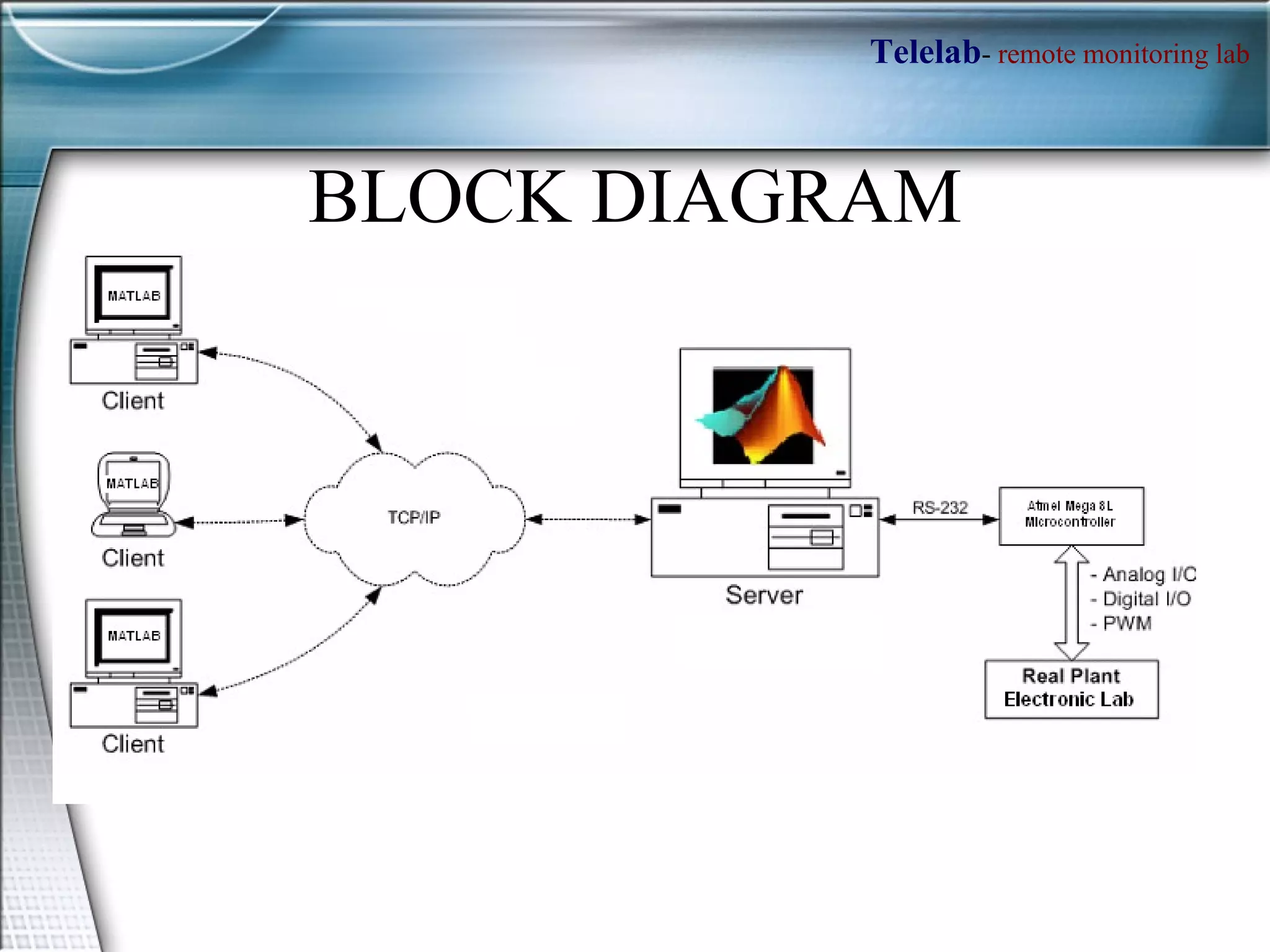
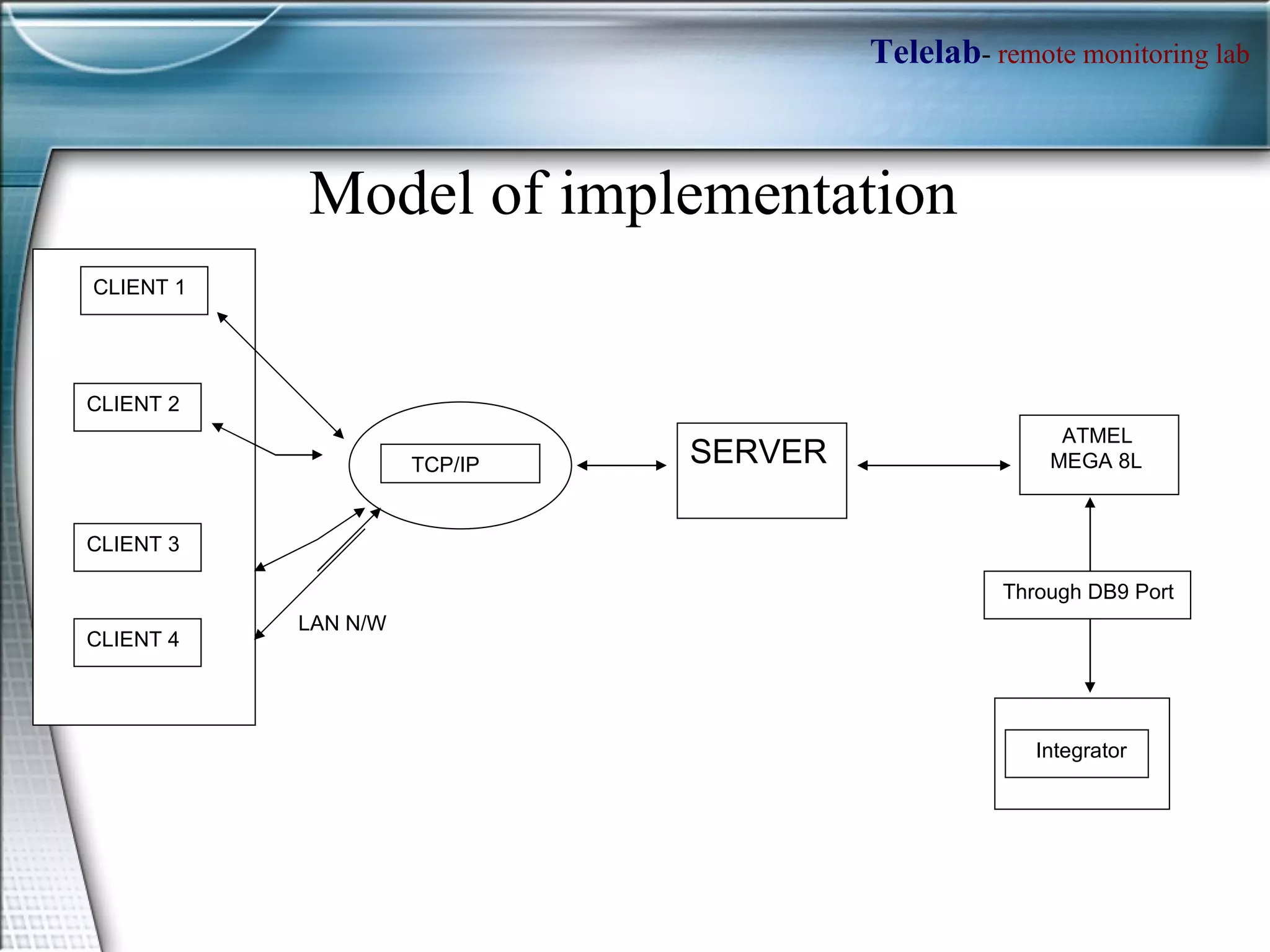
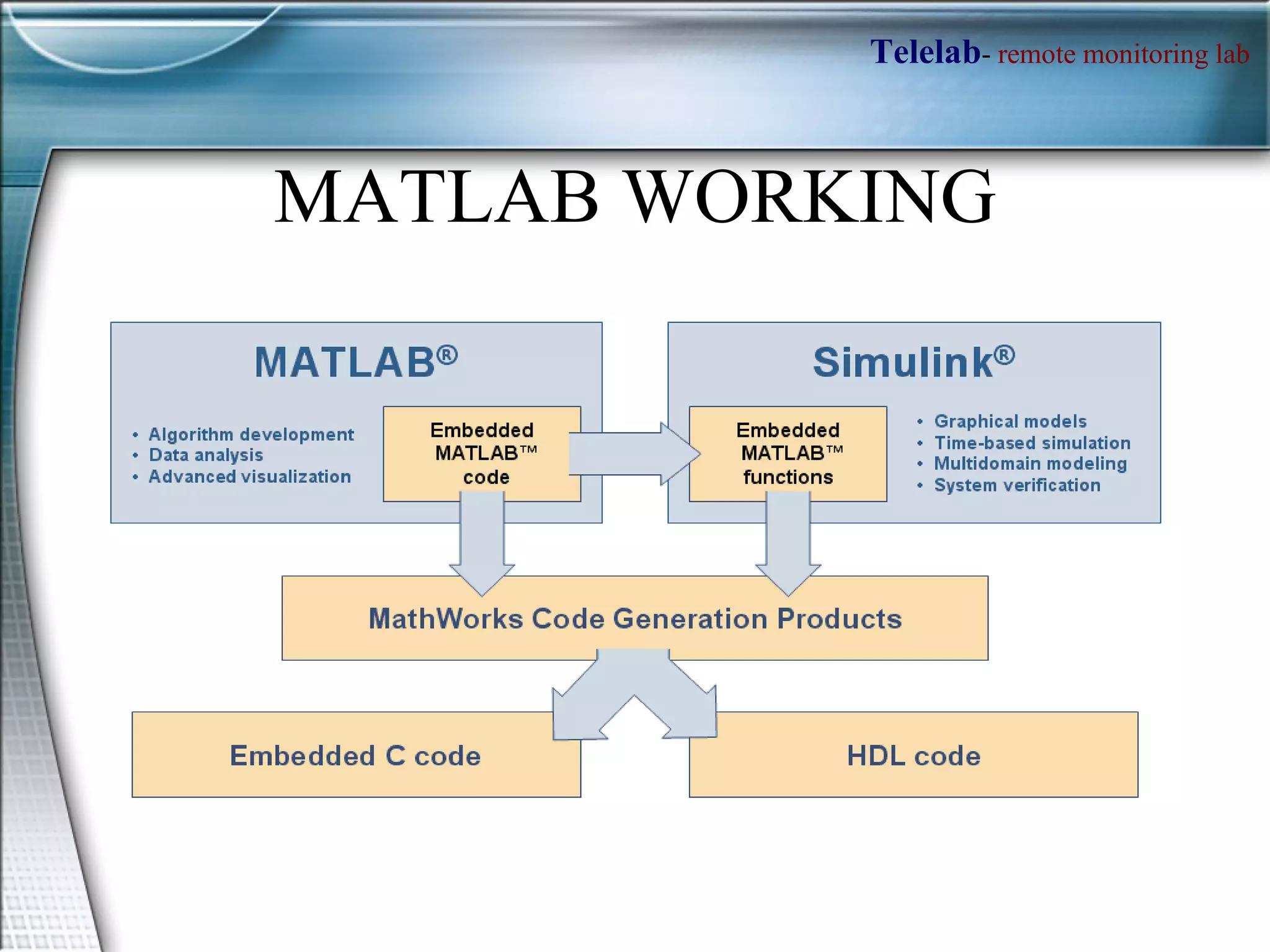
