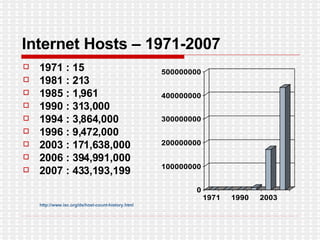
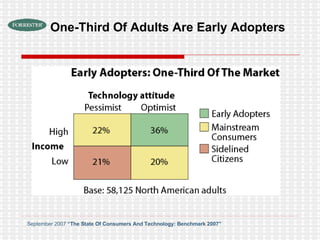
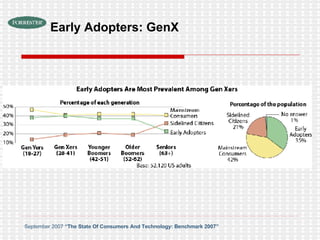
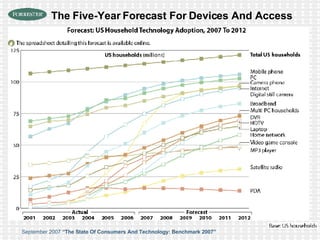
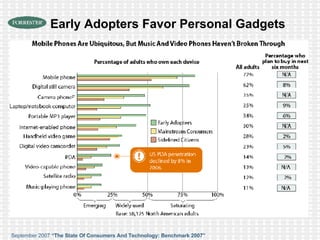
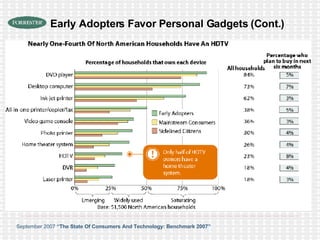
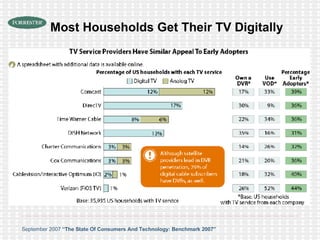
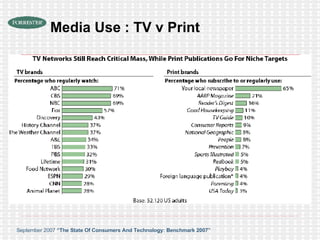
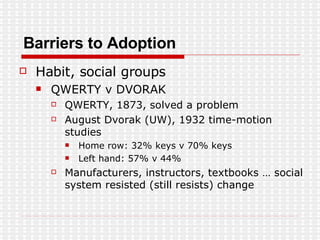
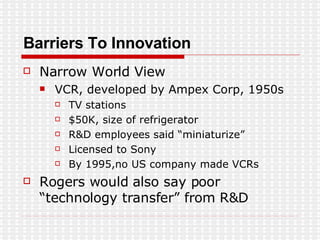
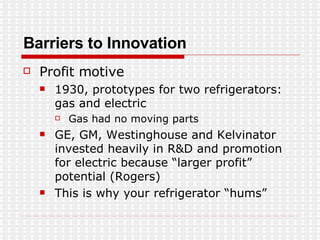
The document discusses the evolution of digital media technologies and diffusion theory. It covers Rogers' linear innovation-diffusion theory involving five steps of adoption. It also discusses categories of adopters including innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards. The document then provides examples and statistics about early adopters from a 2007 report and barriers to adoption and innovation such as profit motives, habit and social groups. It also discusses the social construction of technology and shaping of technologies by military and customers.








![Picking Up Speed 1987 : Apple’s Hypertext 1991 : Tim Berners-Lee at European Particle Physics Laboratory in Geneva conceived/birthed the World Wide Web 1993 : National Center for Supercomputing Applications [NCSA] - University of Illinois created a WWW browser named Mosaic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/com-546-week-4-1193187337636054-5/85/COM-546-Week-4-22-320.jpg)
![Faster... faster... faster April 94 : Mosaic Communications [Clark & Andreessen] Oct 94 : Netscape Beta Released Nov 94 : Mosaic Co ==> Netscape Aug 9, 1995 : Netscape IPO Initial Public Offering, to “go public” One measure of adoption: hosts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/com-546-week-4-1193187337636054-5/85/COM-546-Week-4-23-320.jpg)