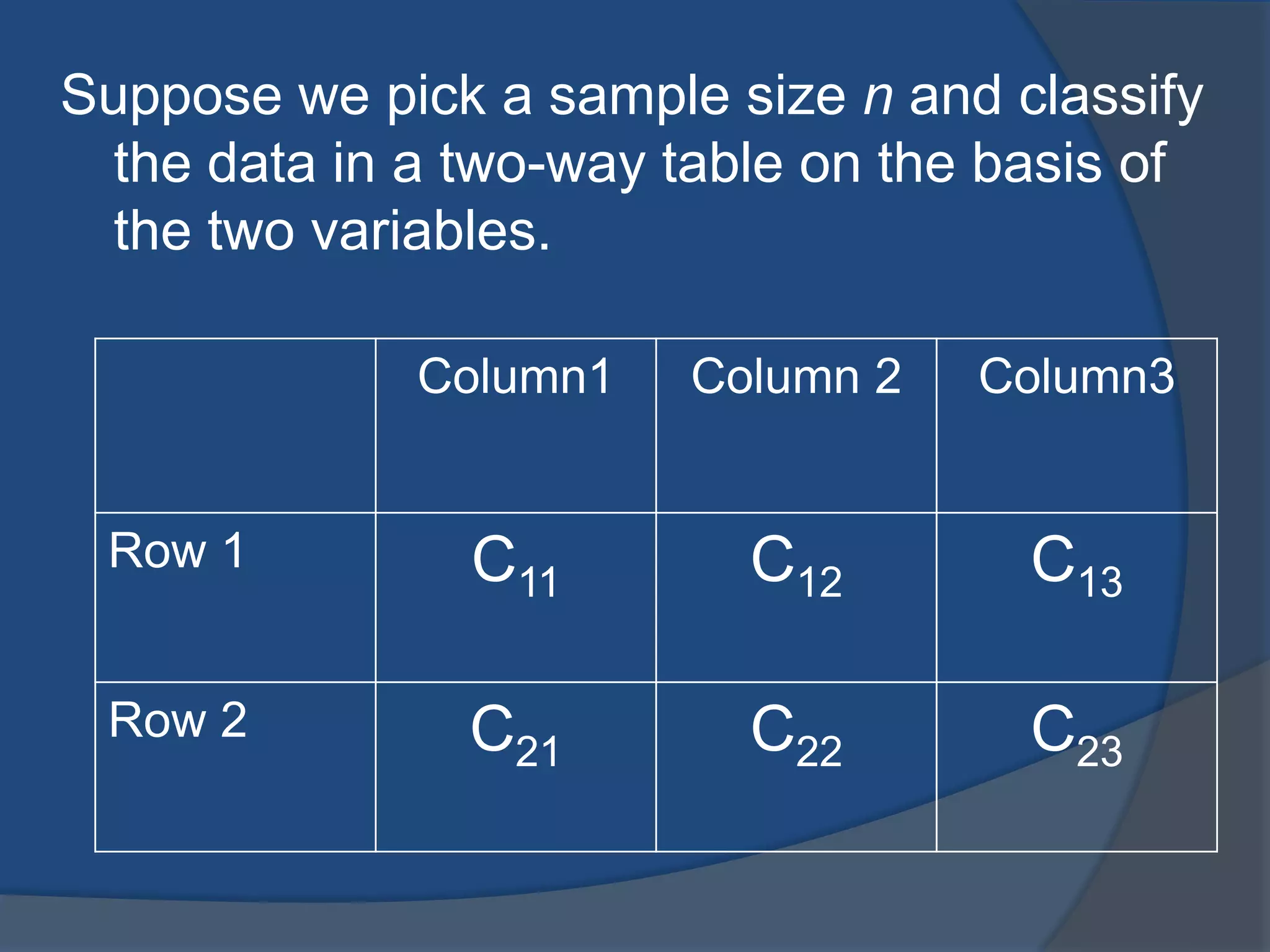
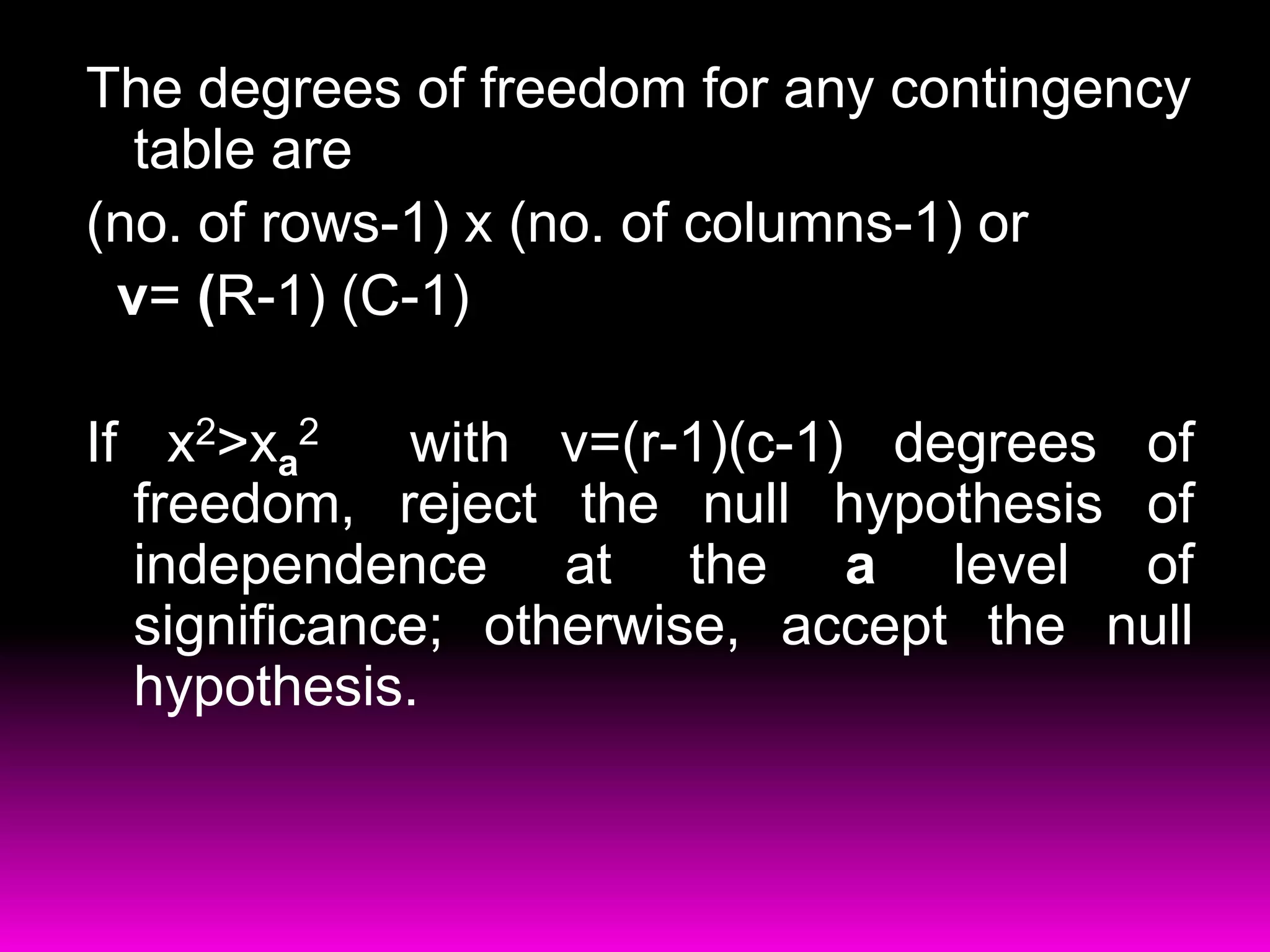
