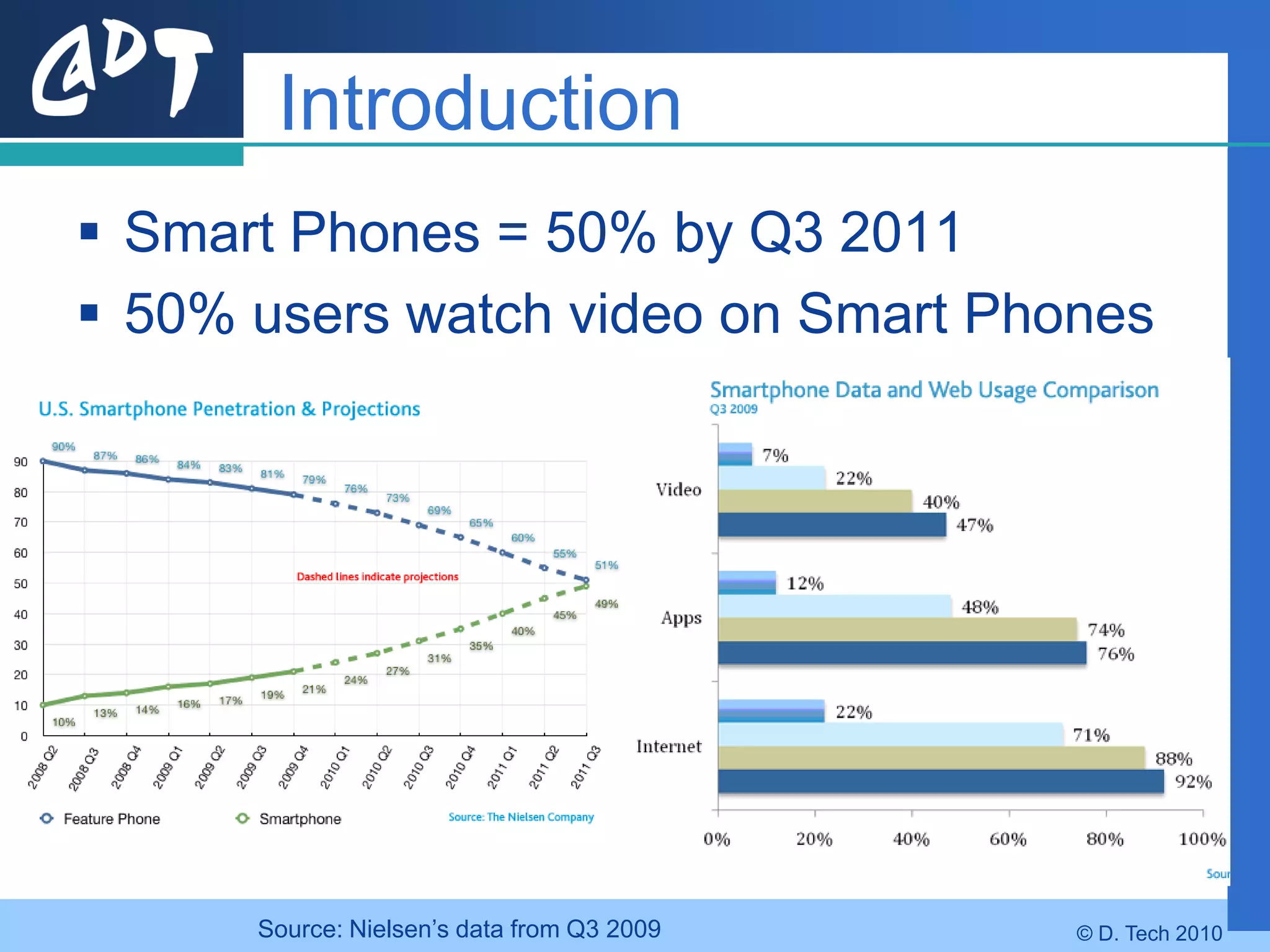
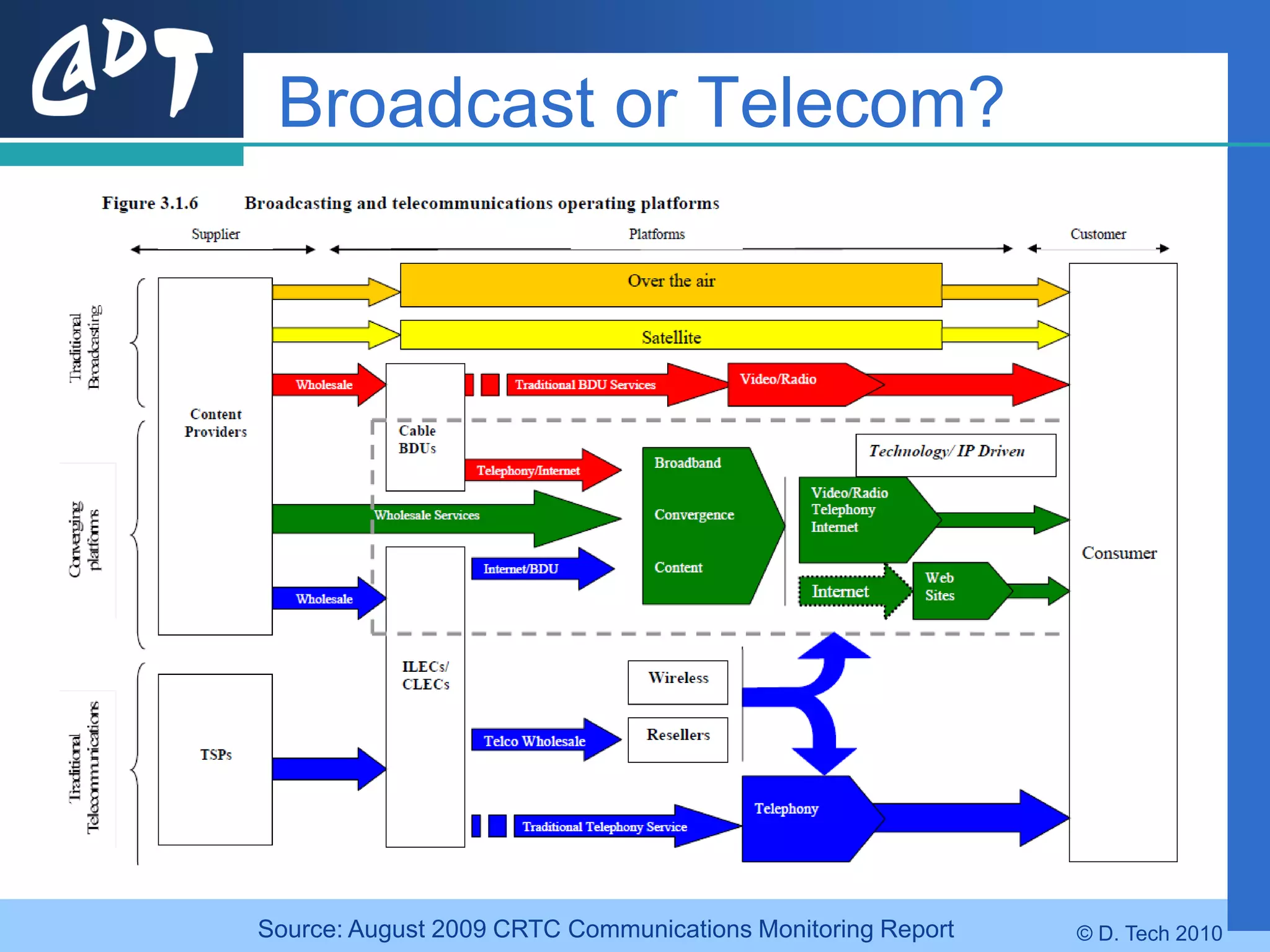