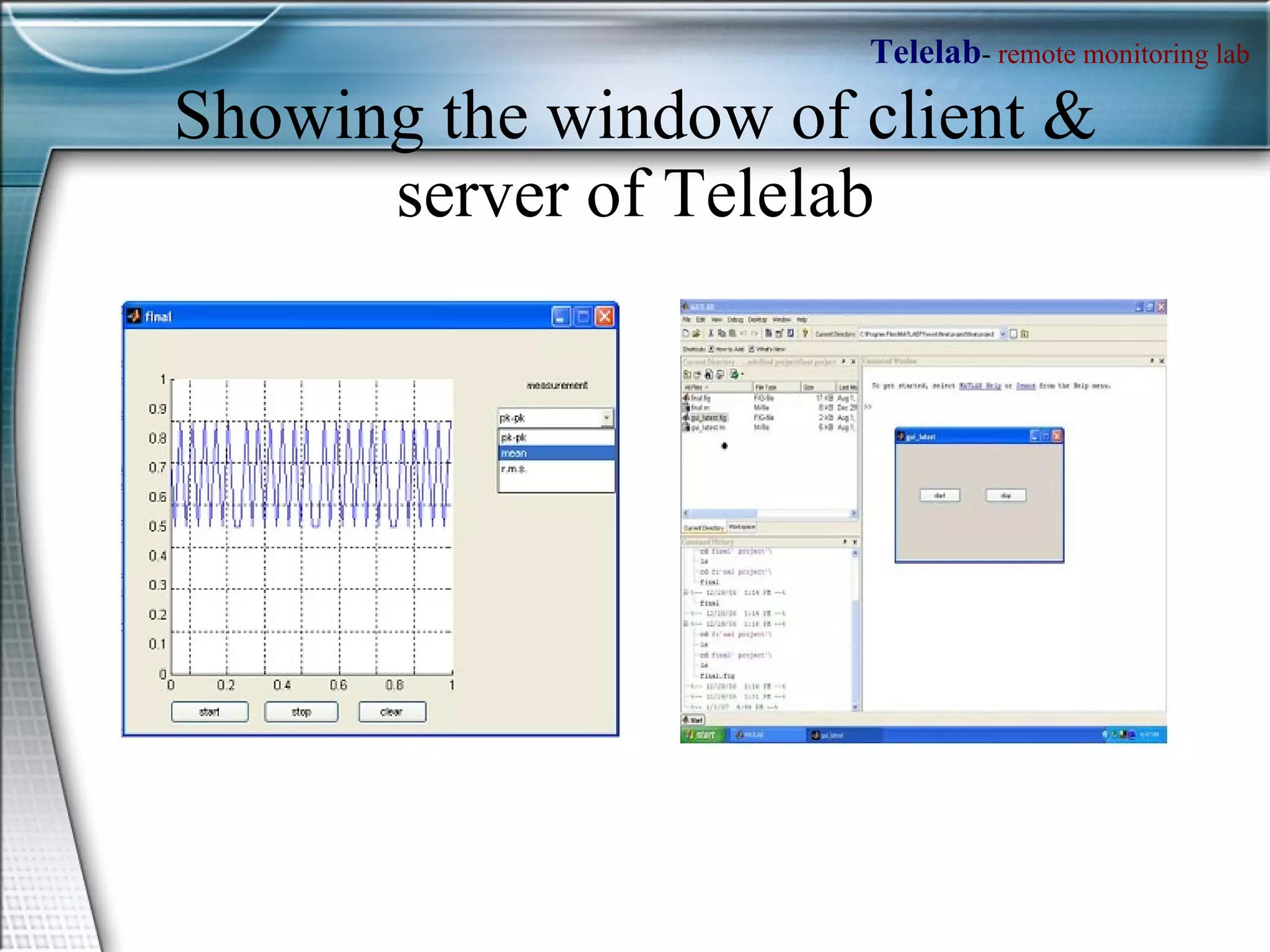
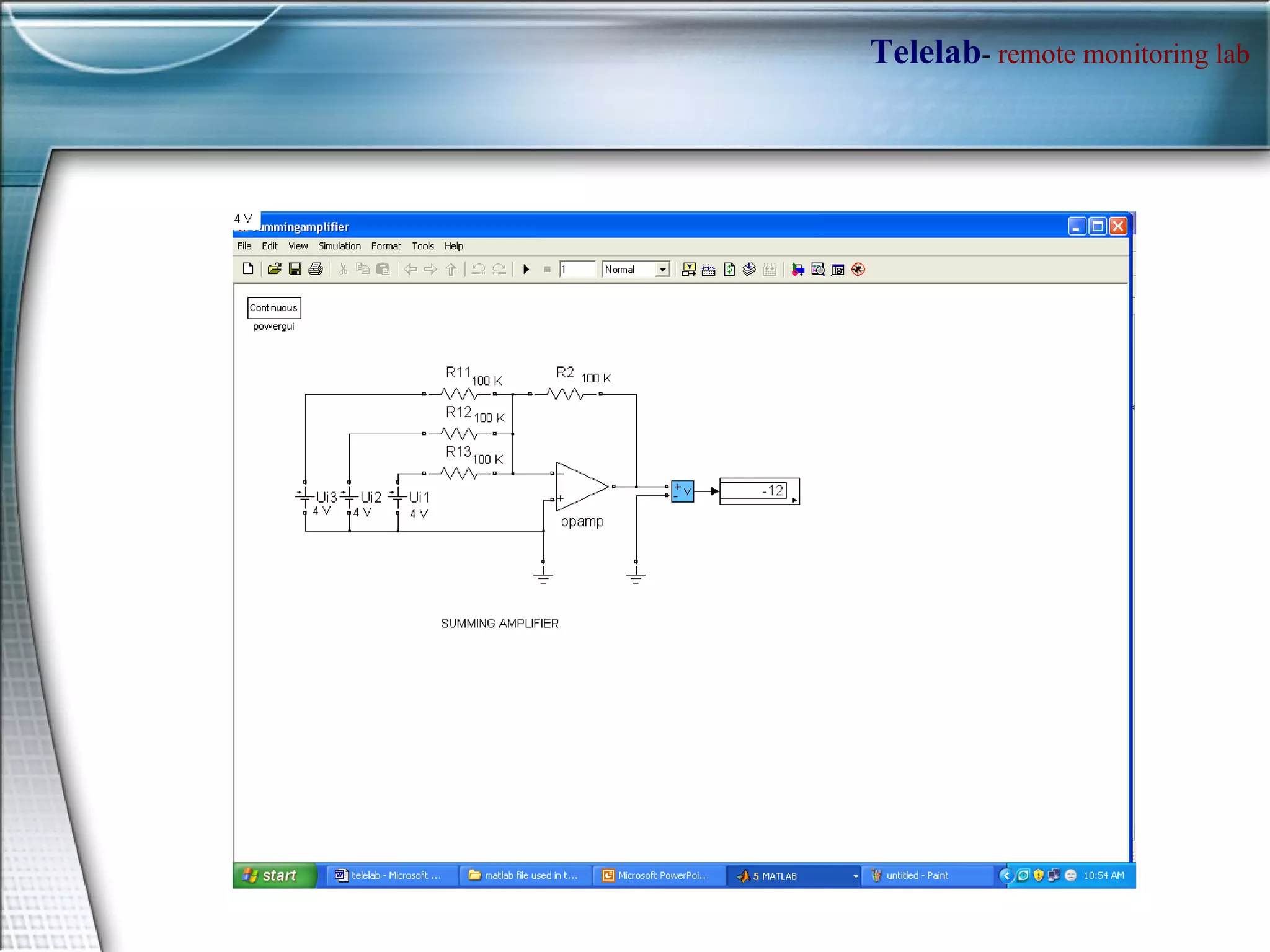
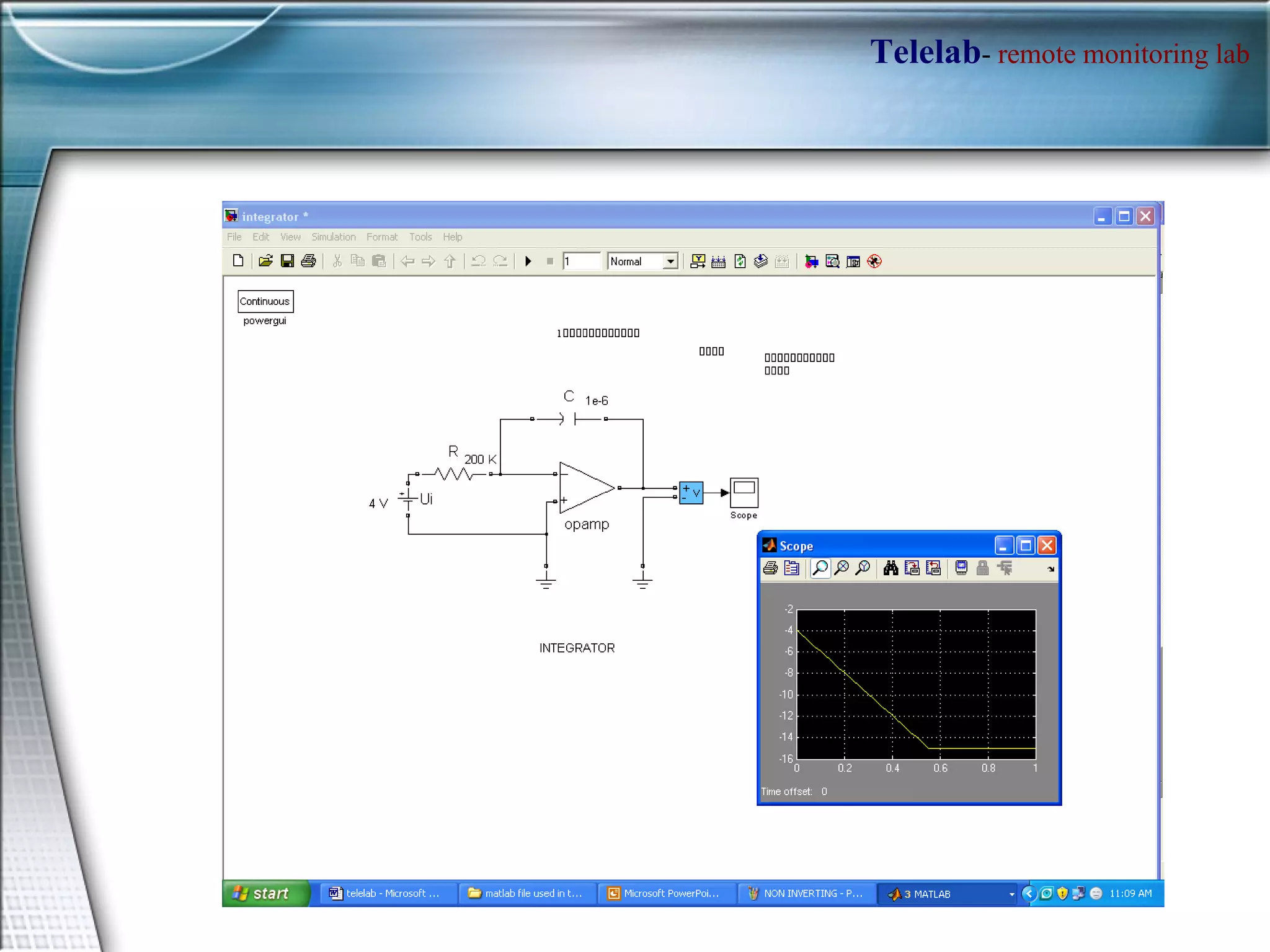
