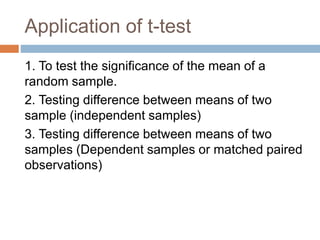
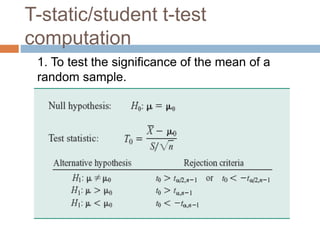
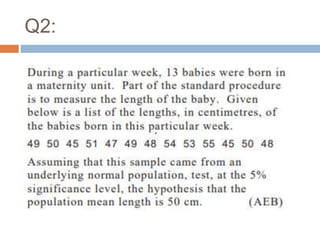
This document discusses the t-test and z-test statistical tests. It explains that the t-test is used for small sample sizes (less than 30) when the population standard deviation is unknown, while the z-test is used for large sample sizes (greater than 30) when the population parameter is known. The t-test can test the significance of a single mean, the difference between two independent sample means, or the difference between two dependent/matched sample means. Examples are provided for using the t-test to test the significance of a single mean and the difference between two independent sample means. The z-test is briefly explained as well.