This document summarizes key concepts from diffusion of innovations theory, including Rogers' linear innovation-diffusion model and its core elements of innovation, communication channels, time, and social systems. It also discusses Rogers' innovation-decision process and adopter categories, and provides examples of technology adoption forecasts and disruptive innovations.





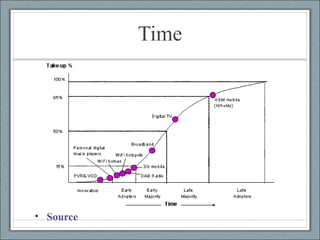
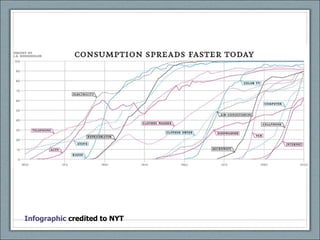





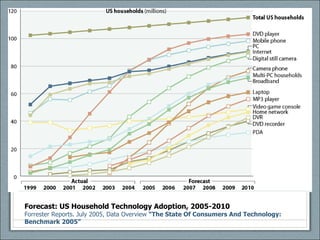
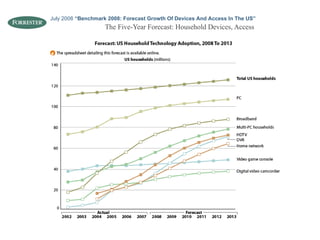



![Credits Presentation by Kathy E. Gill, [email_address] , @kegill CC share-and-share alike, non-commercial use “ S-curve” from http://www.ofcom.org.uk/research/cm/cm05/overview05/keycomms/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week04-1233190527043424-2/85/COM546-Week-4-24-320.jpg)