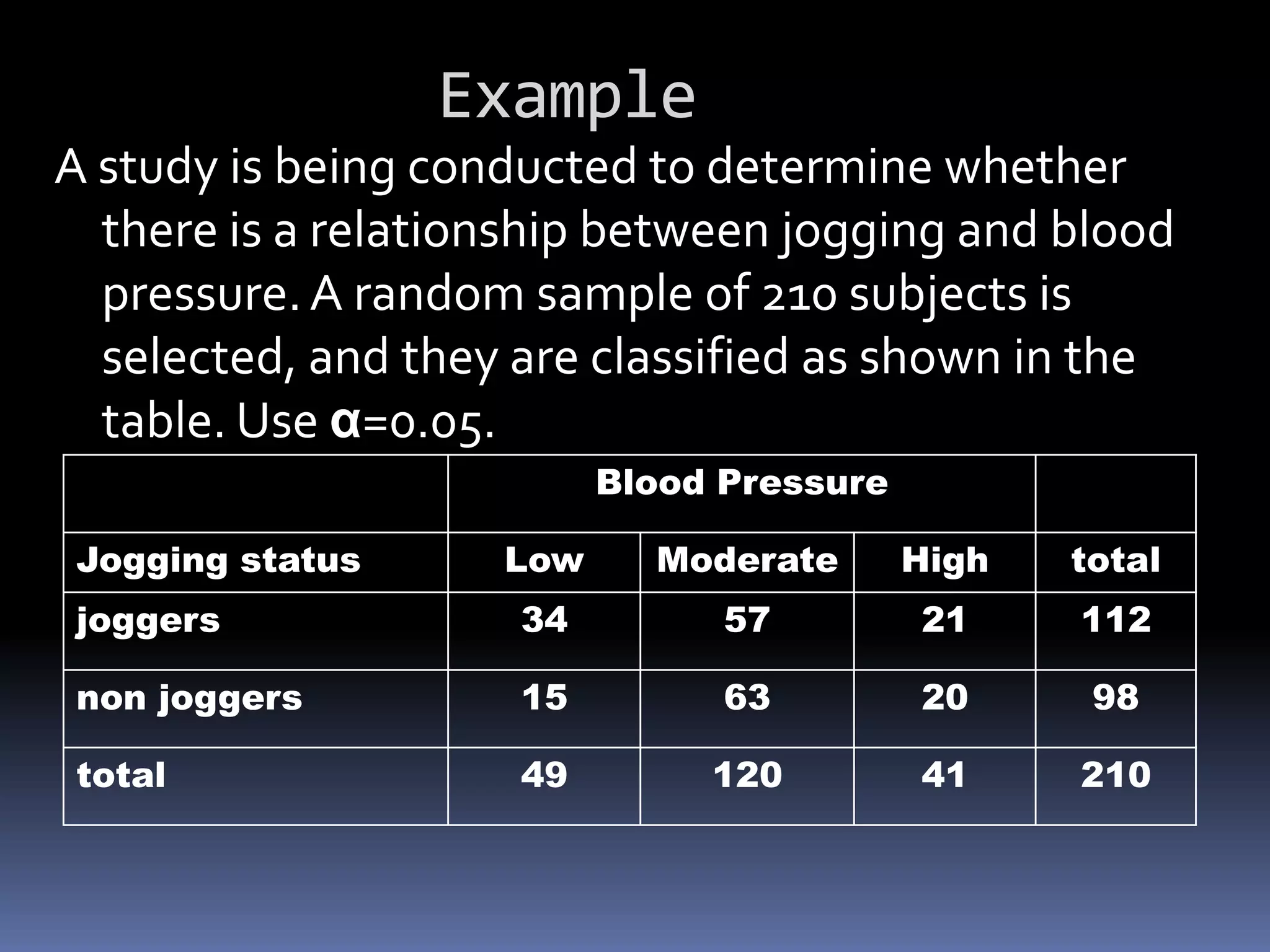
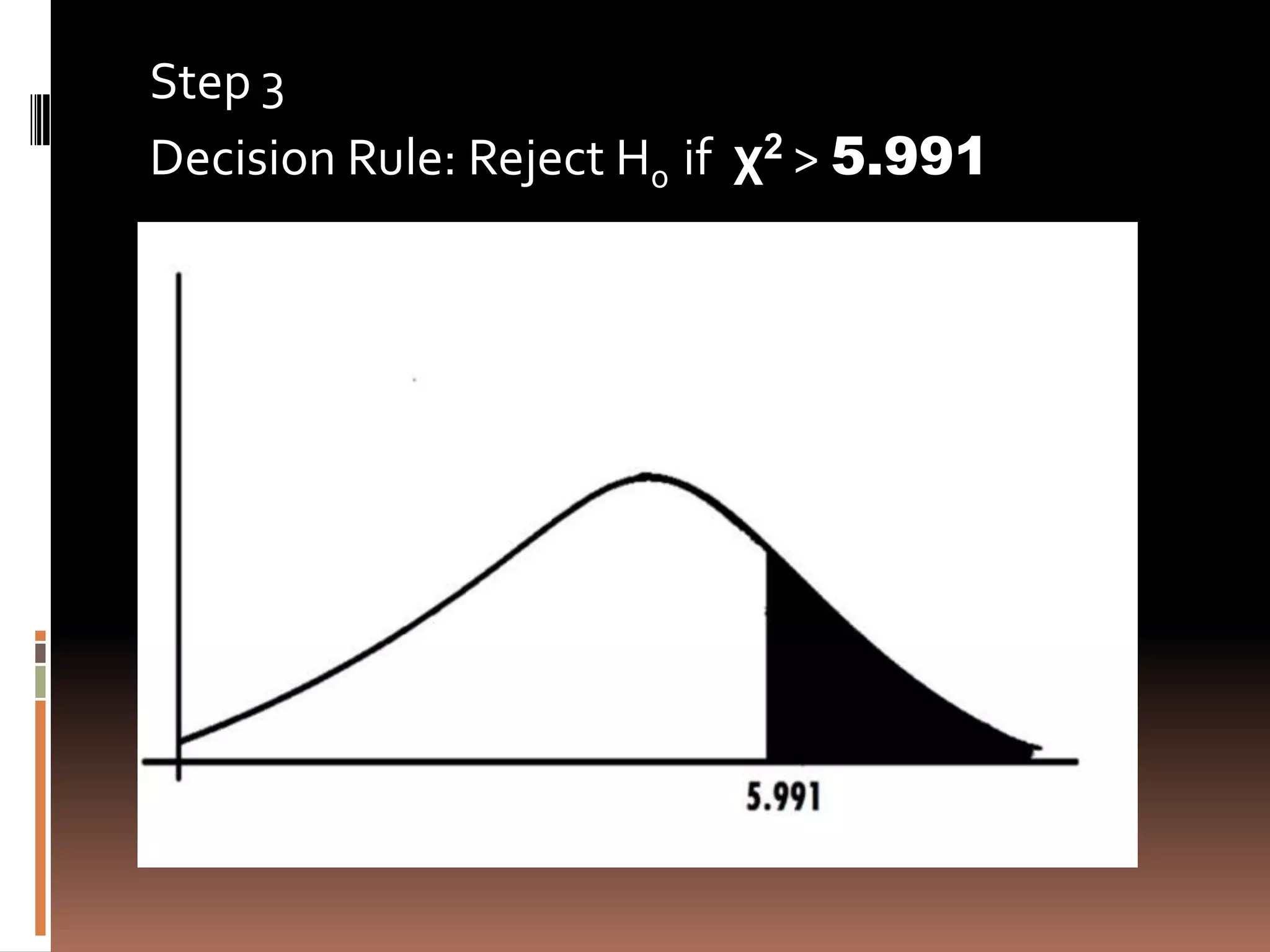
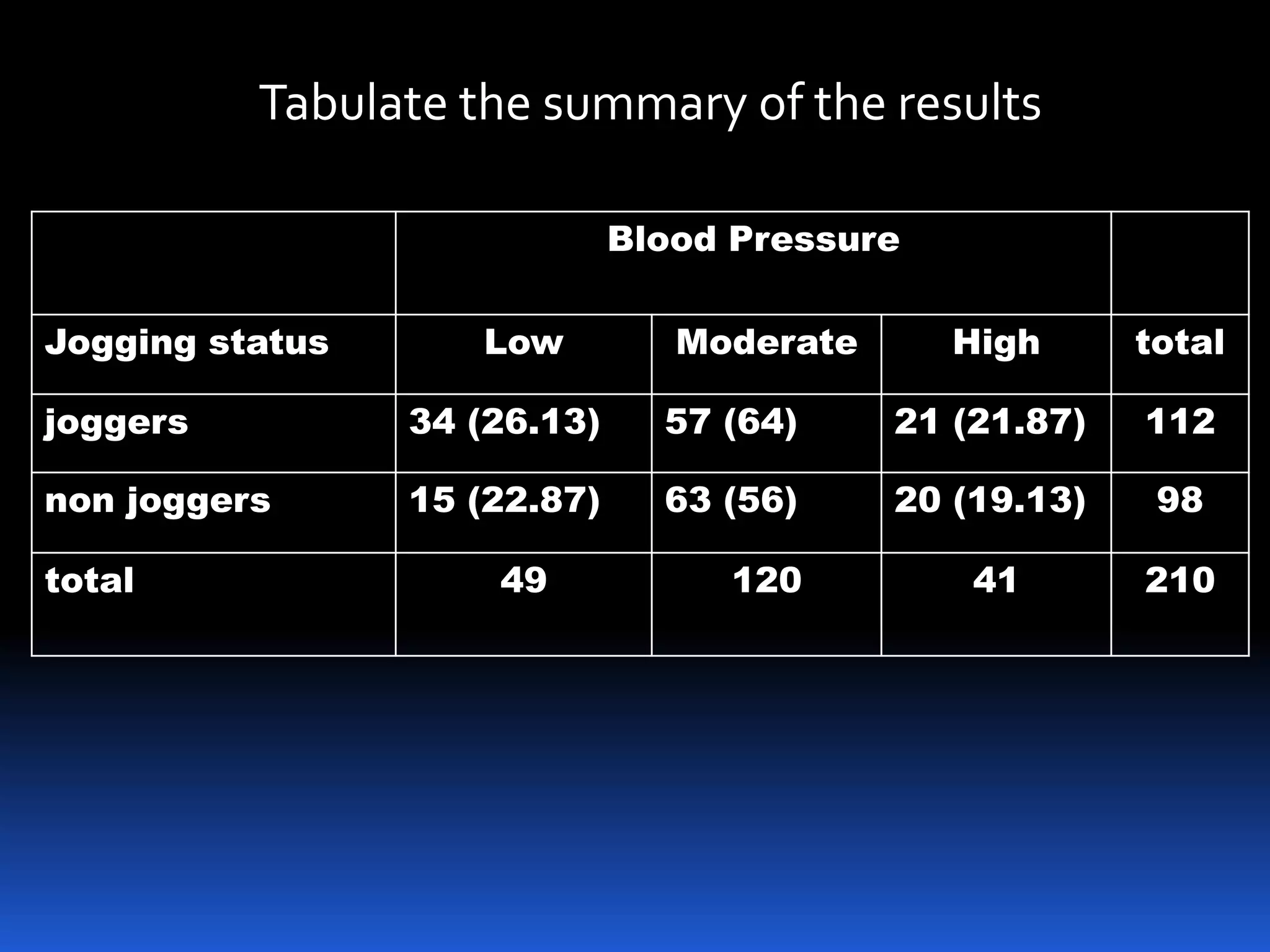
