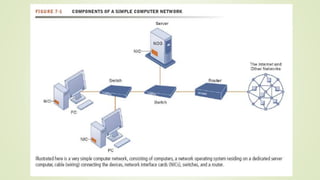
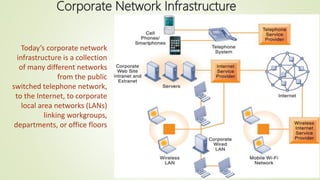
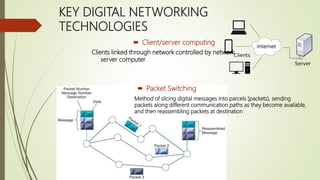
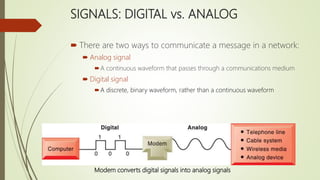
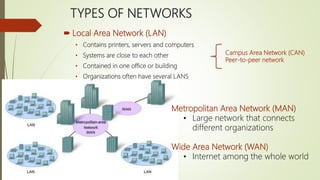
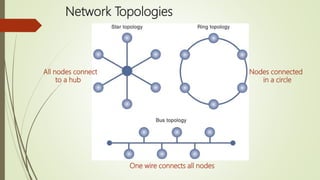
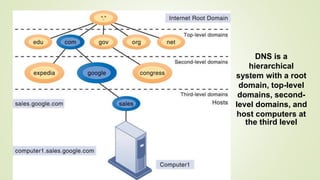
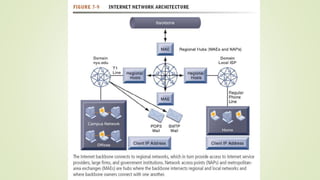
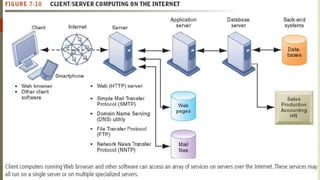
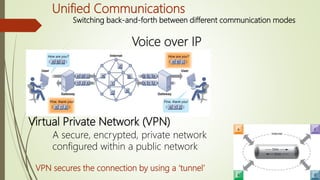
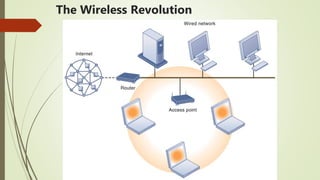
The document discusses various topics related to telecommunications, the internet, and wireless technology. It covers the convergence of telephone and computer networks through technologies like smartphones. It also describes broadband connections provided by telephone and cable companies at speeds of 1-15 Mbps. Finally, it notes that voice and data communication as well as internet access are increasingly taking place over broadband wireless platforms.