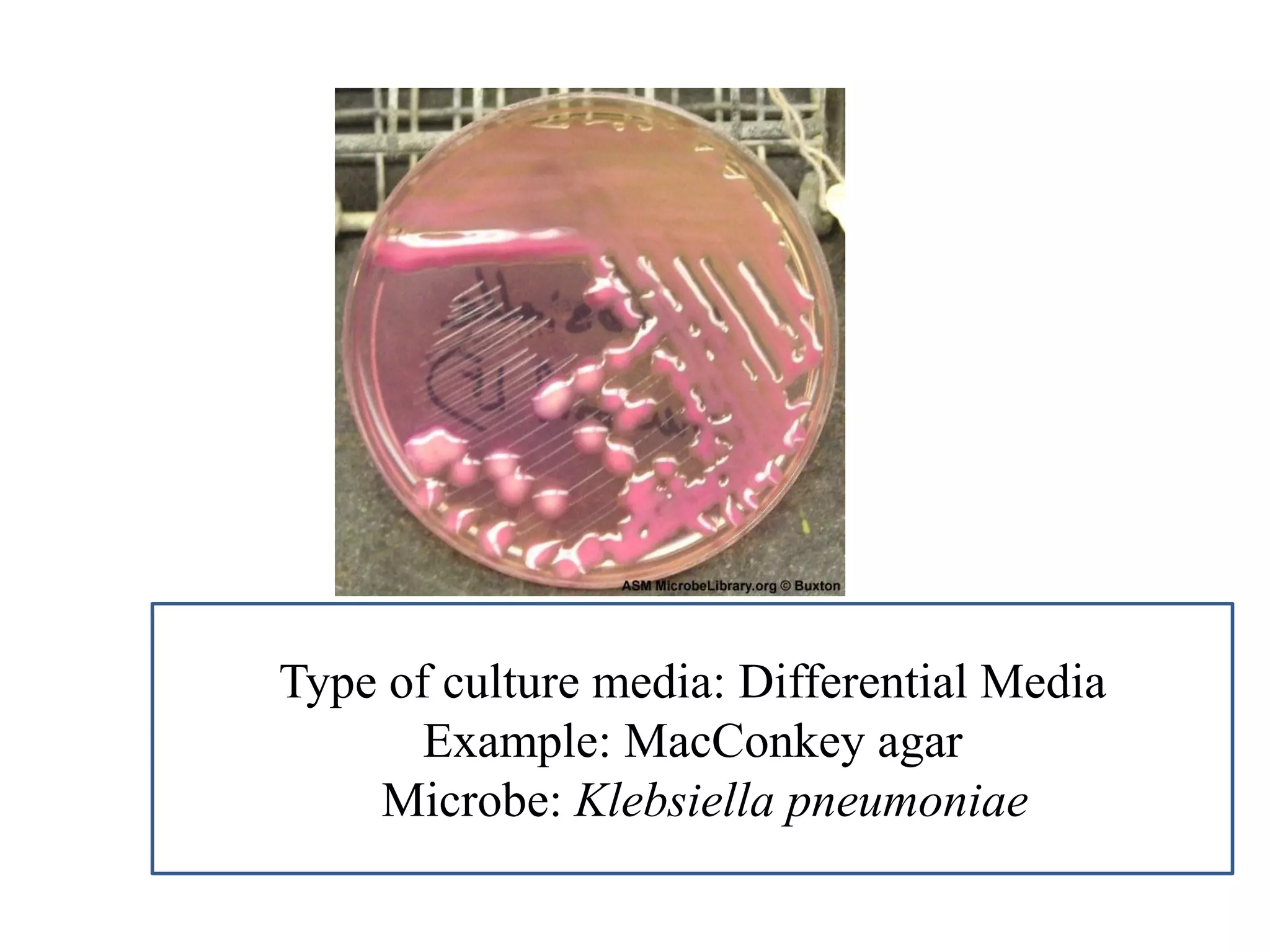
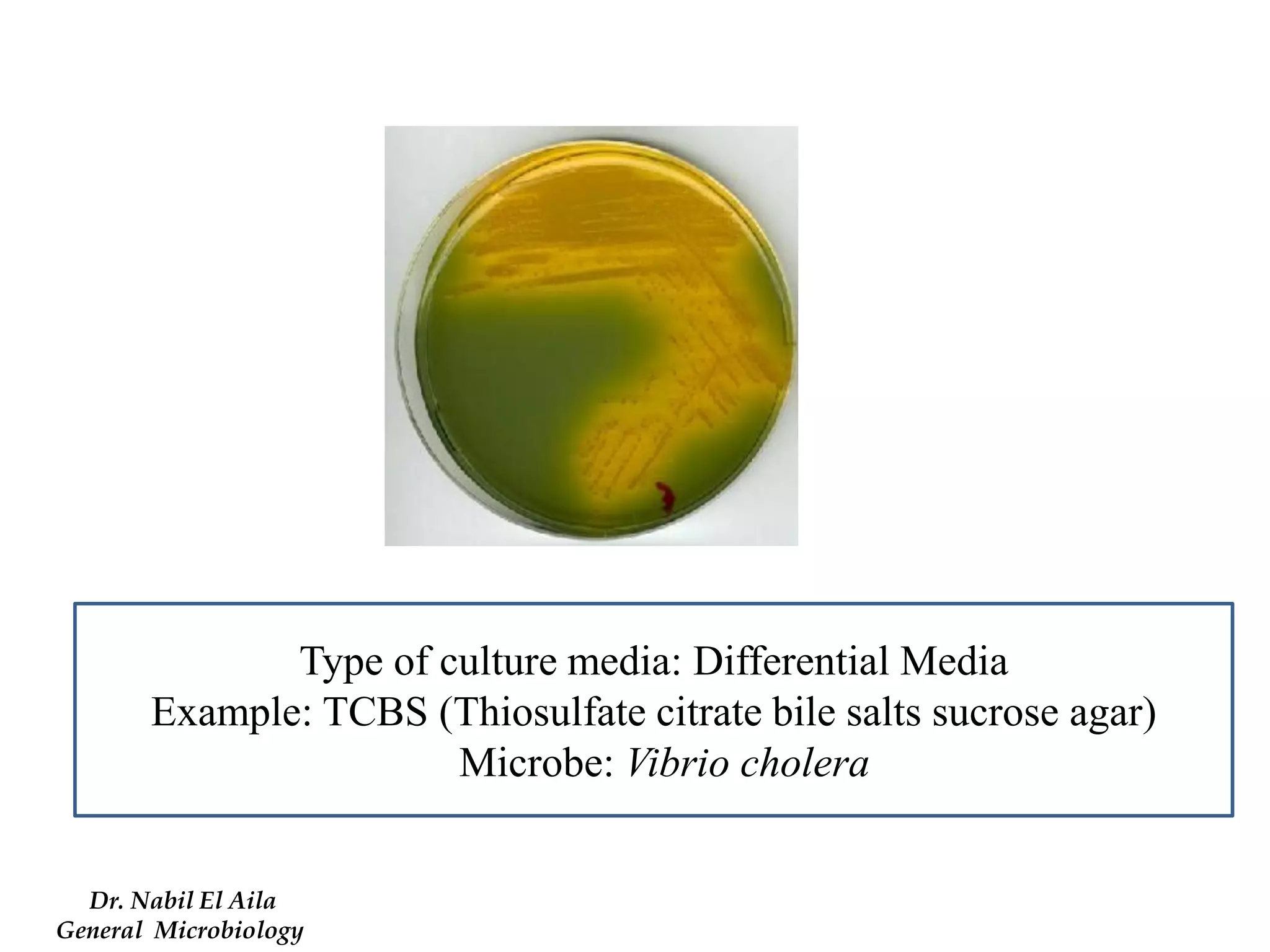
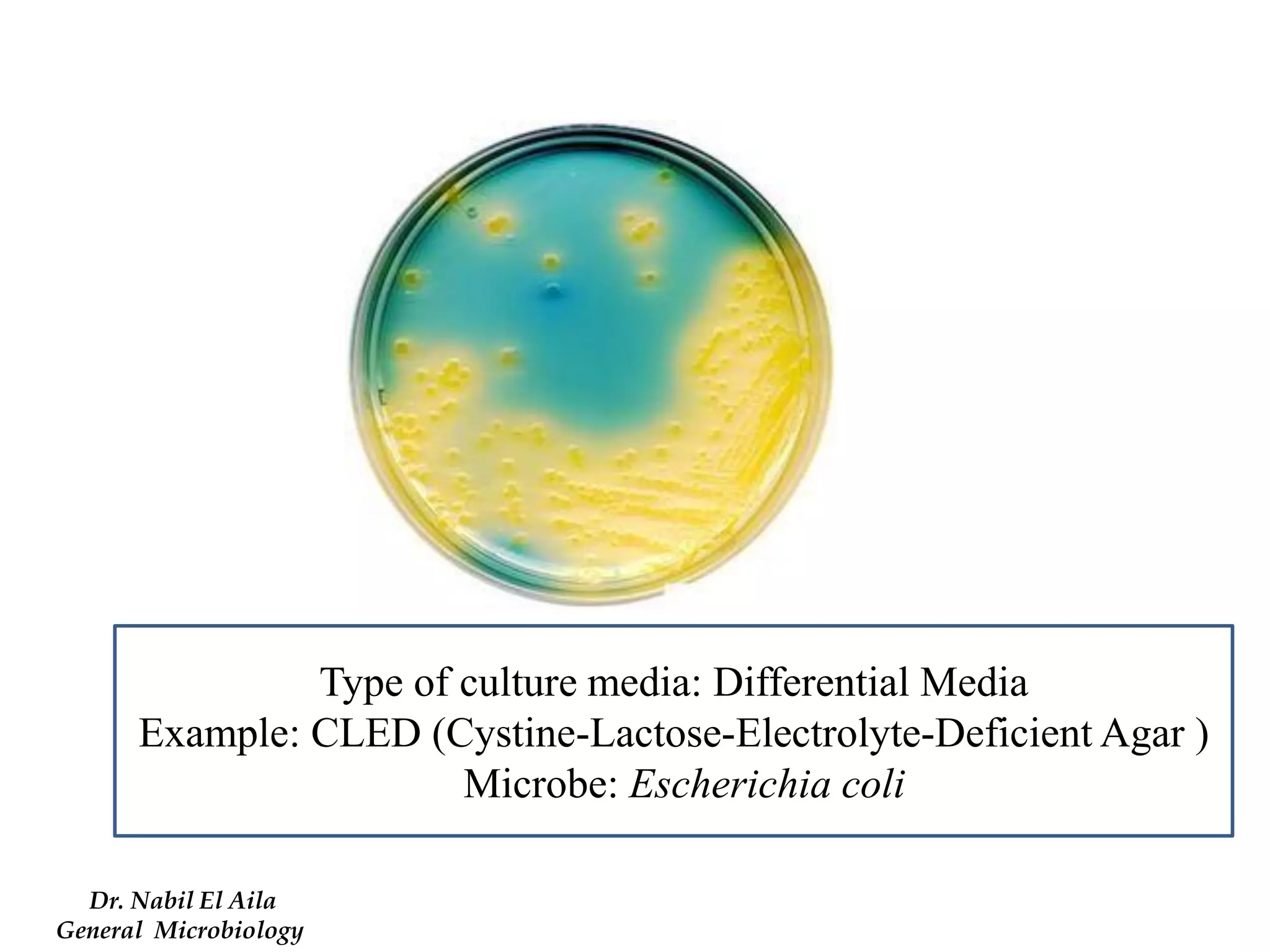