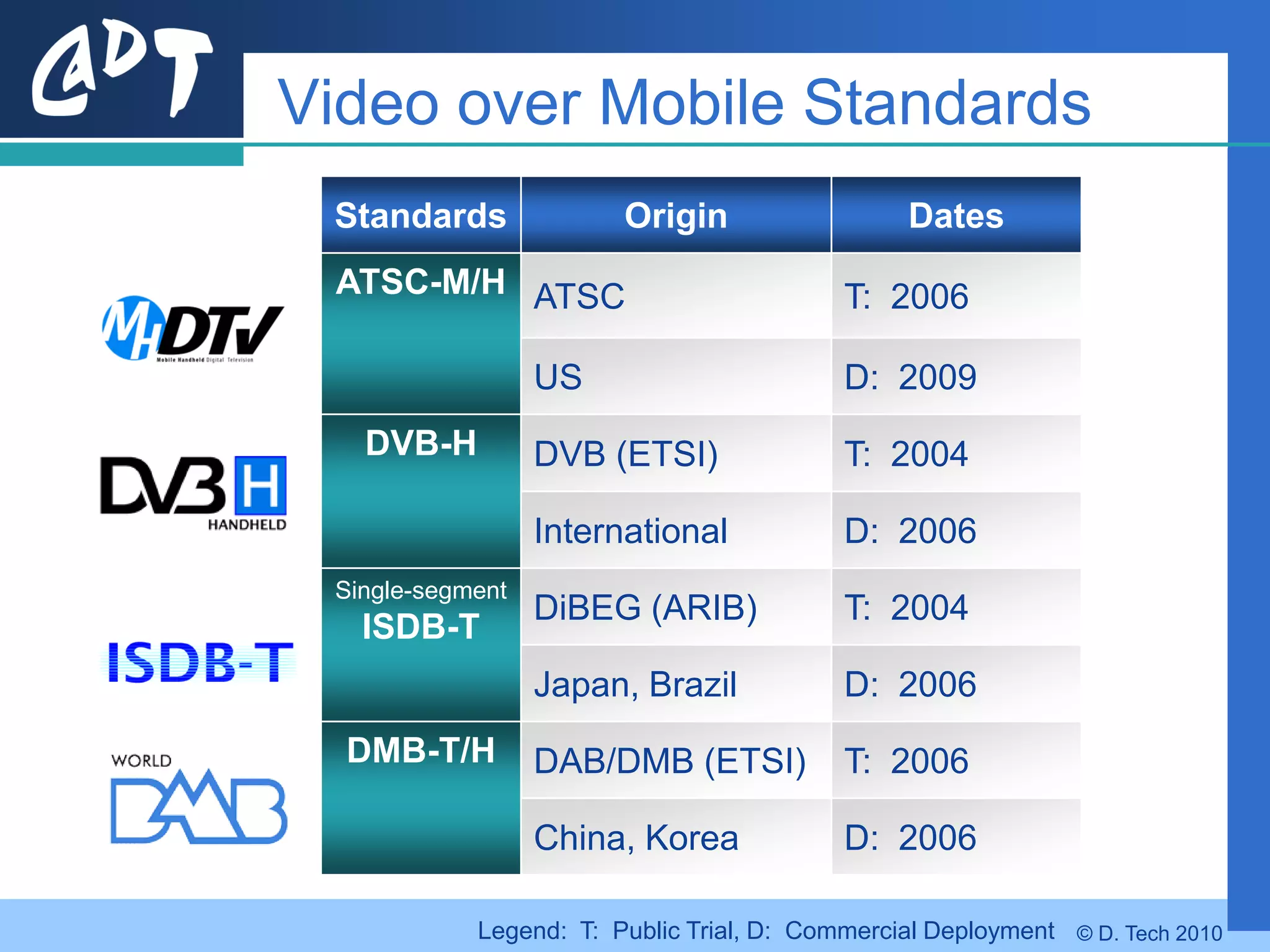
