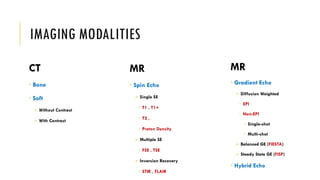
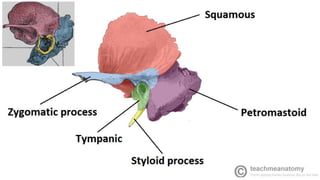
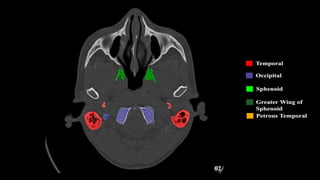
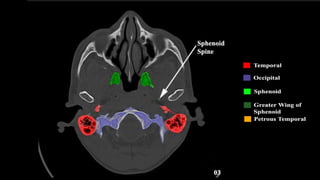
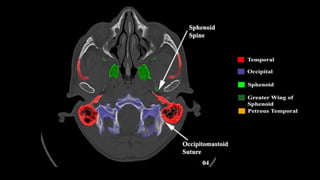
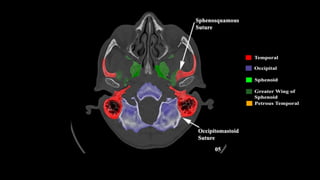
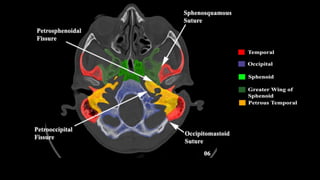
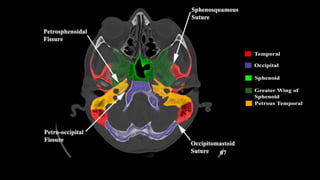
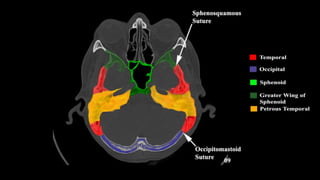
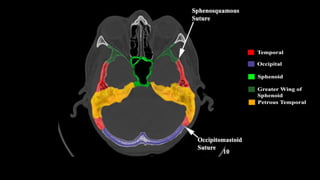
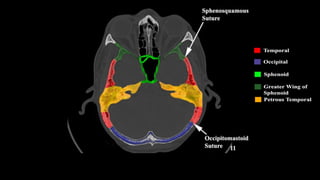
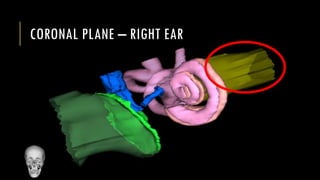
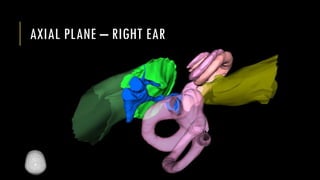
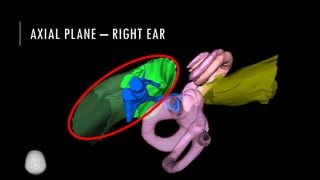
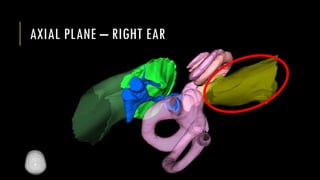
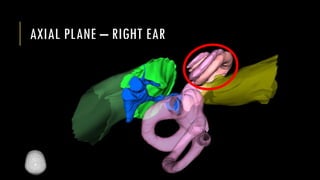
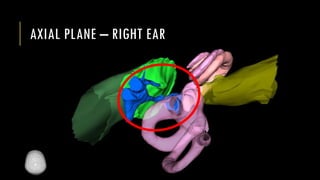
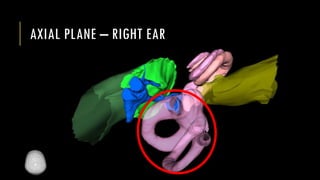
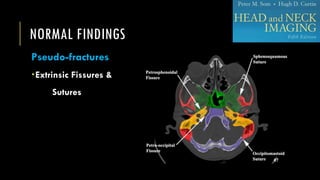
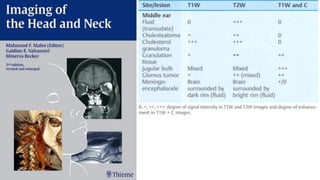
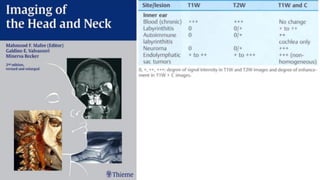
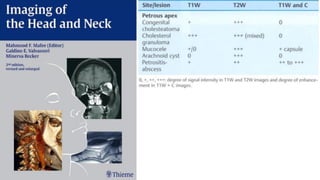
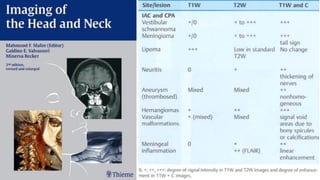
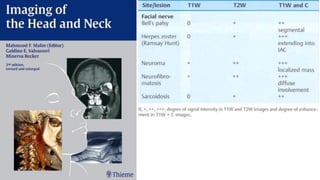
This document discusses imaging techniques for the temporal bone, detailing various CT and MR modalities used to assess structural abnormalities. It outlines the anatomical compartments of the temporal bone and highlights both normal and abnormal findings, including differential diagnoses for common conditions. References to additional resources for further study are also provided.