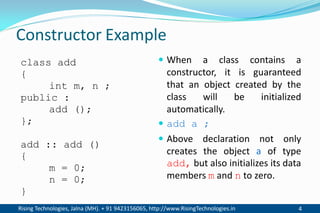
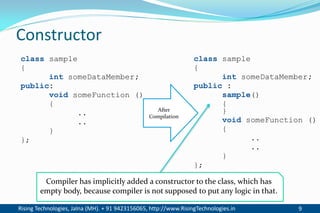
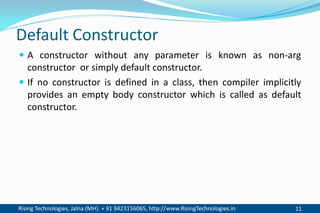
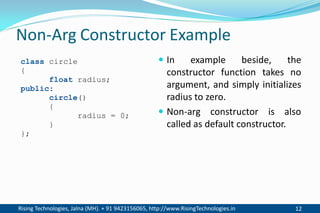
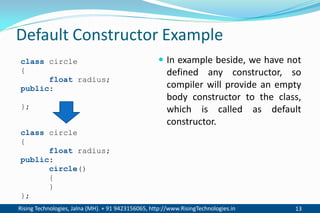
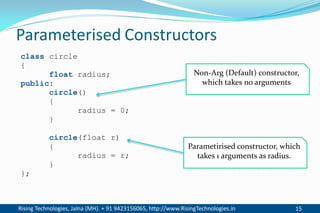
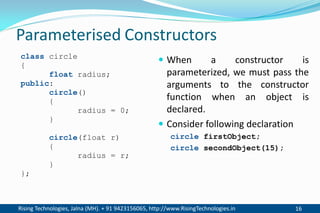
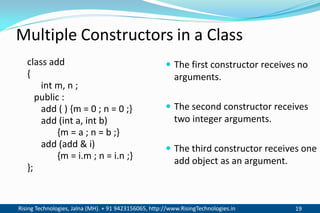
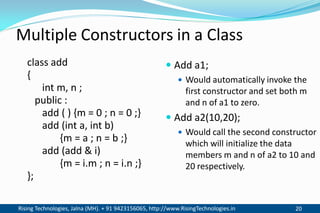
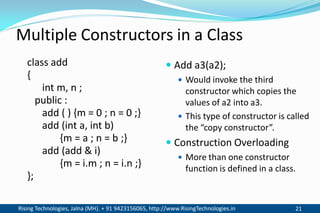
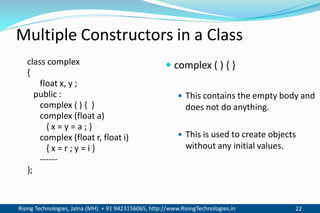
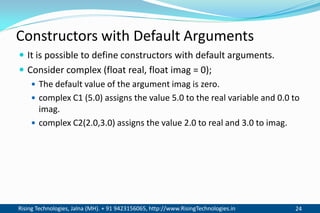
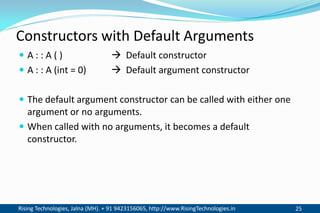
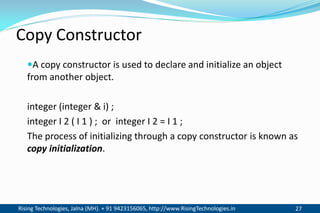
The document discusses different types of constructors in C++ including default, parameterized, copy, and dynamic constructors. It explains that a constructor is a special member function that is called automatically when an object is created to initialize the object's data members. Constructors have the same name as the class and can take arguments to initialize objects with different initial values. The document provides examples of different constructor types.