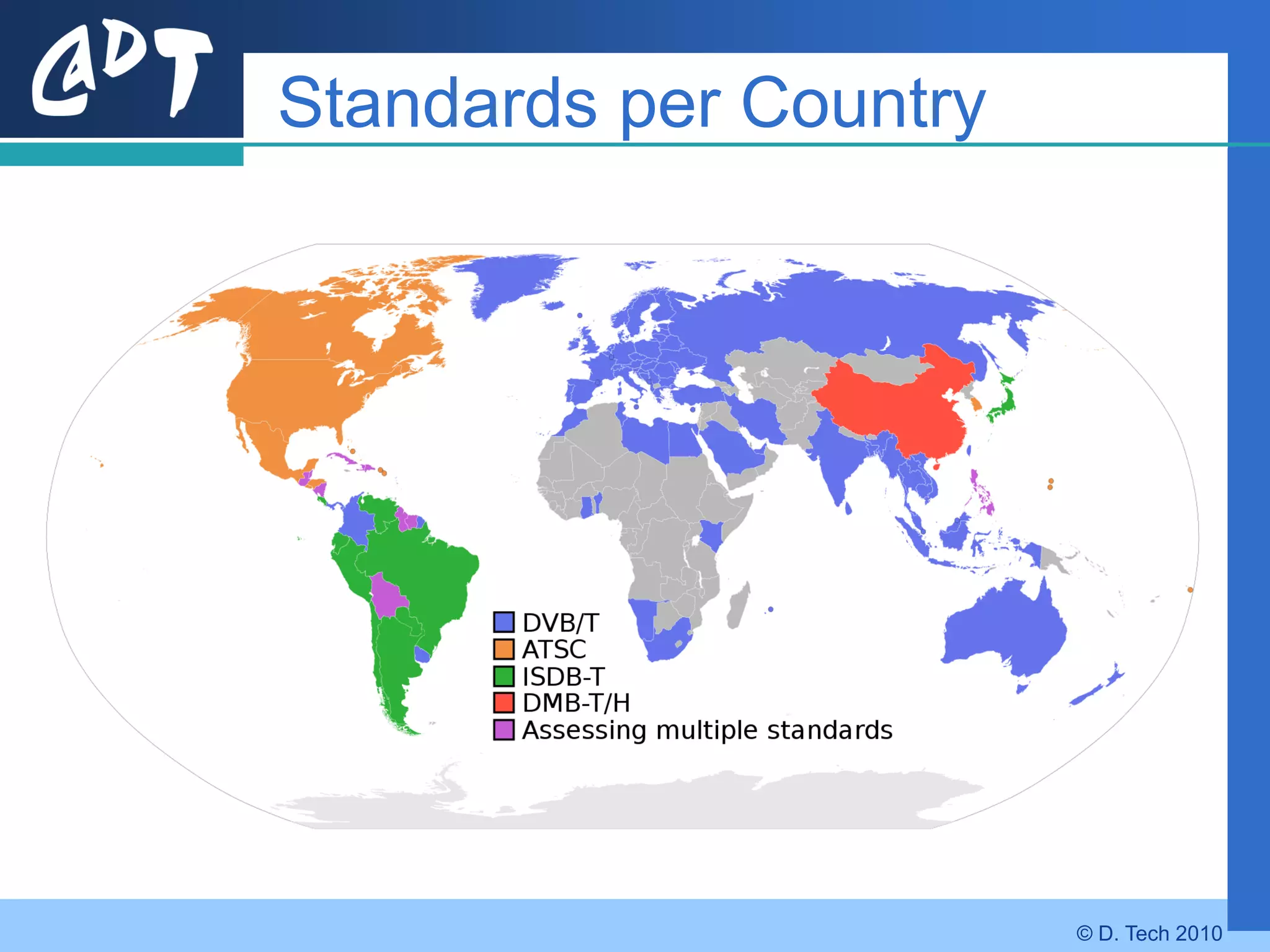
