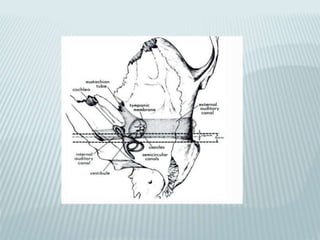
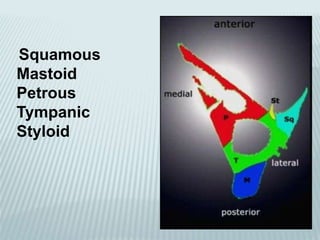
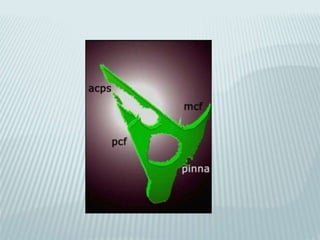
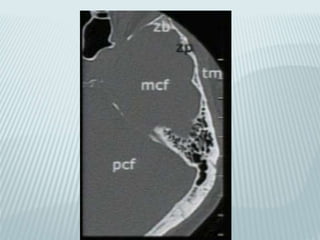
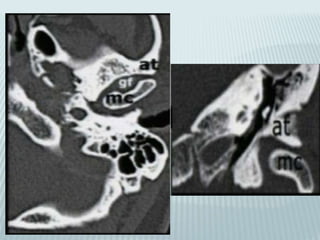
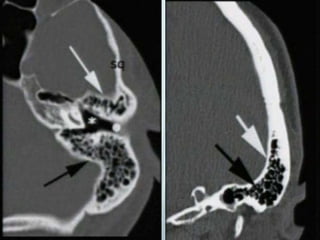
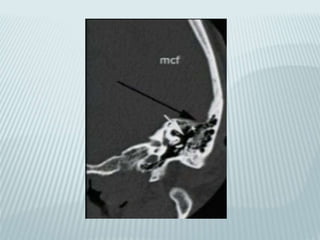
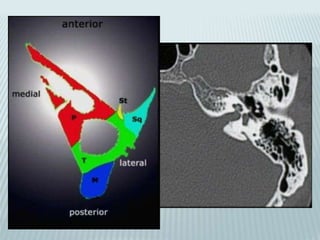
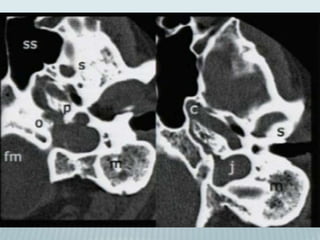
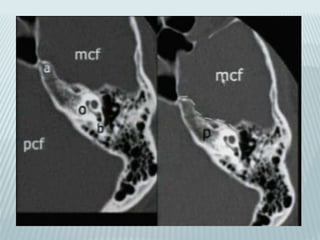
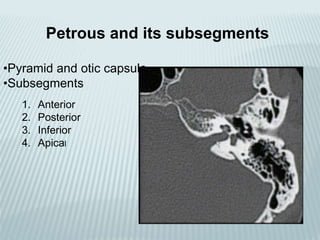
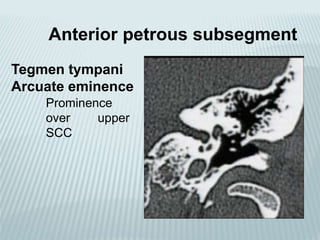
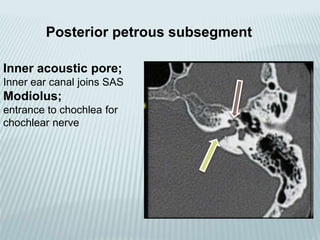
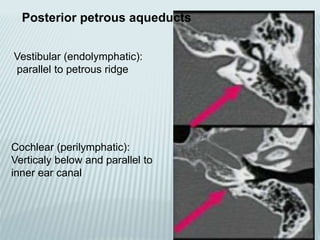
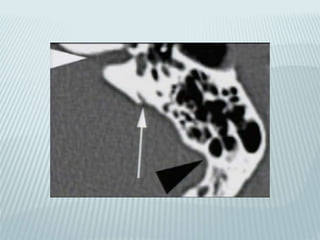
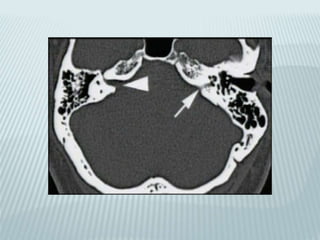
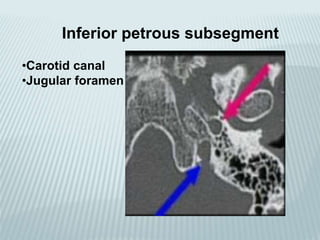
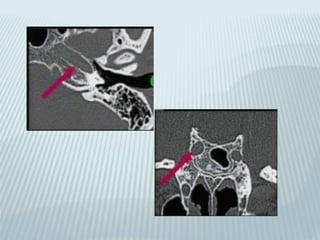
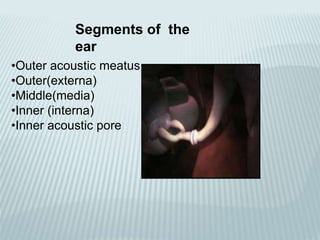