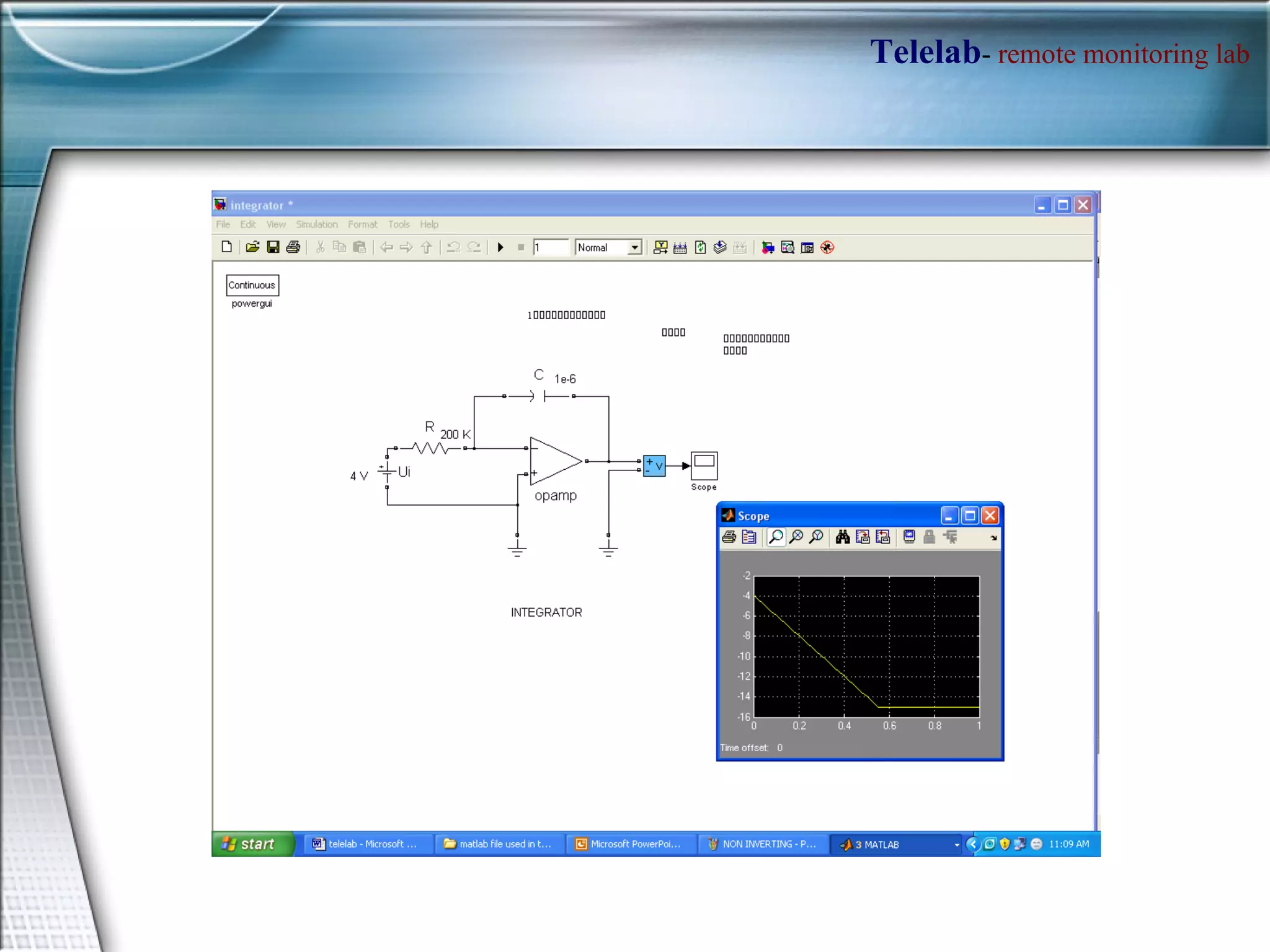
TELELAB is a remote monitoring and control system that allows experiments to be observed and controlled from a web browser without being physically present. A centralized server connects multiple remote PCs running experiments to clients over the internet. This reduces costs and facilitates collaboration between laboratories. The system uses MATLAB to program controllers that can be automatically uploaded to remote PCs to guarantee real-time performance during remote experiments.