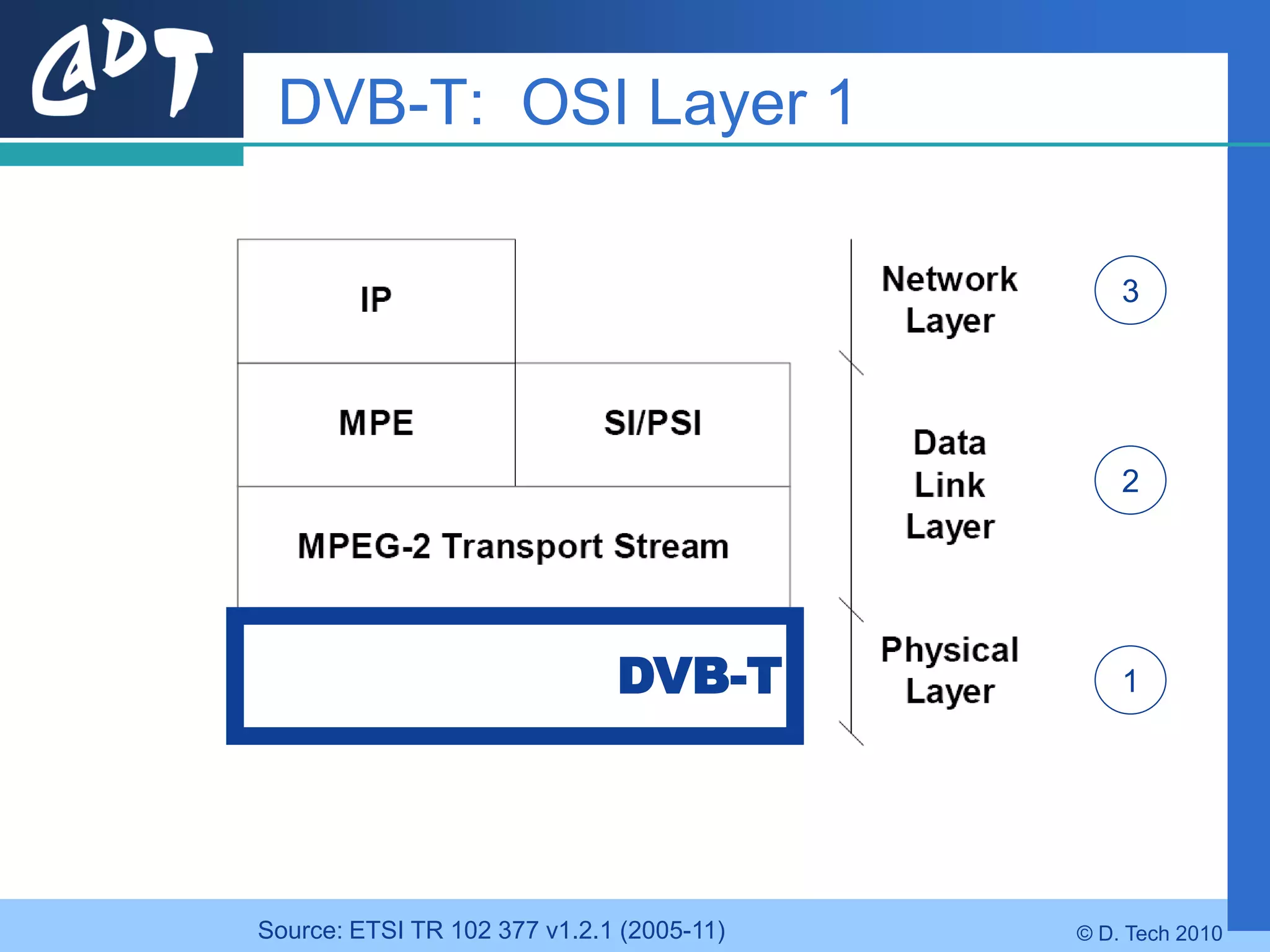
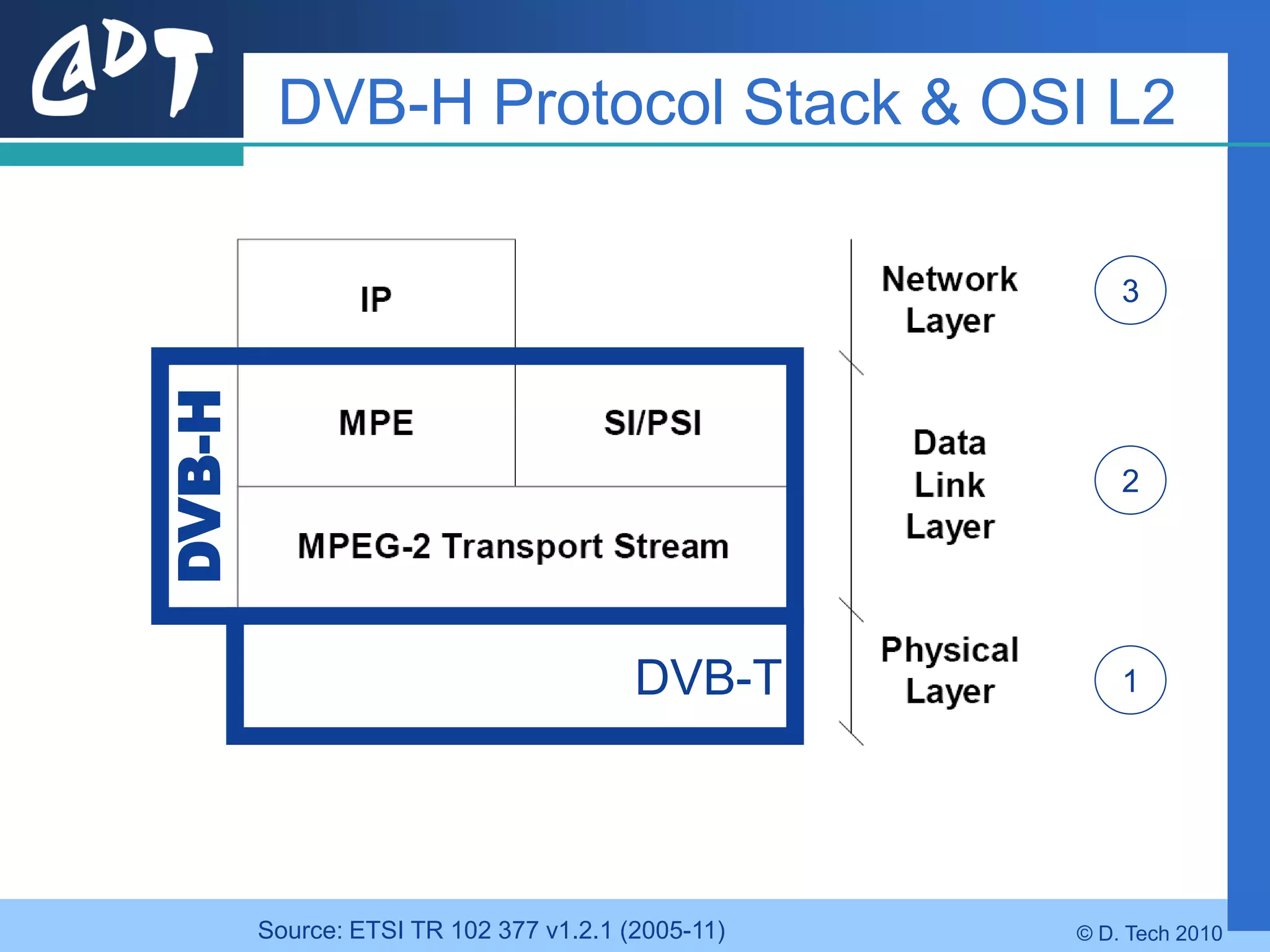
