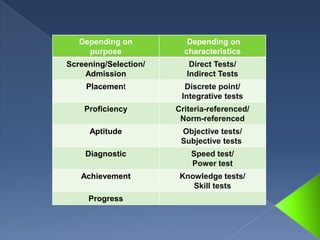
This document discusses testing and test construction. It begins by defining testing and tests, and outlines the main purposes of tests, including informing students of strengths and weaknesses, motivating review, and determining if learning objectives were achieved. It then describes different types of tests based on purpose (screening, proficiency, etc.) and characteristics (direct, indirect, objective, subjective). The document concludes by discussing guidelines for test construction, including moderating tasks, controlling difficulty levels, avoiding bias, and standardizing examiners to ensure a common criteria for scoring.