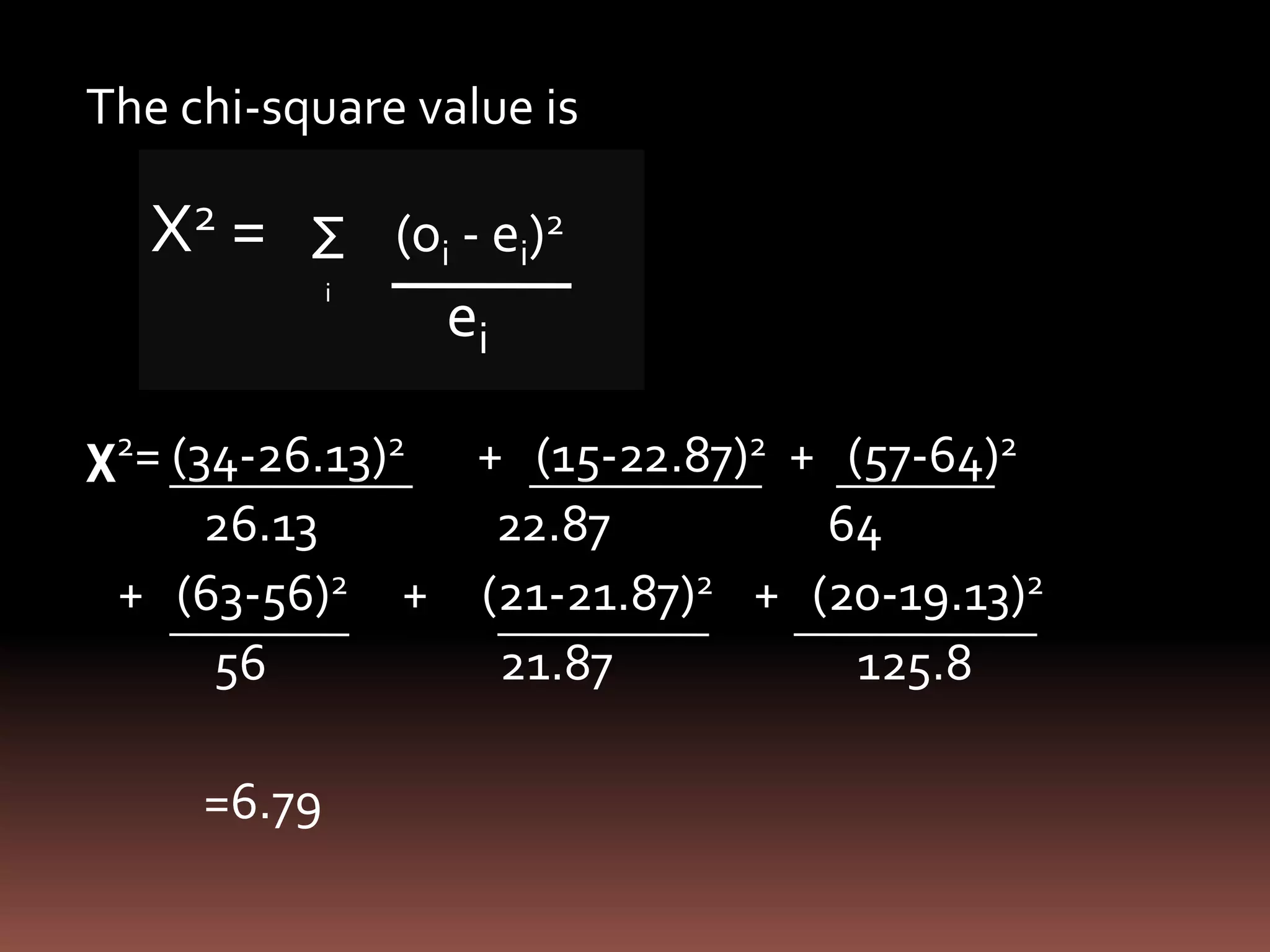
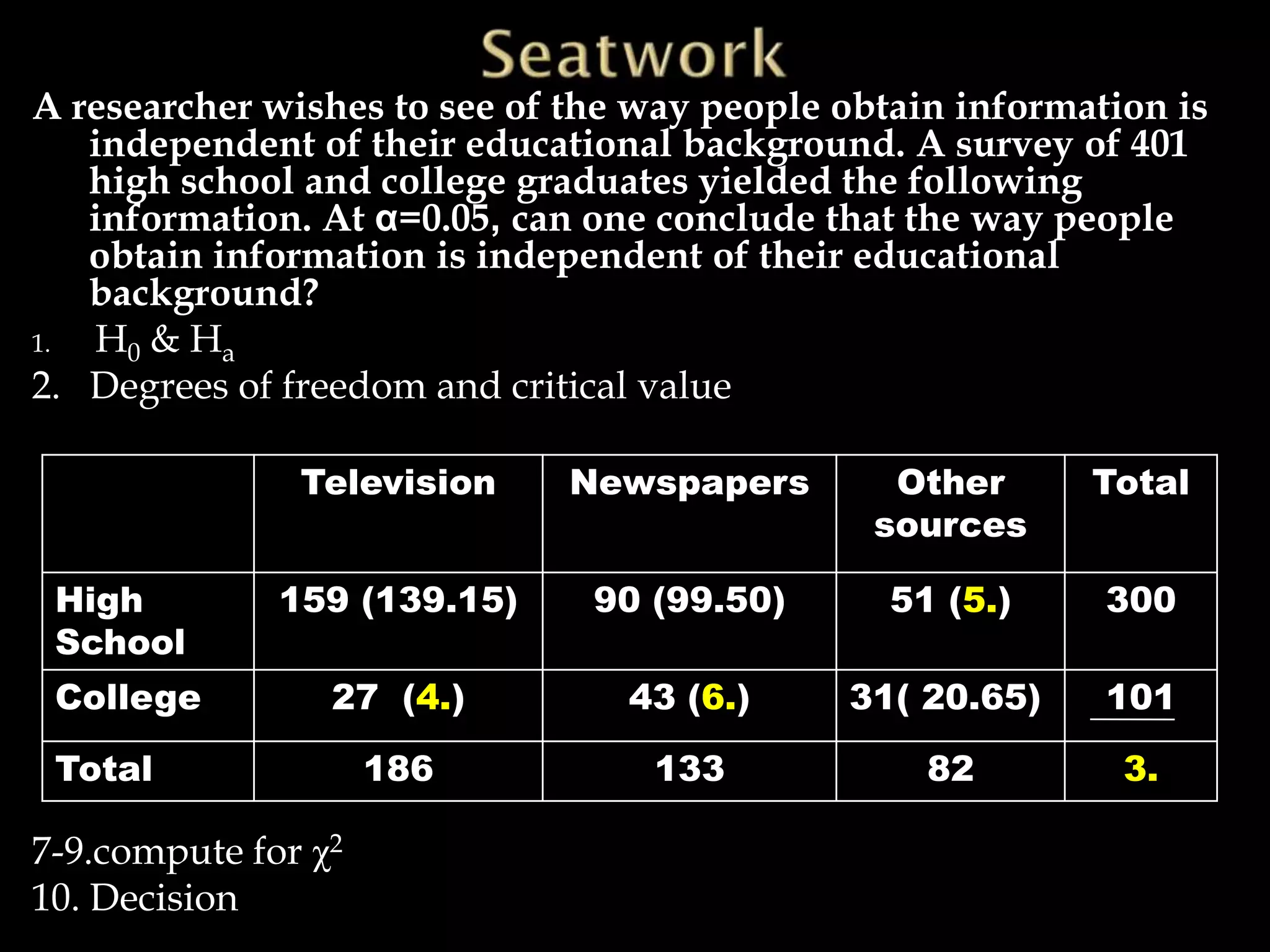