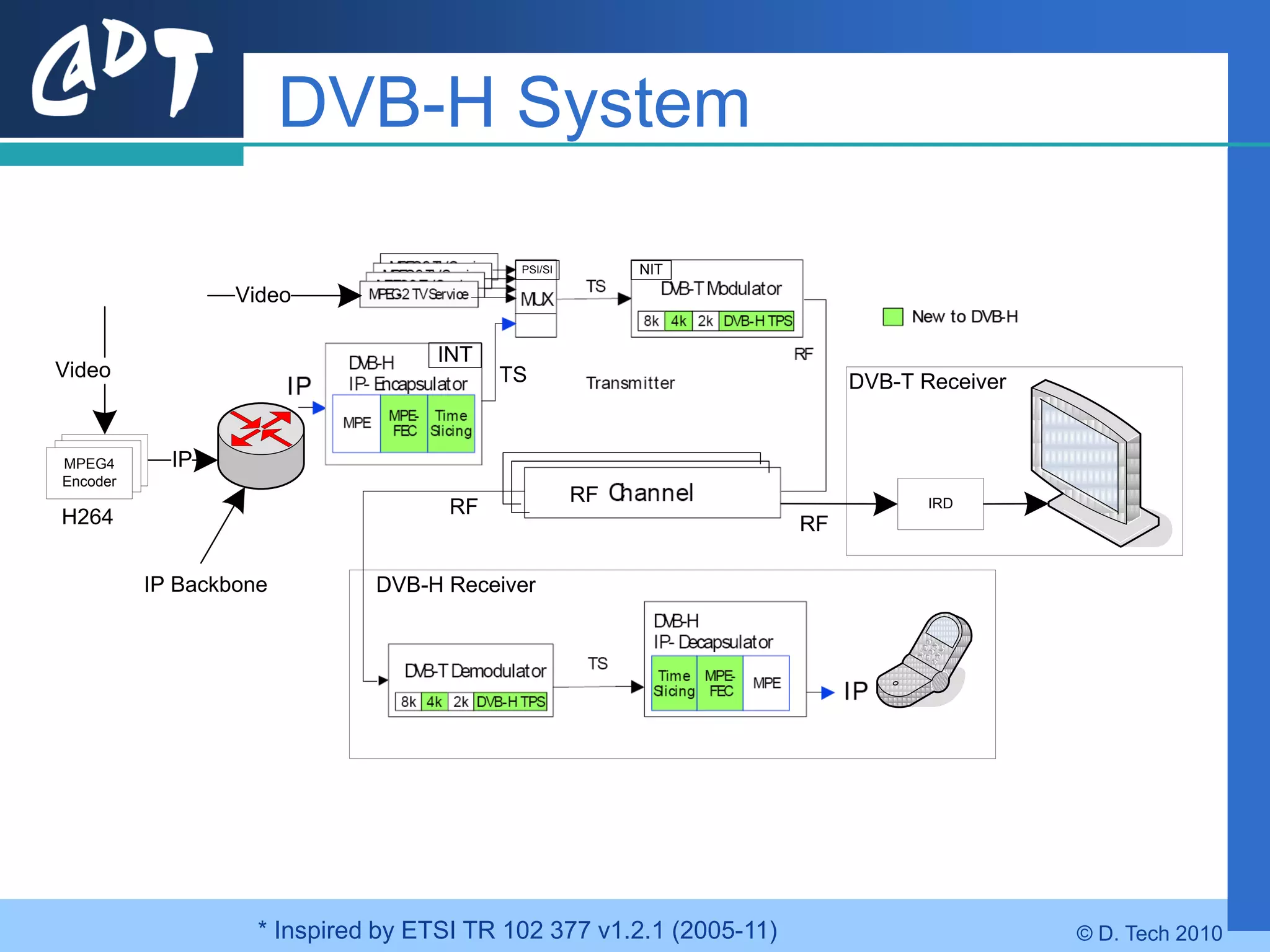
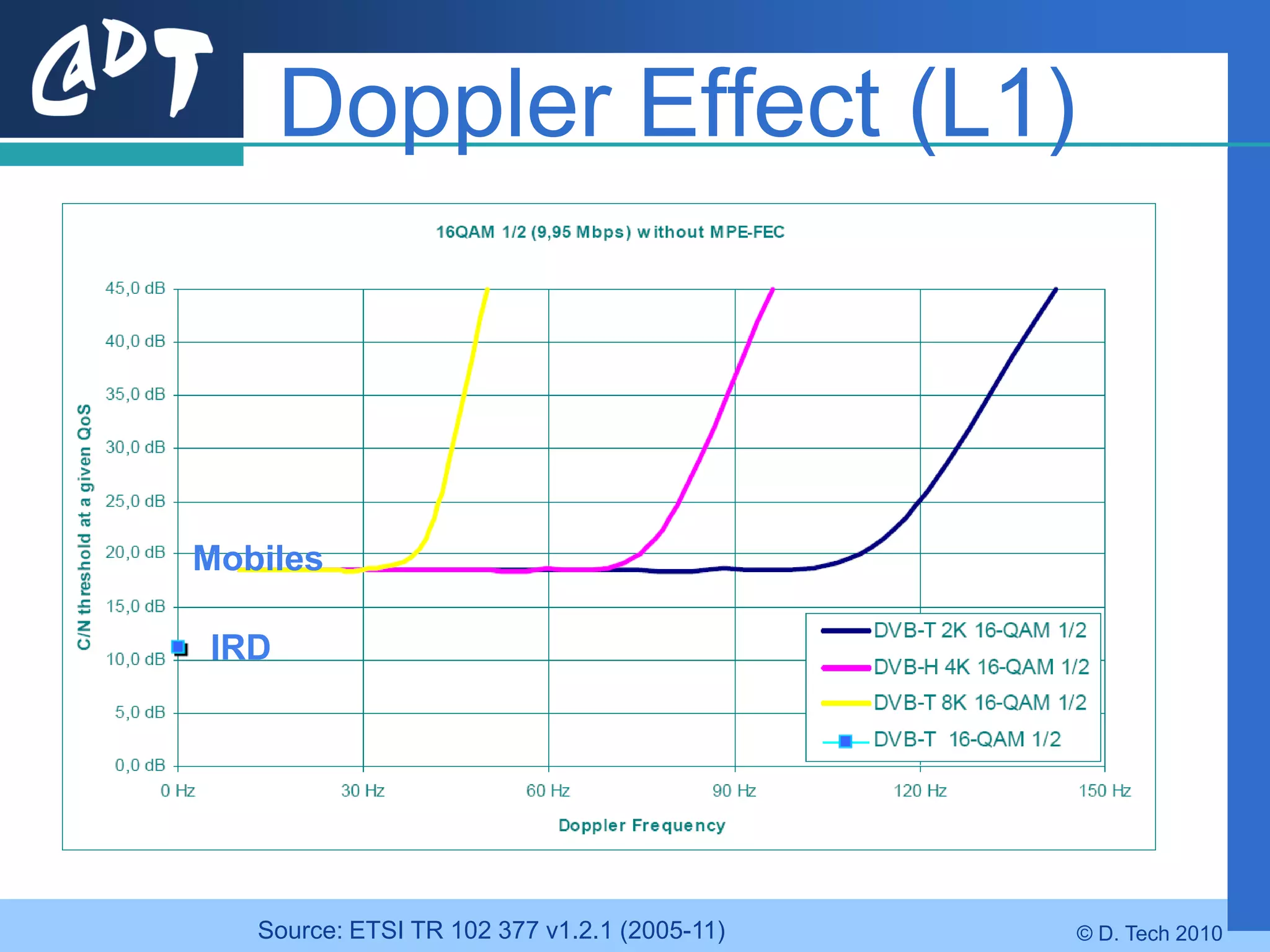
