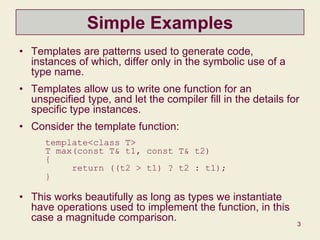
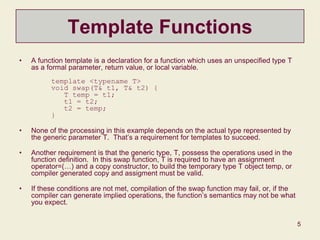
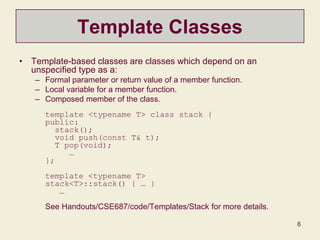
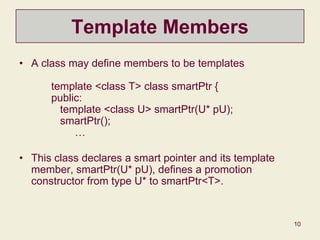
This document discusses templates in C++ and provides examples of template functions, classes, parameters, members, and specializations. It covers how templates allow code to be written generically for unspecified types and instantiated for specific types. It also discusses container classes, iterators, reference vs. value semantics, and how templates are used extensively in the Standard Template Library.