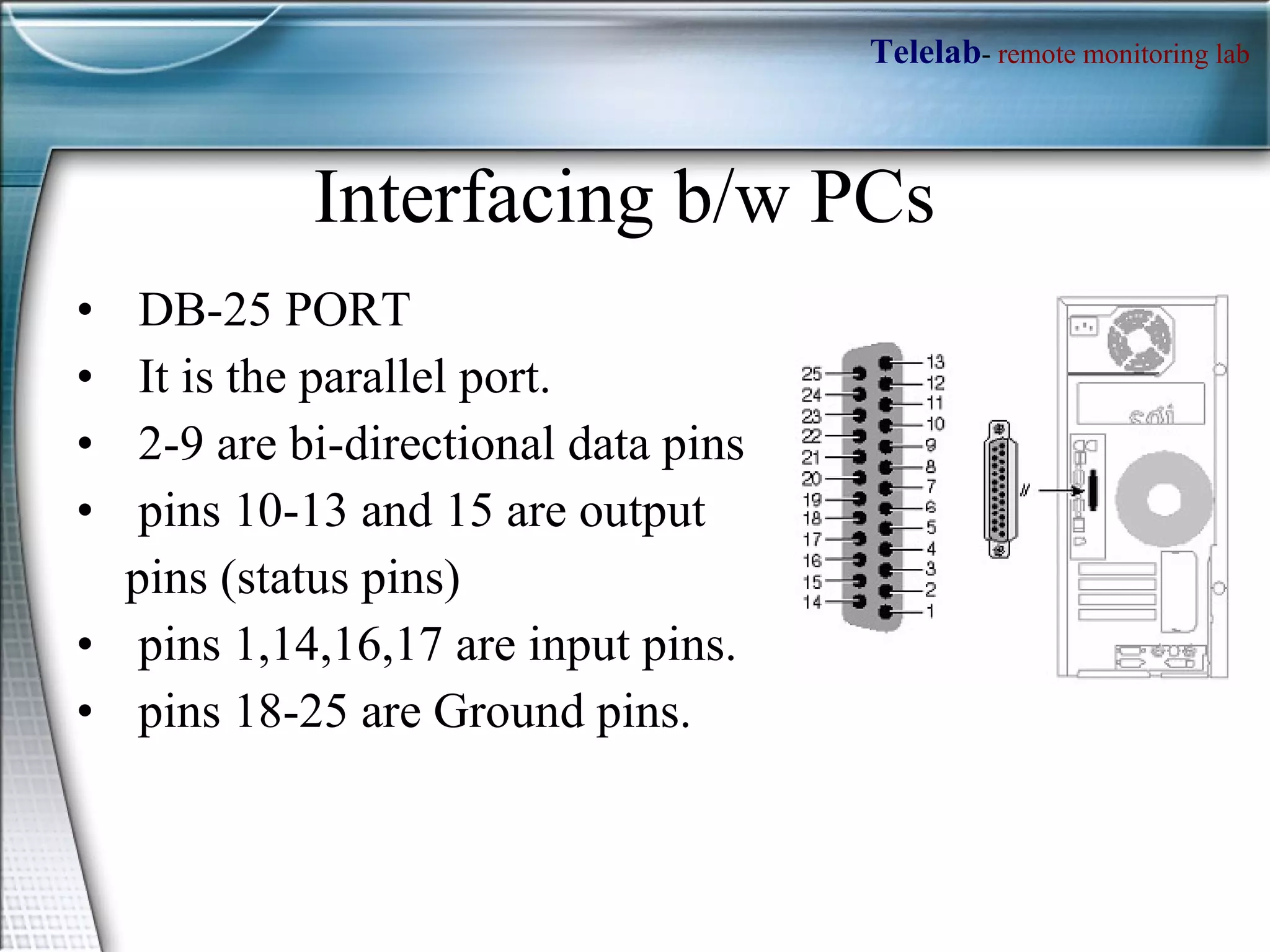
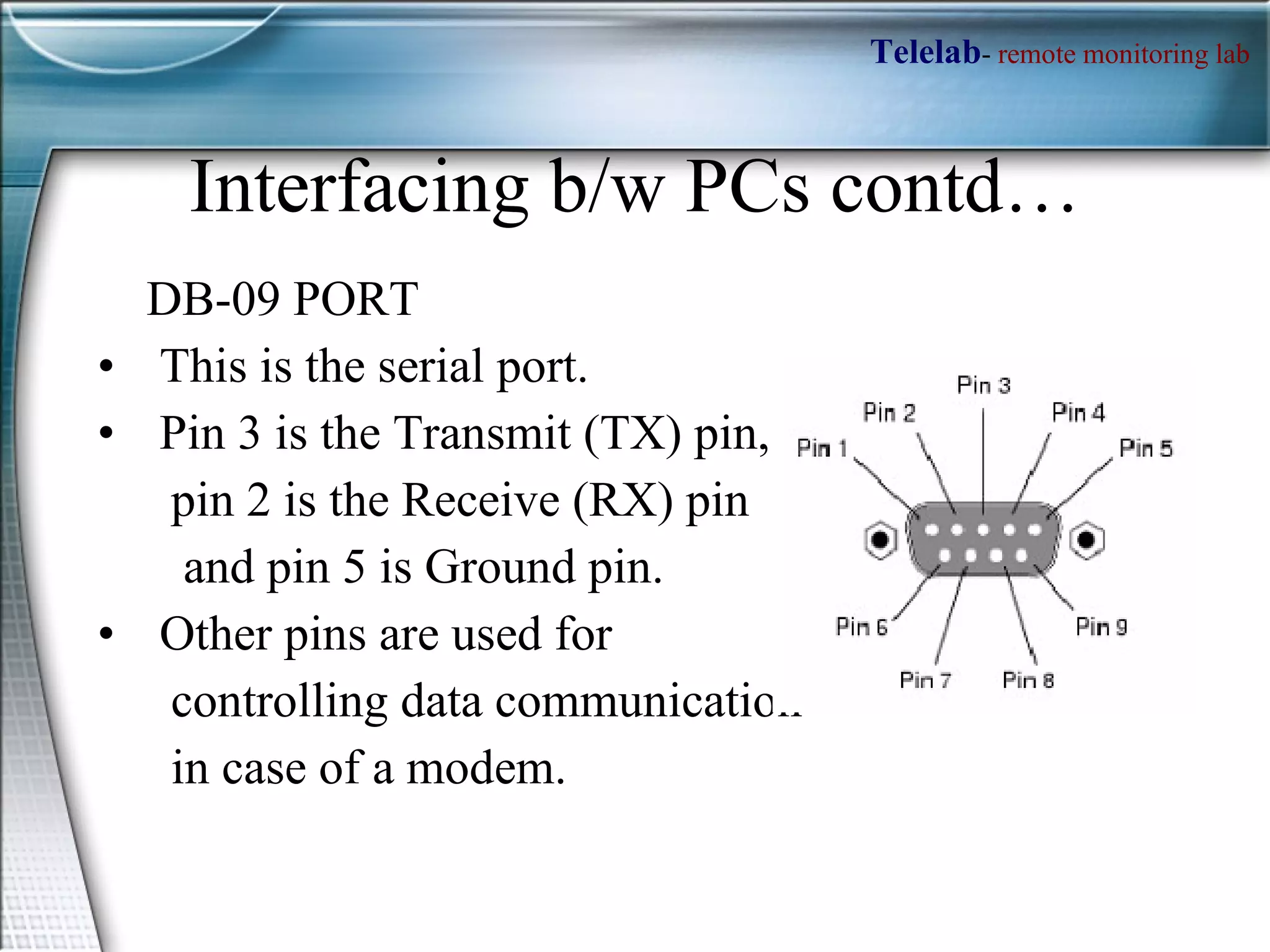
![How access the Parallel port ?? MATLAB has an adaptor to access the parallel port . To access the parallel port in MATLAB, define an object >> parport= digitalio('parallel','LPT1'); obtain the port address using, >> get(parport,'PortAddress') >> daqhwinfo('parallel'); % To get data acquisition hardware information We have to define the pins 2-9 as output pins, by using addline function >> addline(parport, 0:7, 'out') Now put the data which you want to output to the parallel port into a matrix; e.g. >> dataout = logical([1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1]); Now to output these values, use the putvalue function >> putvalue(parport,dataout); Alternatively, you can write the decimal equivalent of the binary data and output it. >> data = 23; >> putvalue(parport,data);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telelab-2-100815103435-phpapp02/75/Telelab-2-13-2048.jpg)

![REFERENCES [1] Matlab help. http://www.mathworks.com/academia/ [2] ‘tcp udp ip’ toolbox for Matlab. http //www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/f ileexchange/ loadF ile.do?objectI d = 345 [3] Instrument Control Toolbox for Matlab. http : //www.mathworks.com/access/helpdesk [4] WinAvr help. [5] Atmel Avr Manuals mega8 and some appnotes. http : //atmel.com/dyn/resources [6] Real Systems in the Virtual Lab 2000. [Online]. Available: http://prt.fernunihagen.de/rsvl [7] Remote Lab Experiment RC Oscillator for Learning of Control. S. Uran, D. Hercog and K. Jezernik. University of Maribor, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Maribor, Slovenia [8] S. Dormido, Control Learning: Present and Future, In Proc. 15 IFAC World Congres on Automatic Control,Barcelona, Spain, 2002. [9] M. Casini, et all, The Automatic Control Telelab, IEEE Control Systems Magazine, vol. 24, No. 3, 2004, pp.36-44.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telelab-2-100815103435-phpapp02/75/Telelab-2-27-2048.jpg)