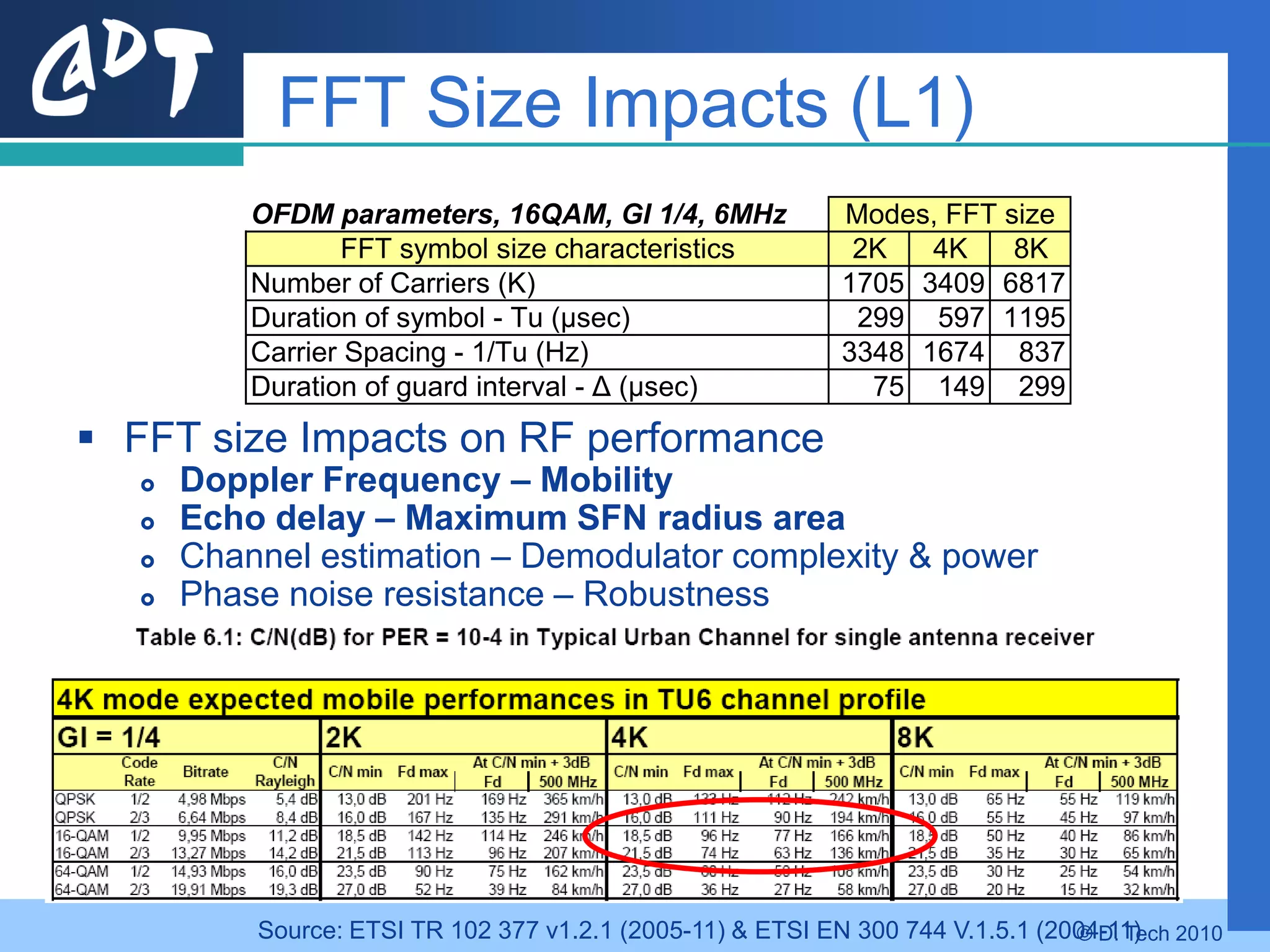
