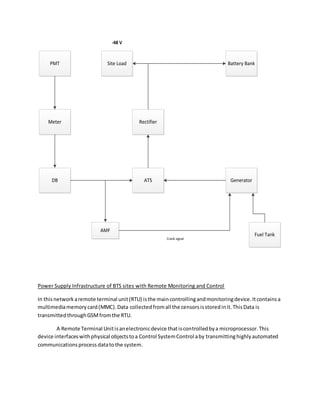
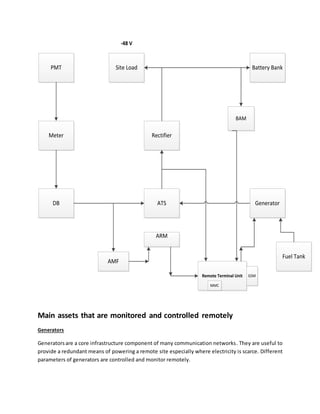
Remote monitoring and control allows organizations to monitor and manage equipment and processes remotely. It has three main components: equipment monitoring using instruments to measure variables like temperature, pressure, and flow; a communication channel to transmit the data; and a monitoring station to receive and analyze the data. This allows large companies to oversee assets spread across wide geographical areas, reducing costs of maintenance, staffing, and travel while improving optimization, safety, and customer satisfaction. Key infrastructure like generators, battery banks, and fuel tanks can have variables like output, temperature, fuel level, and usage remotely monitored and controlled to improve efficiency and prevent issues like equipment failure or fuel theft.