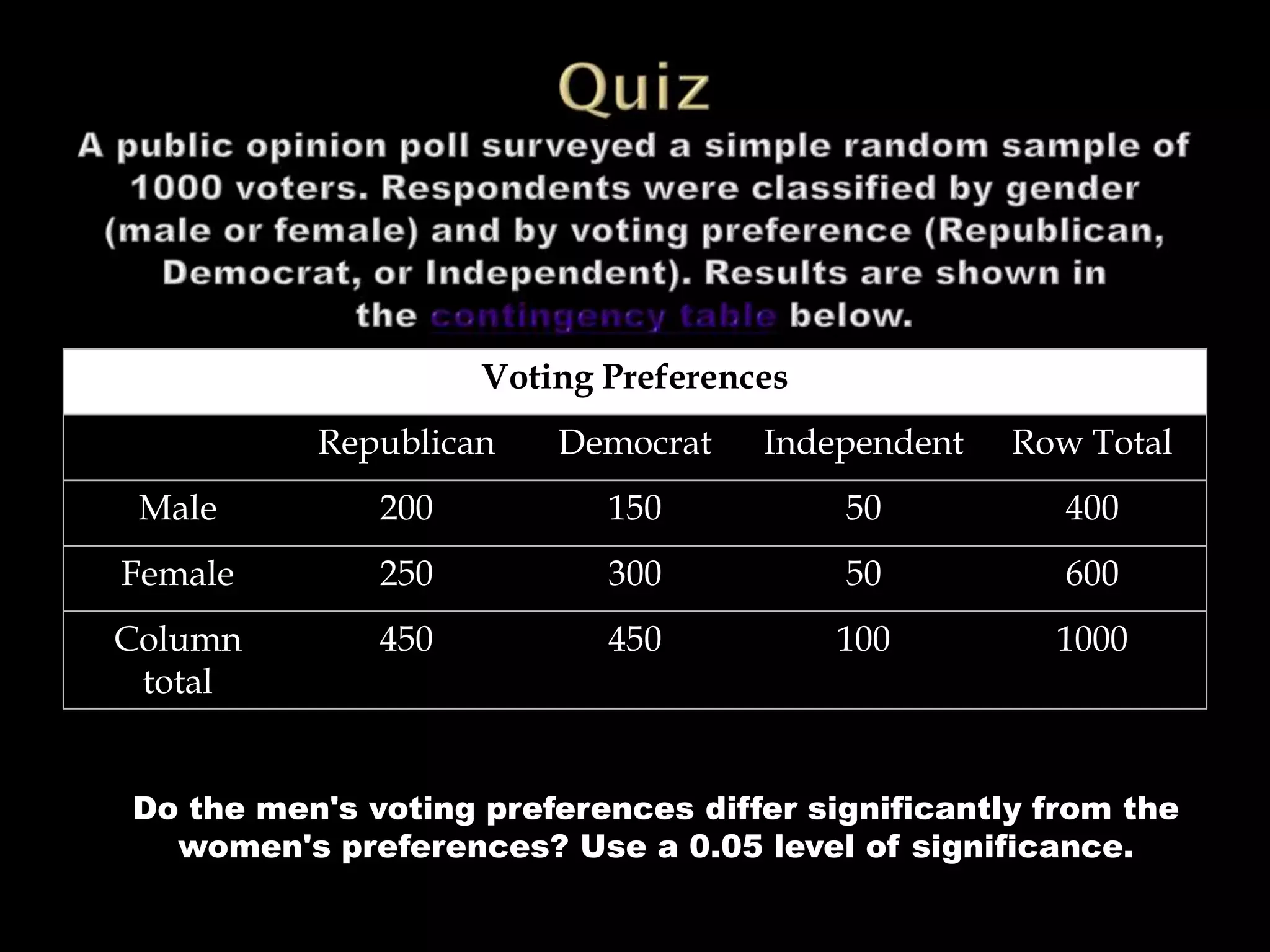
The document discusses testing for independence between two variables using a contingency table and chi-square test. It explains how to set up a contingency table with observed and expected frequencies, and how to calculate the chi-square test statistic to determine if the variables are independent or dependent. An example is provided that tests if blood pressure is independent of jogging status using a contingency table and chi-square test.