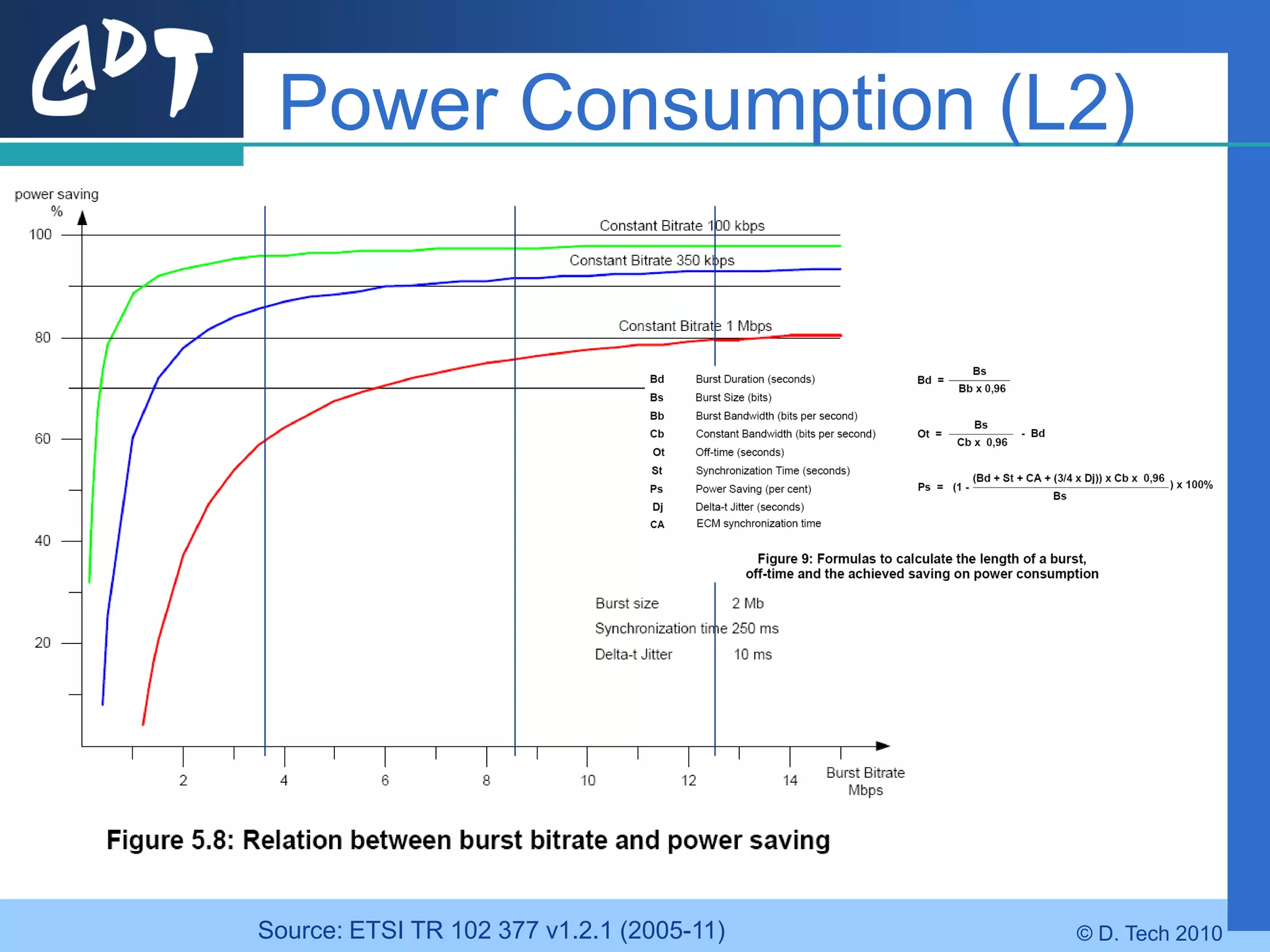
