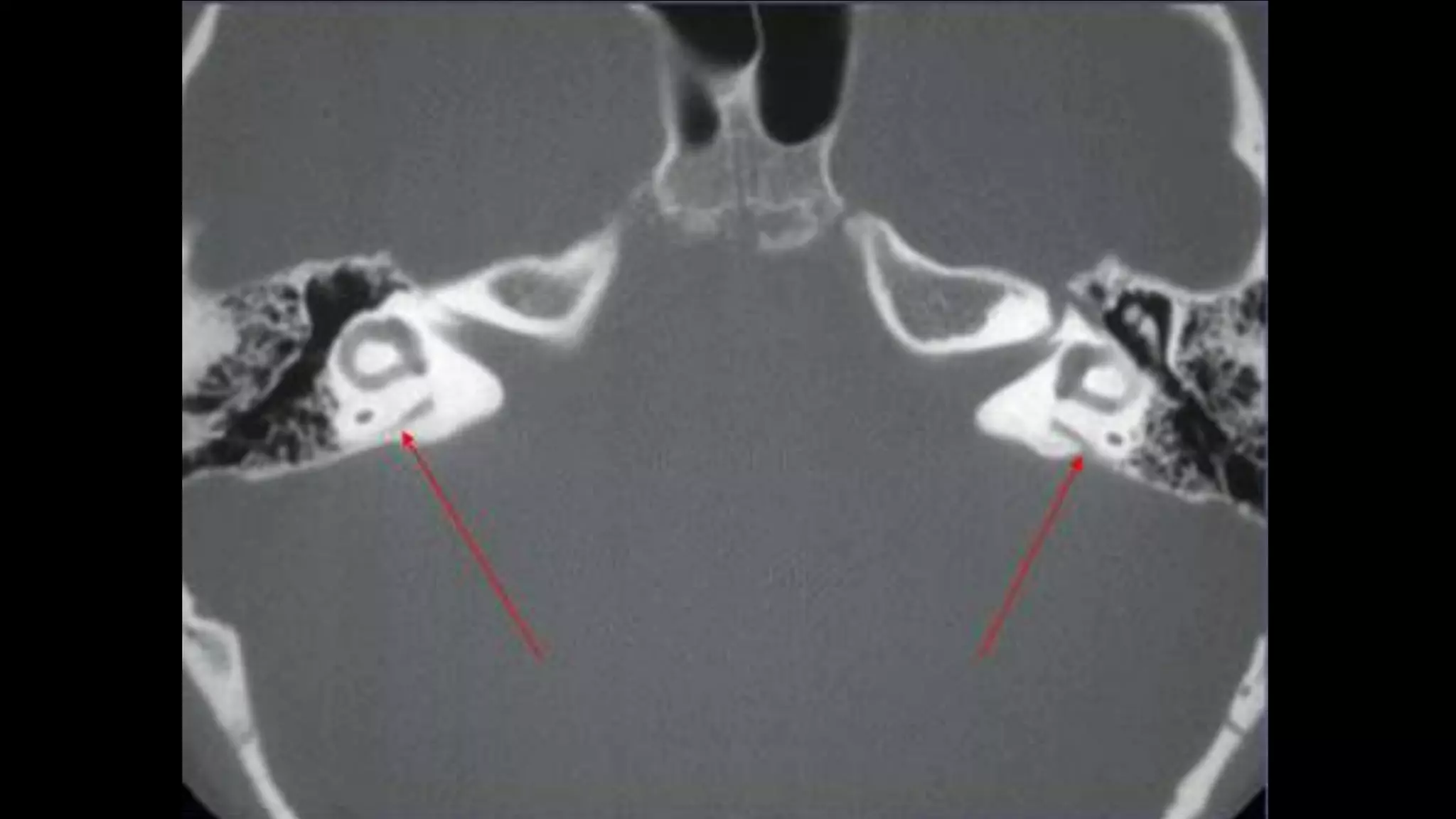
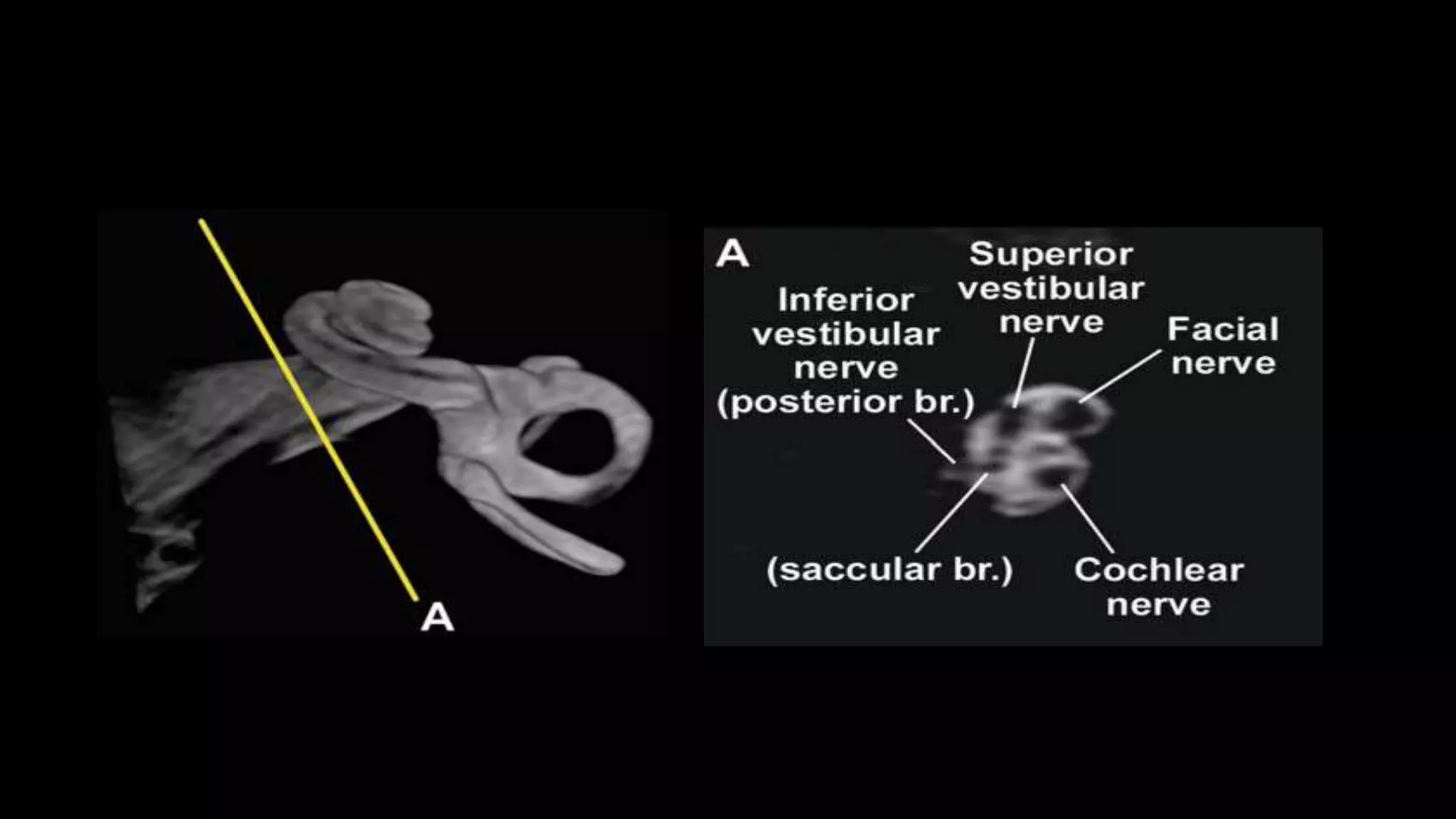
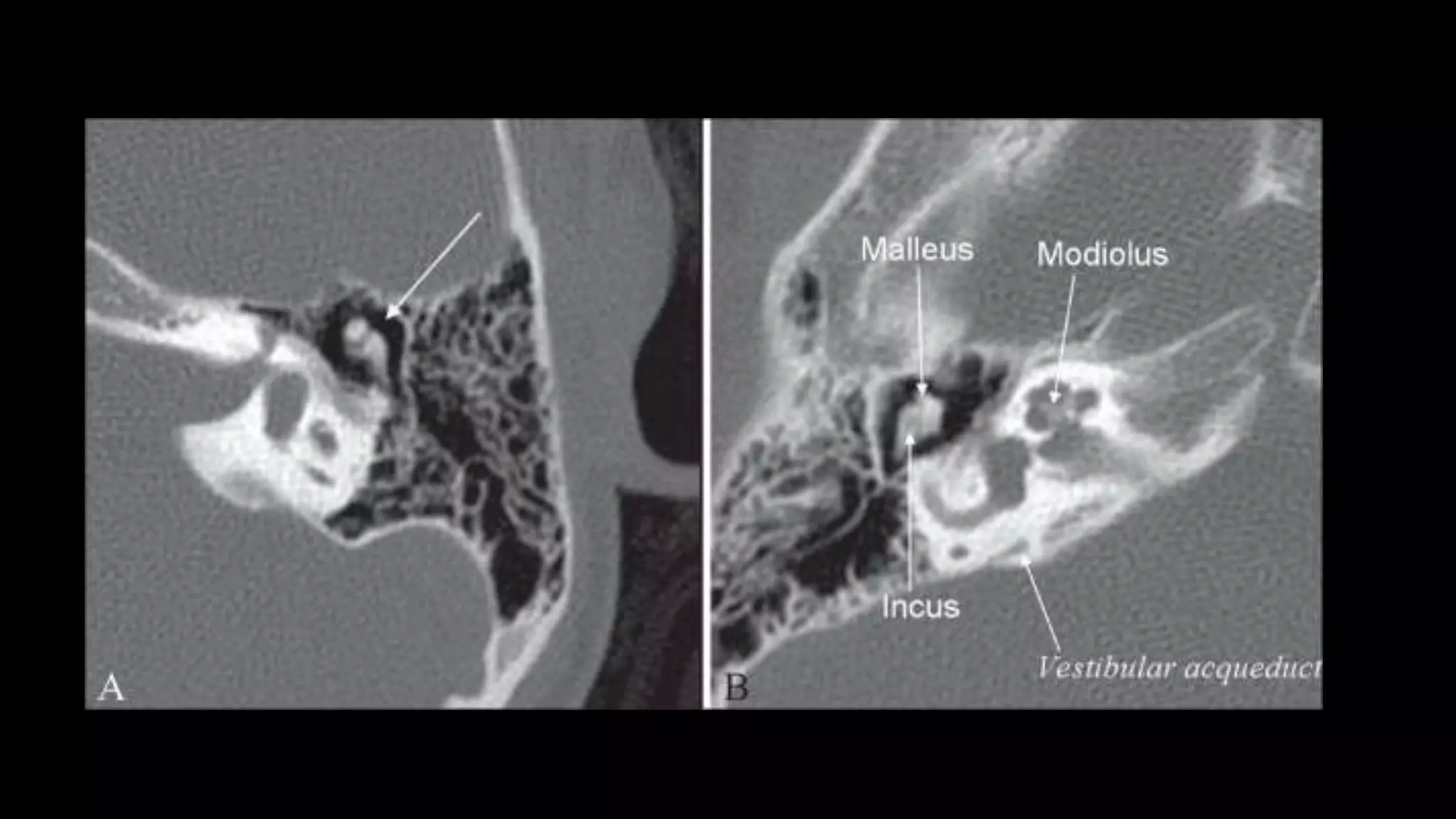
