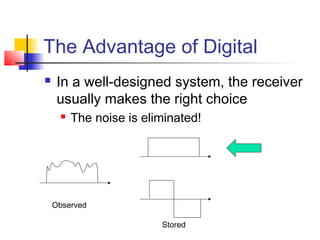
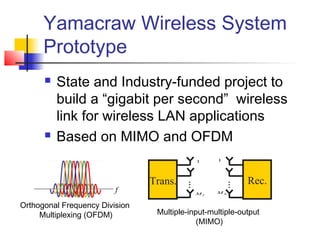
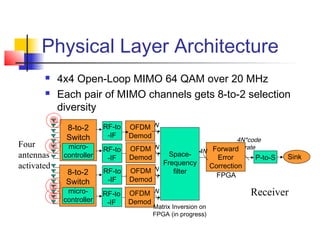
The document discusses the Telecommunications Technical Interest Group (TIG) at Georgia Tech, which focuses on digital communications. It provides an overview of undergraduate and graduate coursework in physical layer communications and networking. Examples are also given of research conducted at Georgia Tech on topics such as optical data storage, satellite communications using adaptive antennas, and high-speed wireless network prototypes.