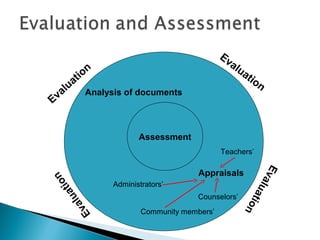
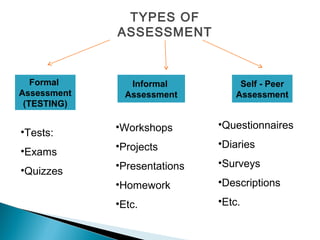
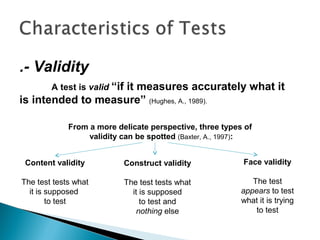
This document discusses evaluation and assessment in education. It covers four generations of evaluation approaches, from measuring participants to negotiating with them. It also discusses types of assessment, including formal testing, informal assessment, and self/peer assessment. Finally, it outlines key principles for developing valid, reliable, practical, and high-quality tests and evaluations, such as ensuring content validity, inter-rater reliability, and contextualized authentic items.