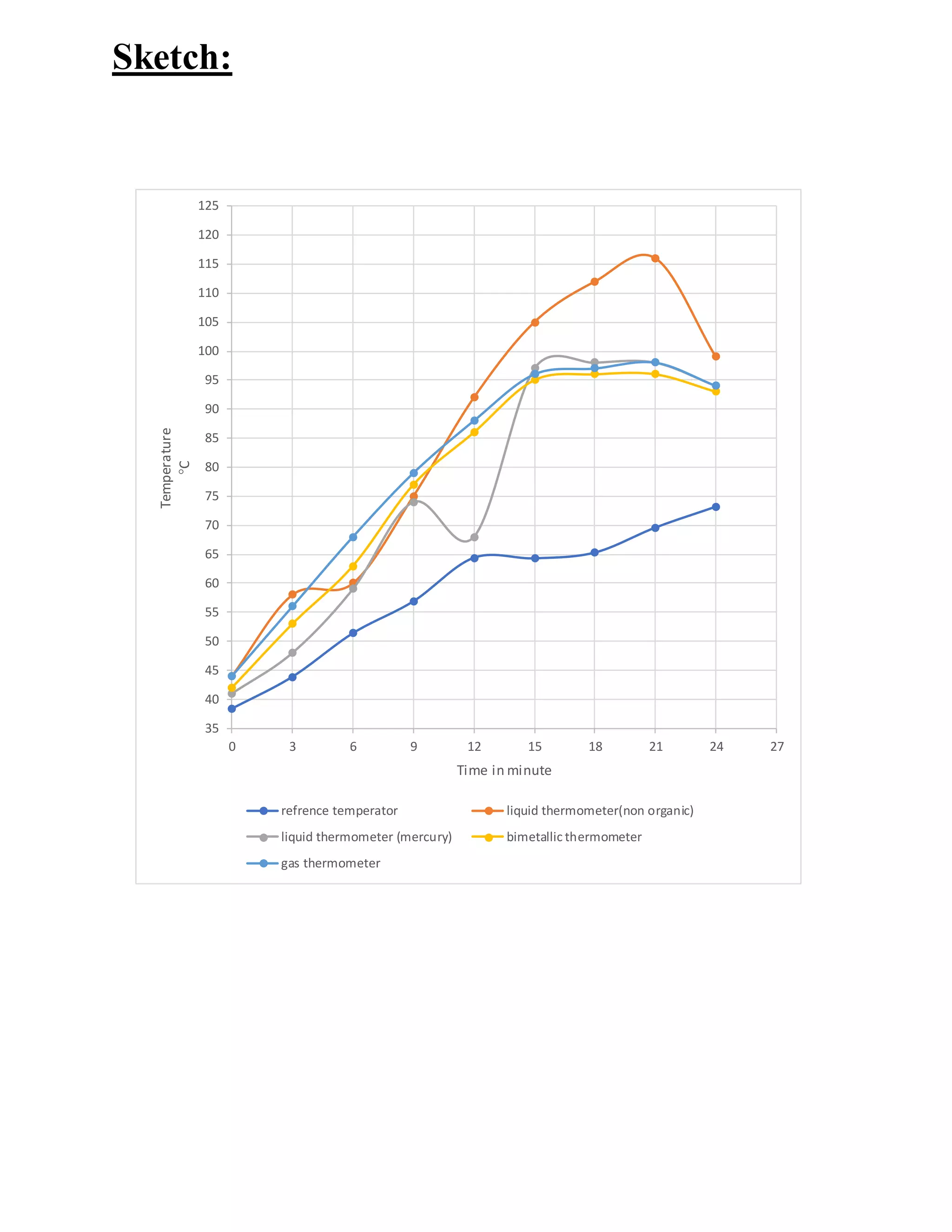
The document describes an experiment conducted at Erbil Polytechnic University focusing on temperature measurement methods, including liquid thermometers, bimetallic thermometers, and gas thermometers. It details the theory, procedure, and data collected, along with a discussion on measurement accuracy and potential errors. The results indicate that gas thermometers provide the best accuracy among the tested methods.