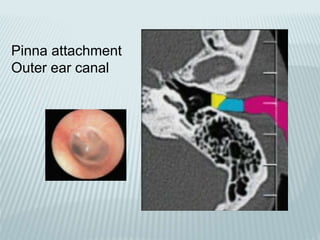
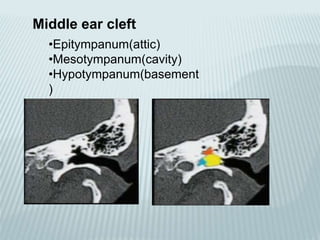
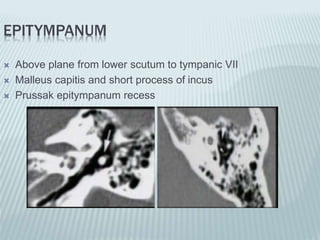
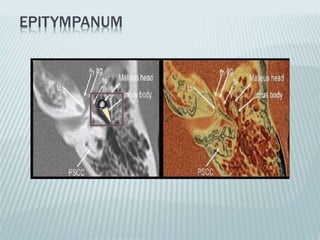
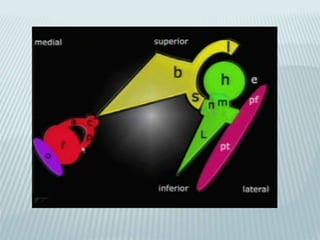
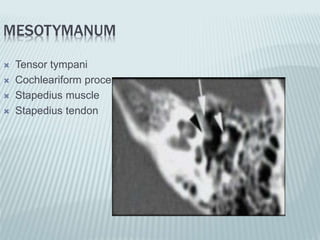
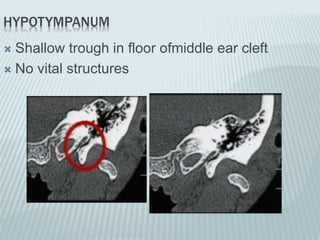
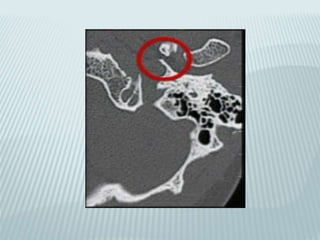
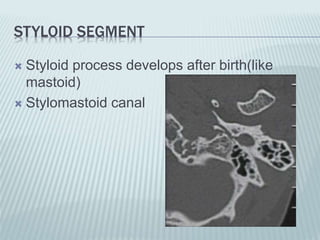
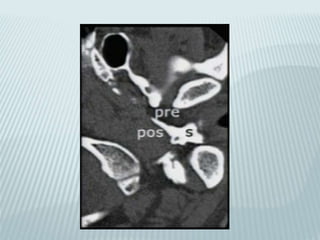
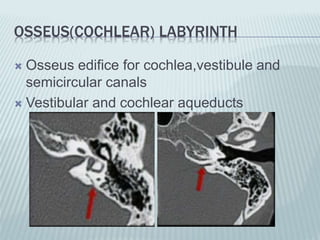
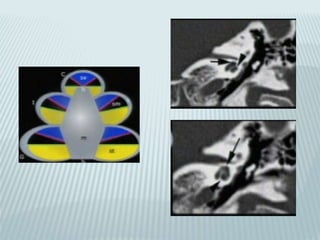
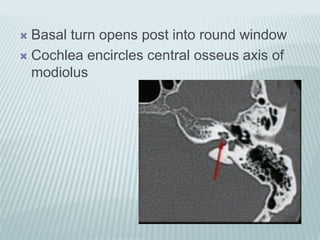
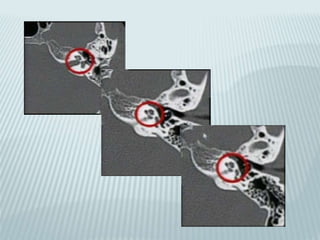
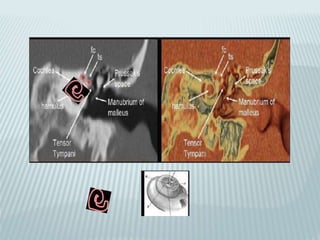
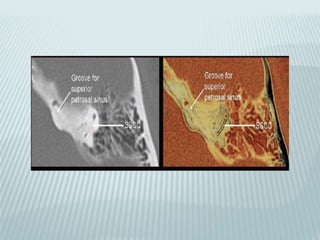
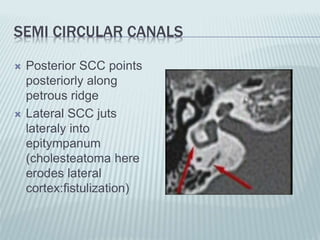
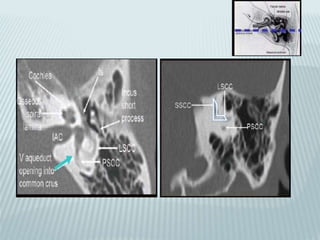
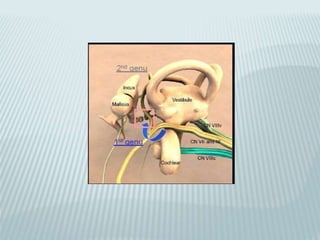
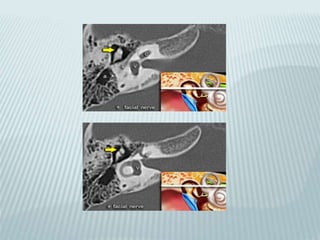