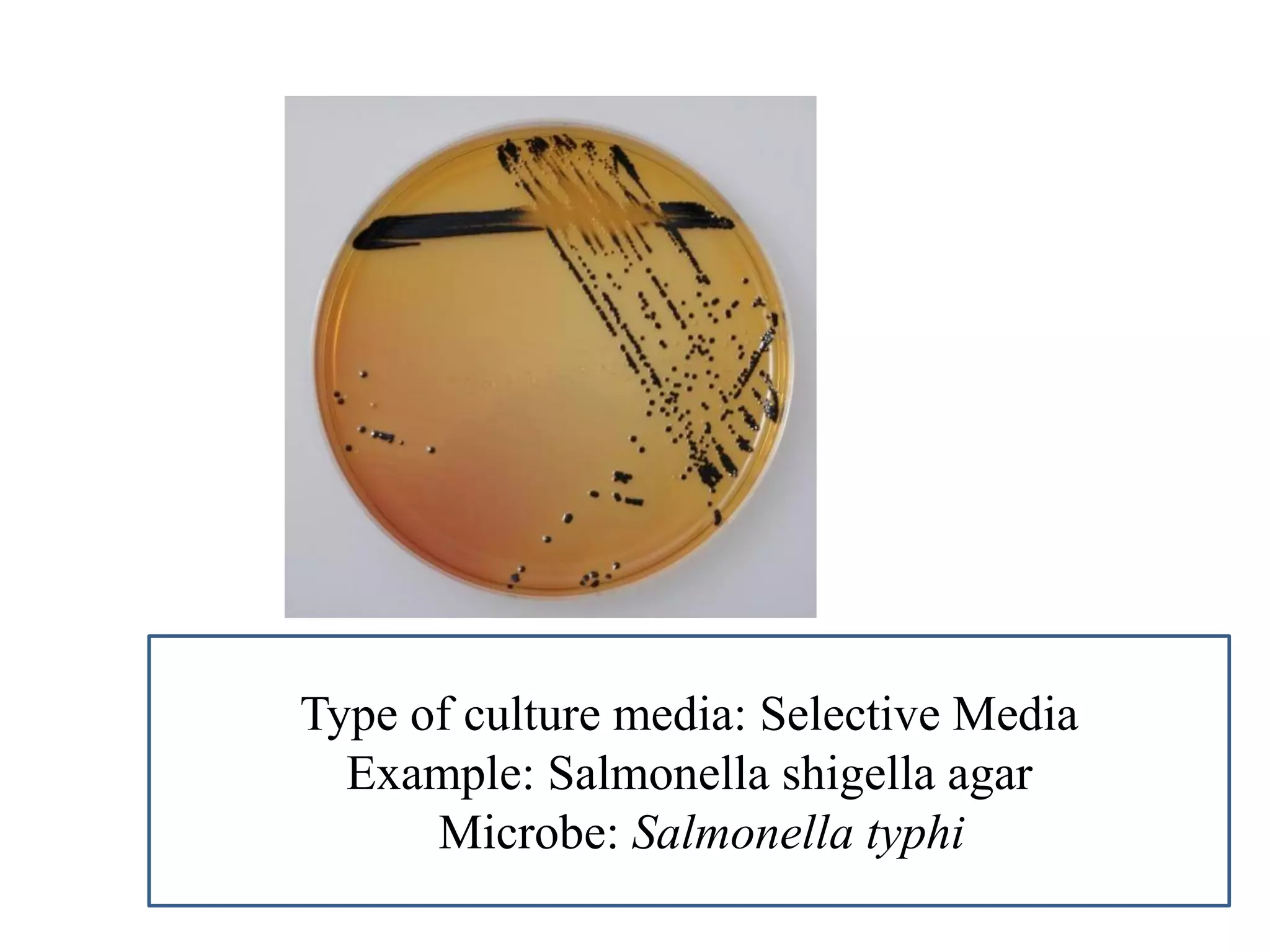
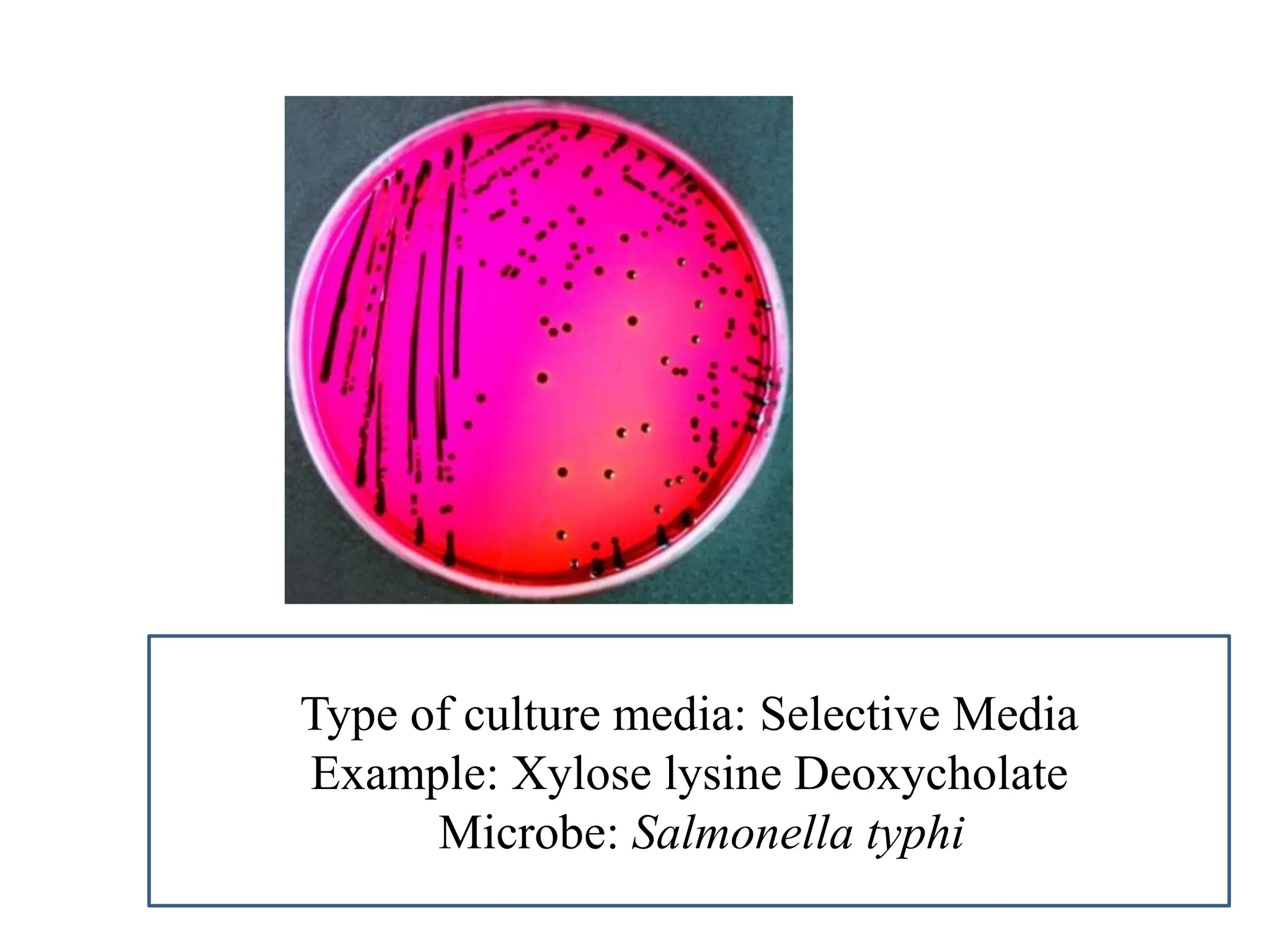
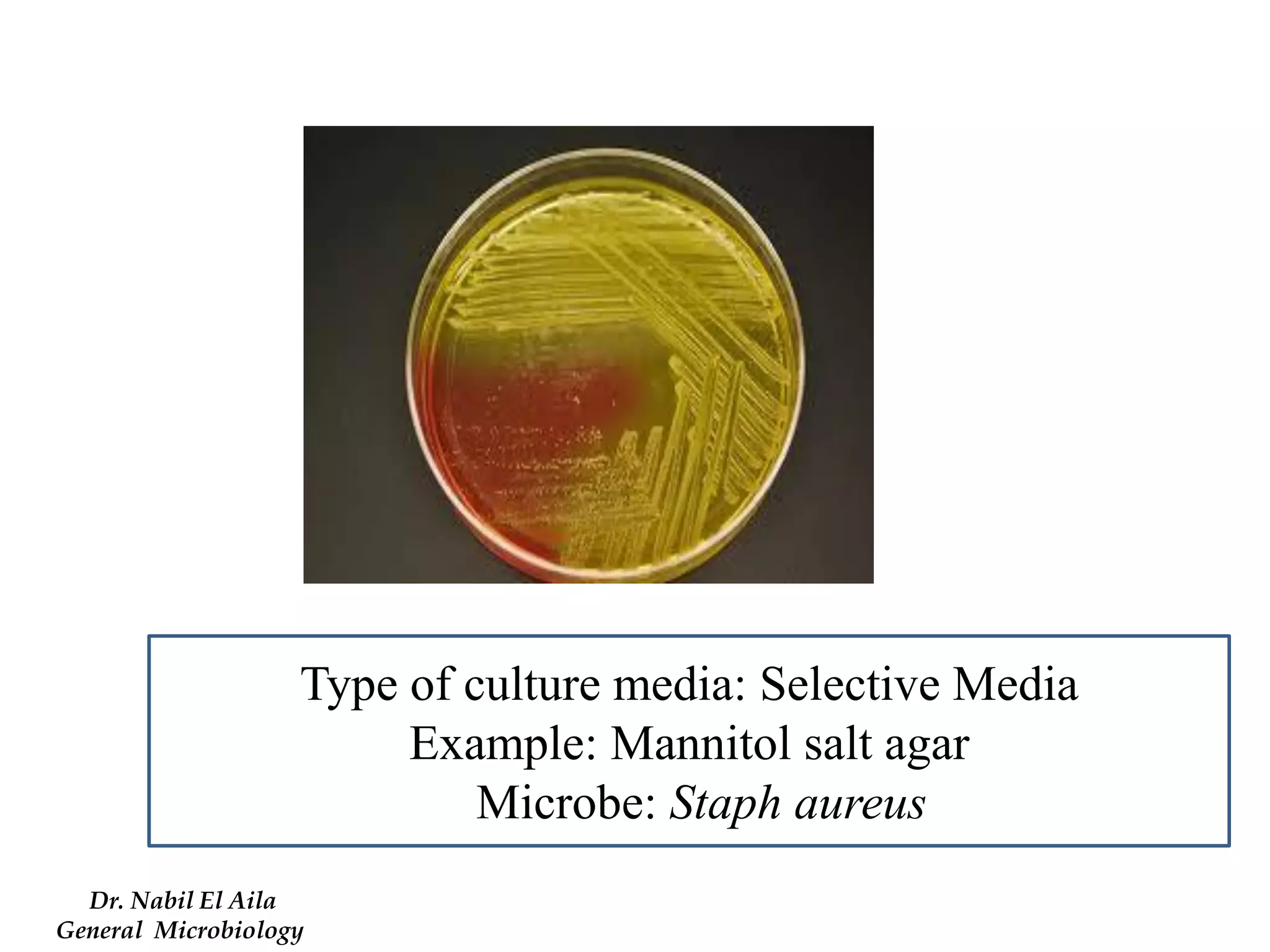