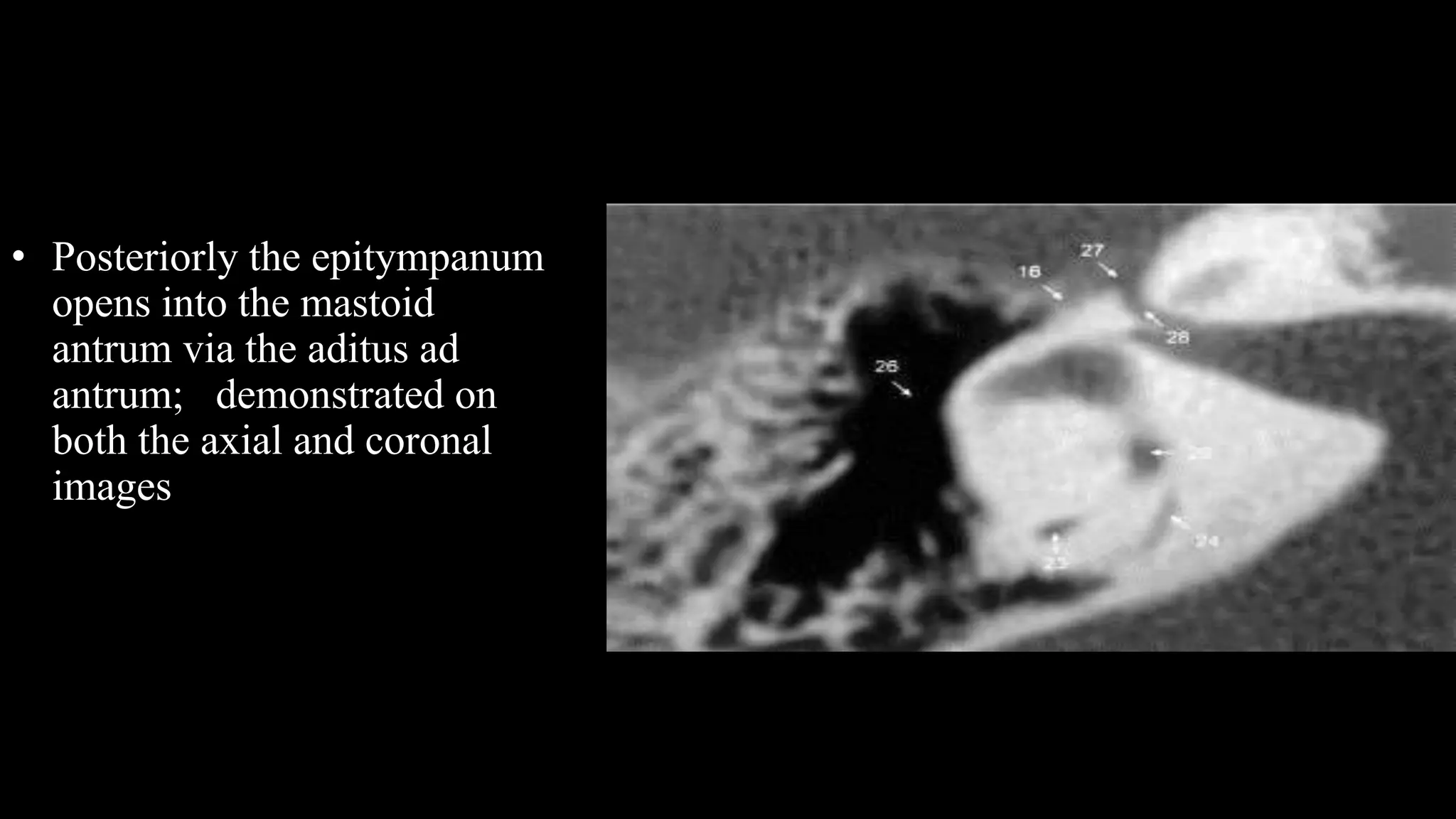
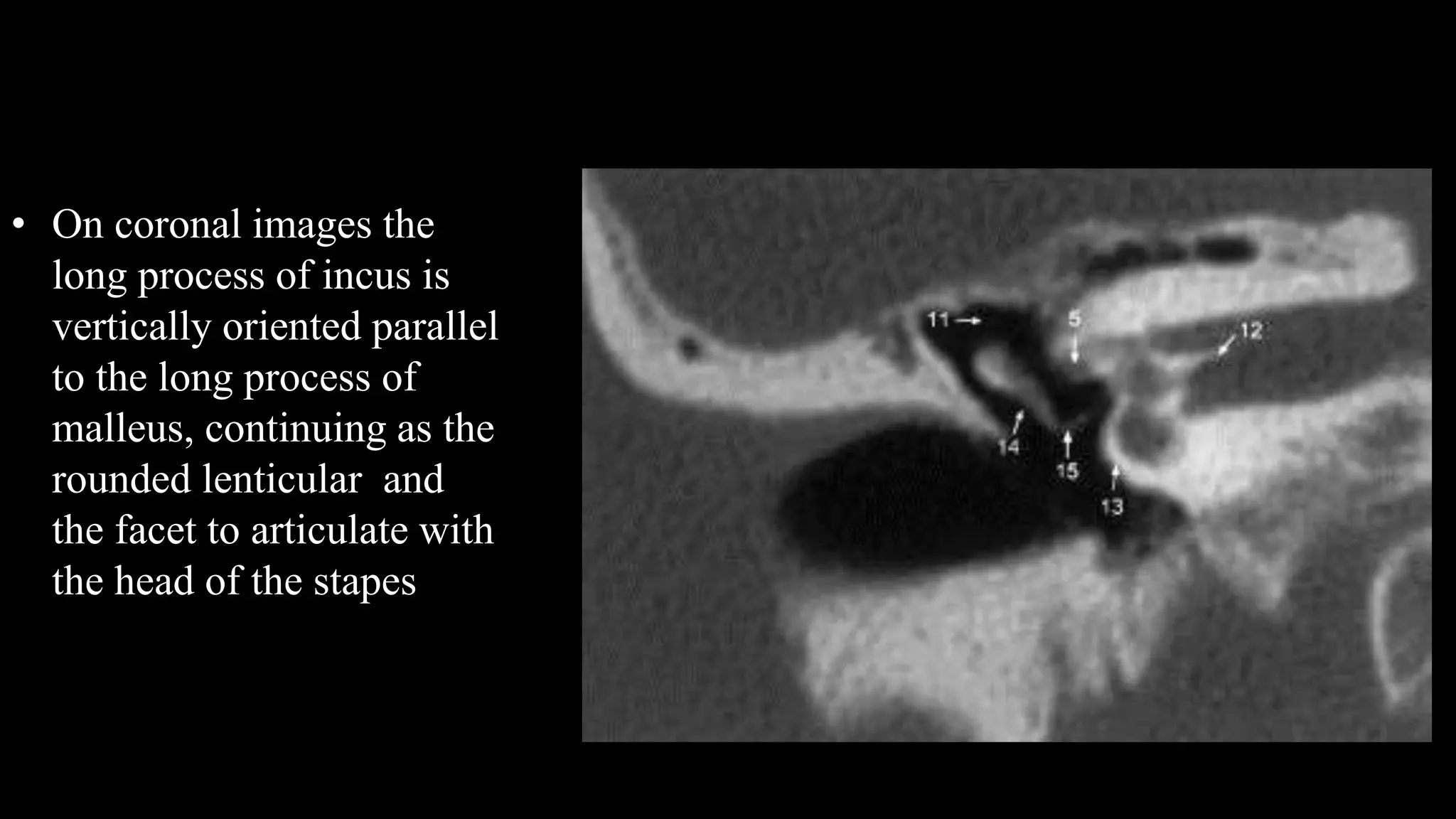
This document discusses the anatomy seen on CT scans of the temporal bone in different planes. It provides details on key structures visible in the axial, coronal, and sagittal planes, including the semicircular canals, cochlea, facial nerve canal, ossicles, and mastoid air cells. Different anatomical compartments of the middle ear are also described based on coronal imaging. The purpose is to identify relevant anatomy, assess disease extension and surgical planning for ear procedures.