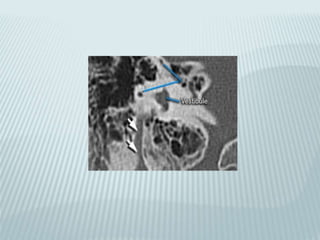
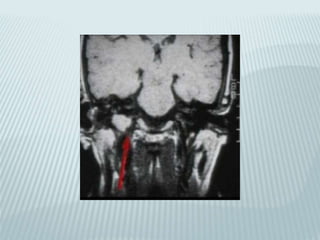
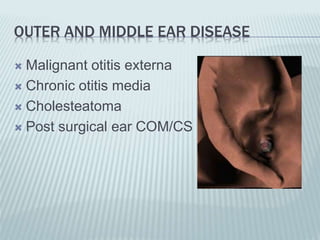
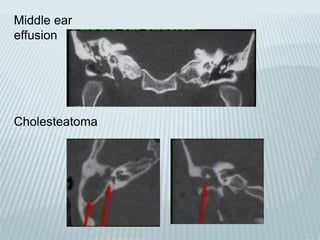
This document provides a detailed overview of CT imaging and anatomy of the temporal bone. It describes the CT imaging protocol used, including axial and coronal views. It then reviews the anatomy of each segment of the temporal bone - squamous, mastoid, petrous, tympanic and styloid. For the petrous segment, it describes the subsegments and key structures like the internal acoustic meatus. It reviews the anatomy of the outer, middle and inner ear, including structures like the cochlea and semicircular canals. Pathologies affecting the temporal bone like otitis externa and cholesteatoma are also summarized.