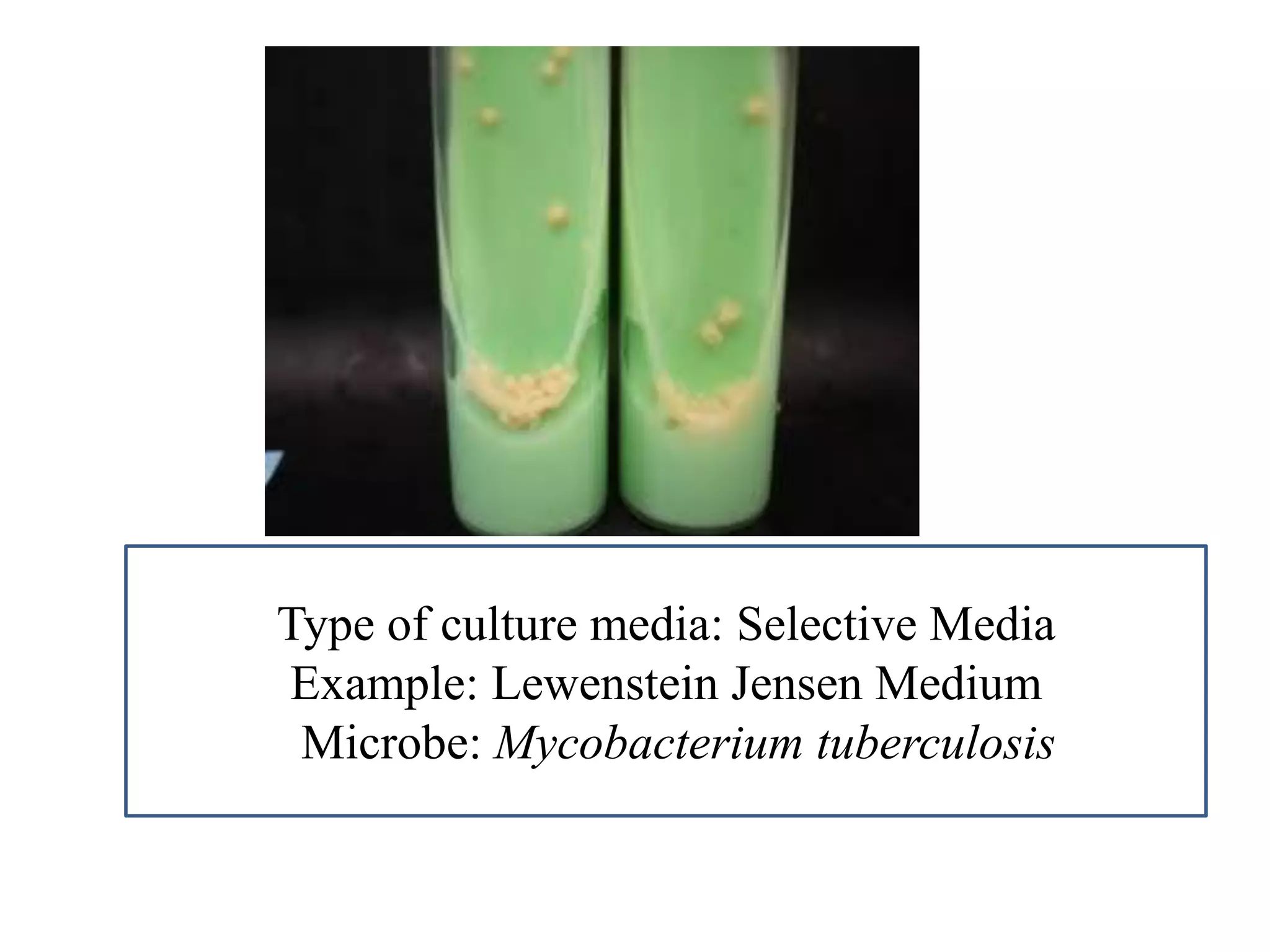
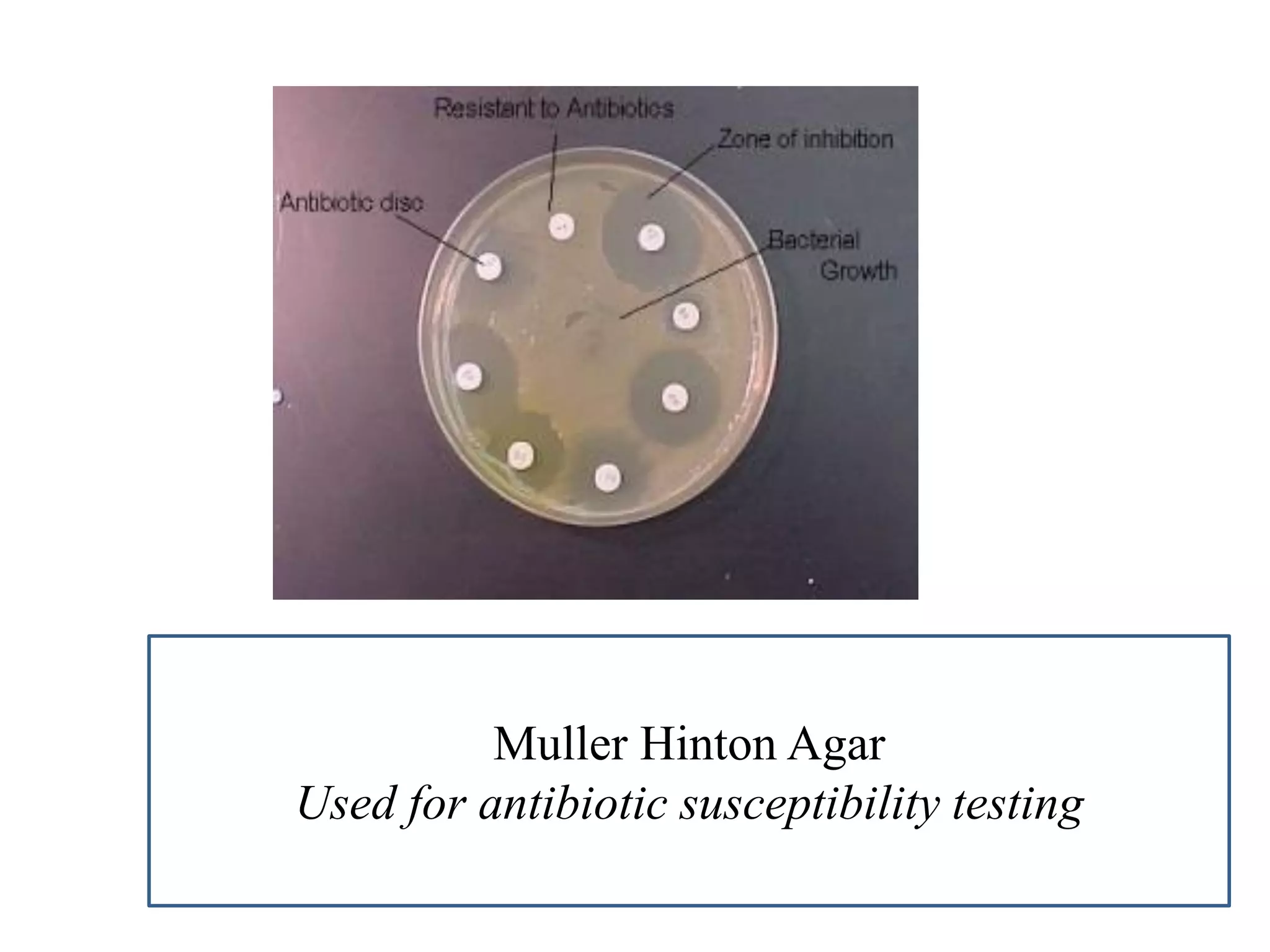
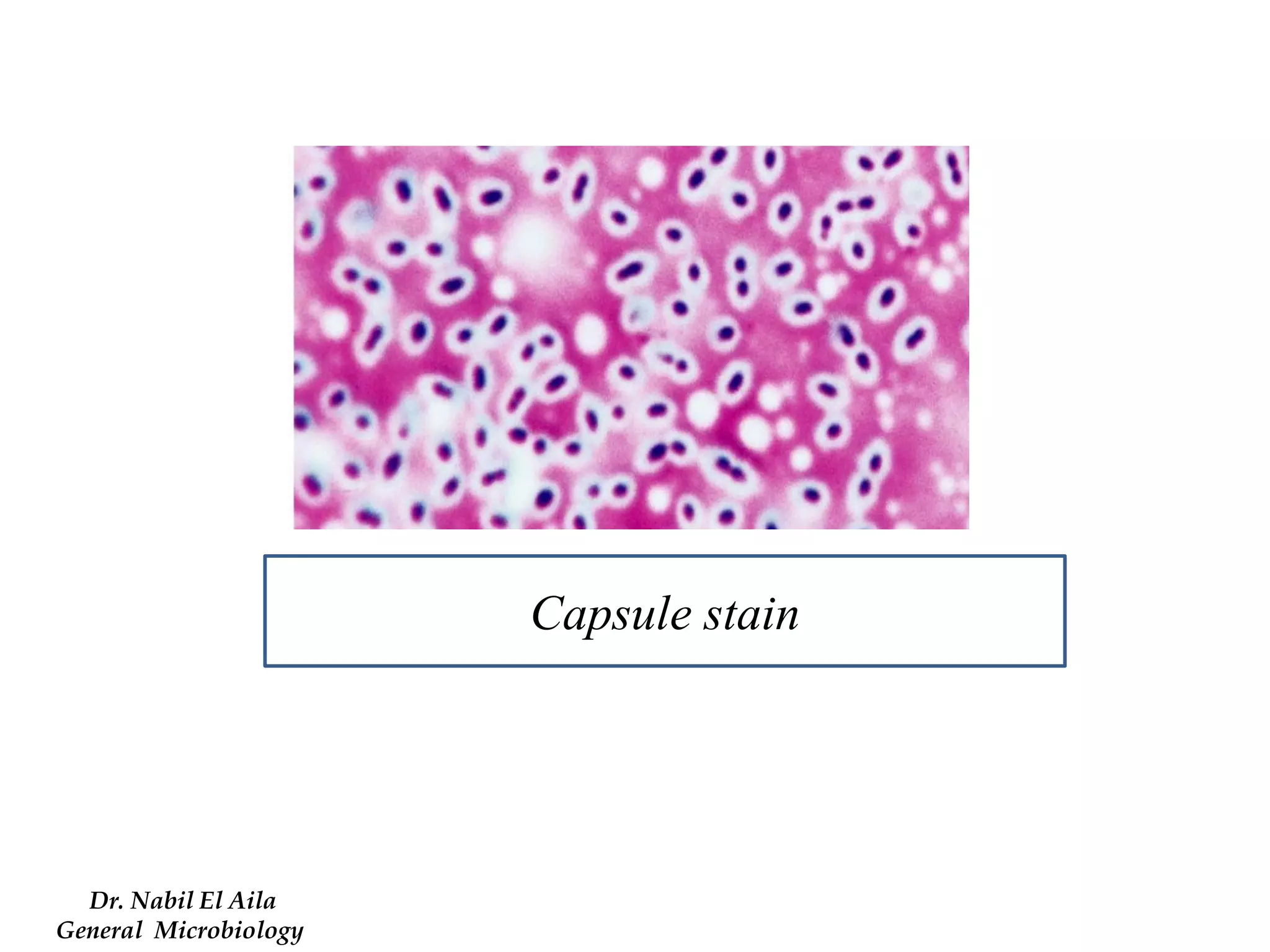
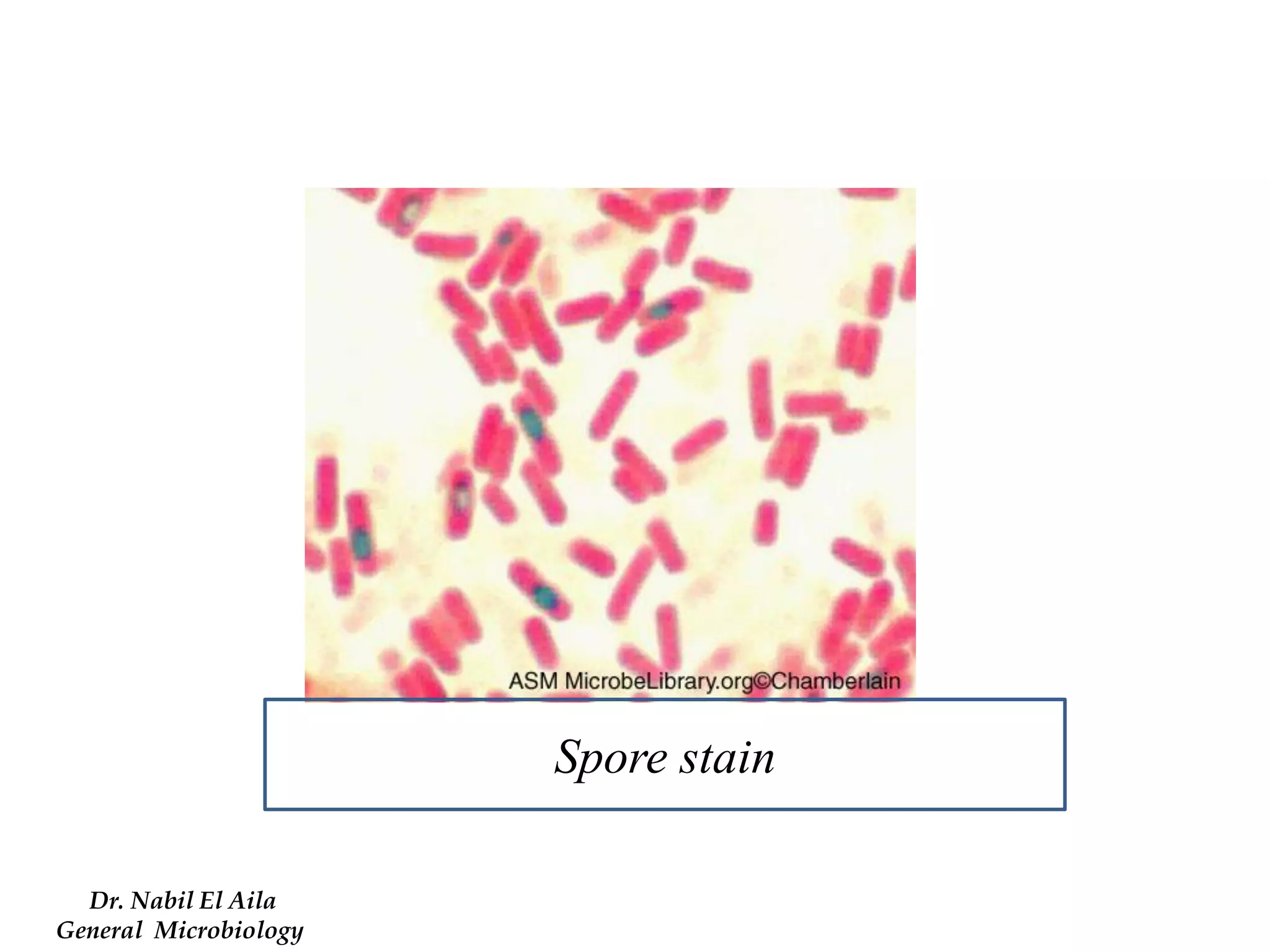
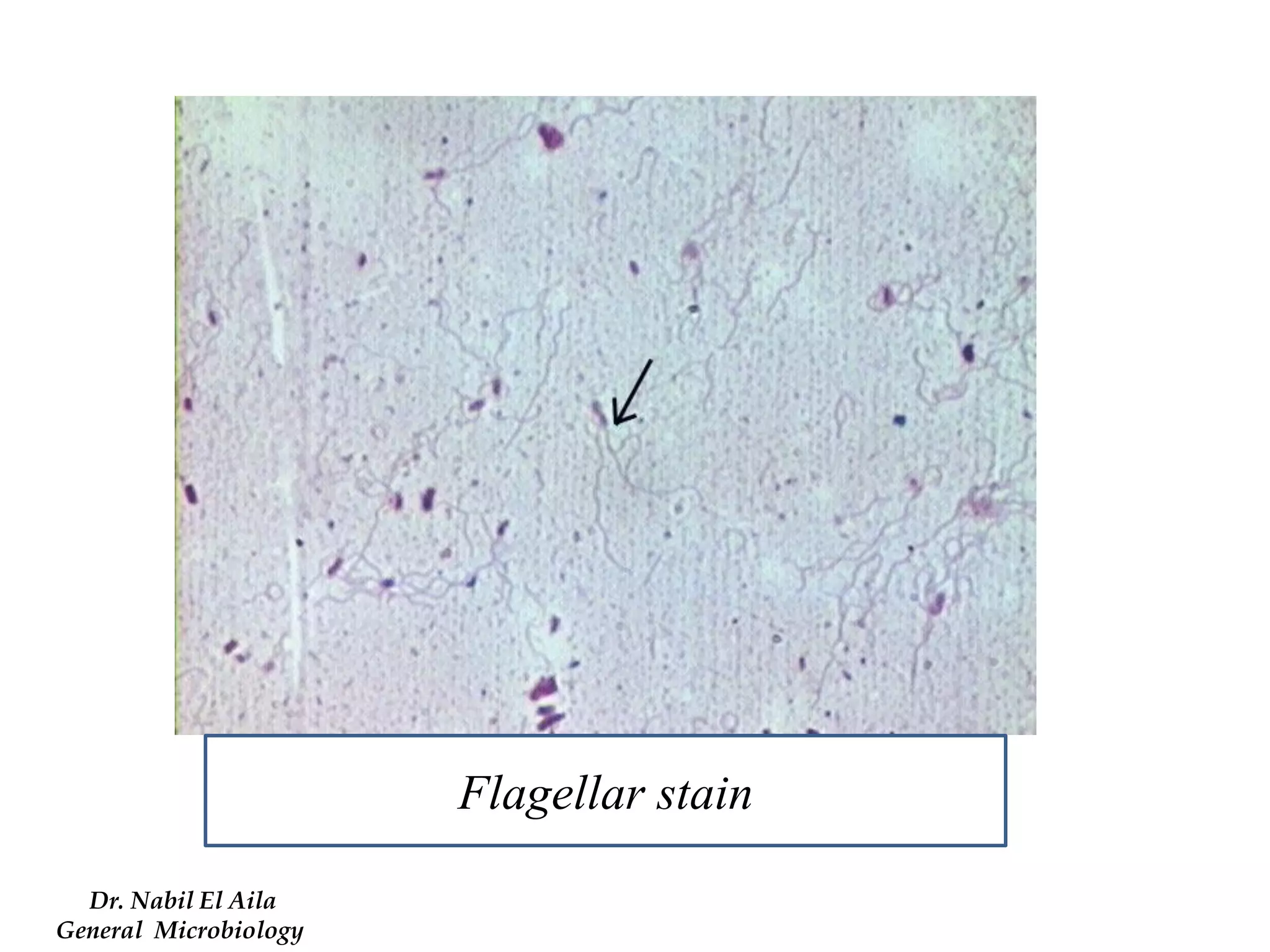
This document provides information on various microbiology tests used to identify bacterial species, including examples of positive and negative results. It describes tests such as the catalase test to distinguish Staphylococci from Streptococci, the coagulase test for identifying Staph aureus, and the DNase test to differentiate Staph aureus from Staph epidermidis. It also summarizes culture-based tests on different media types to isolate and identify bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Streptococcus species.