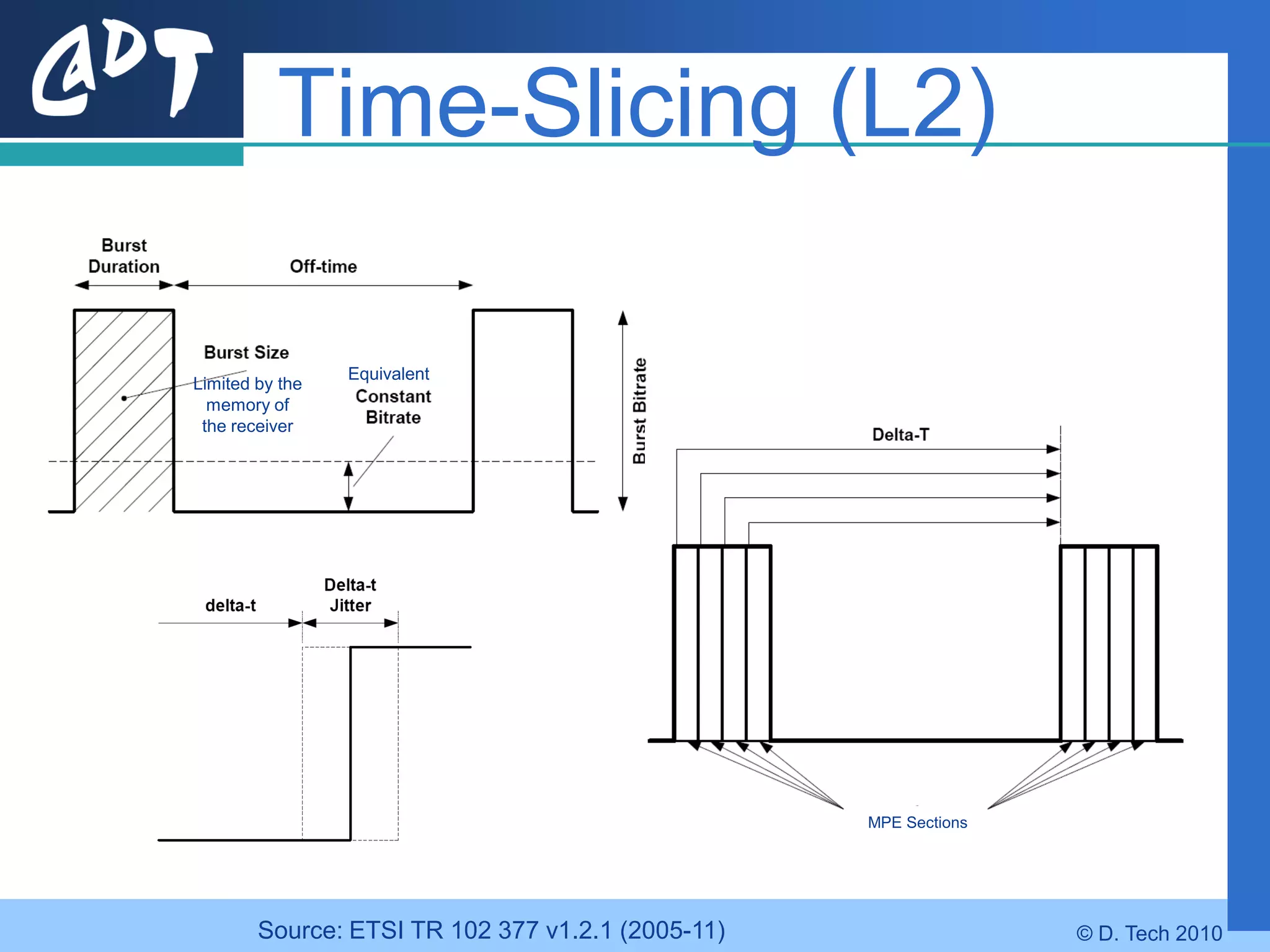
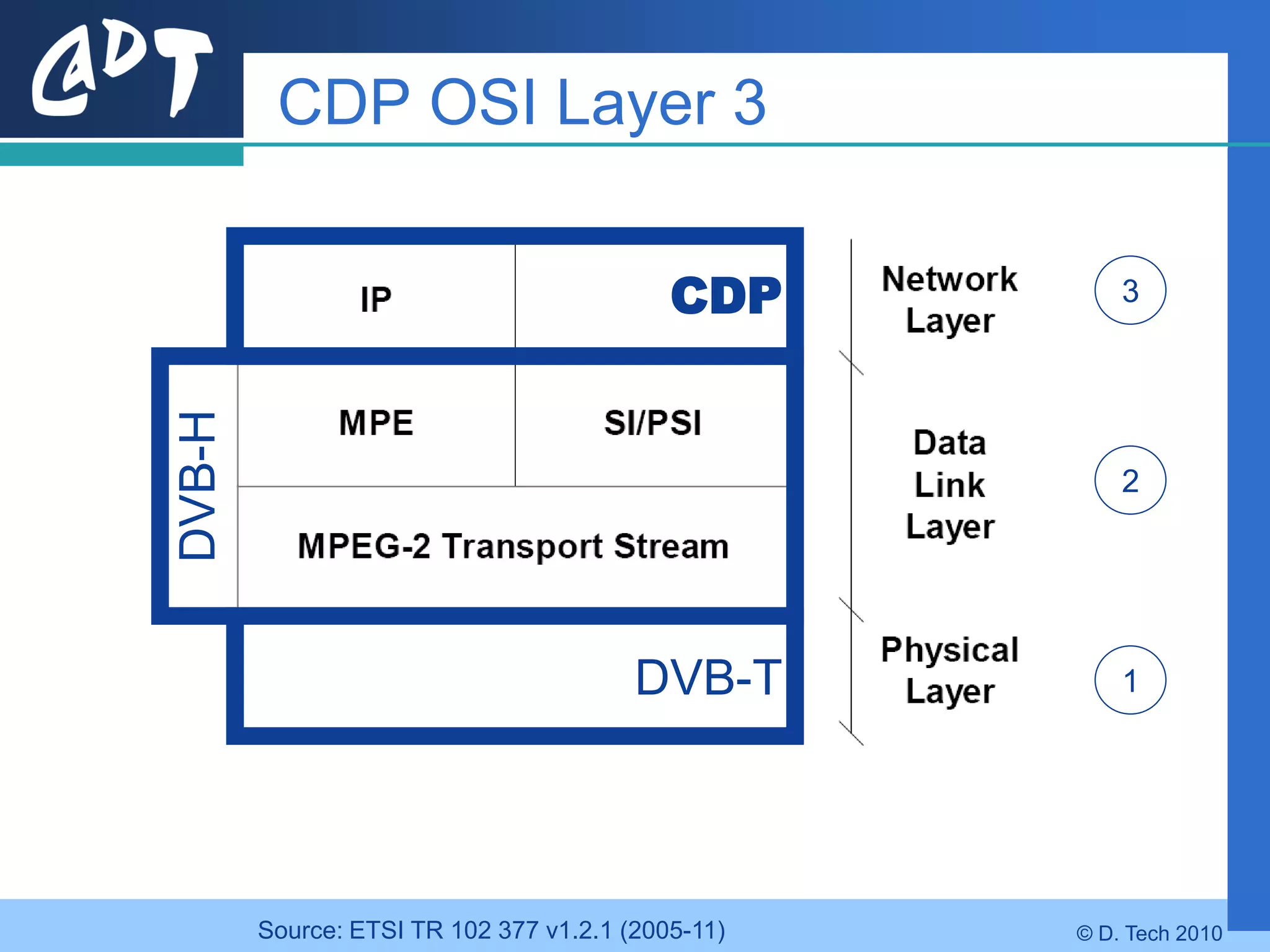
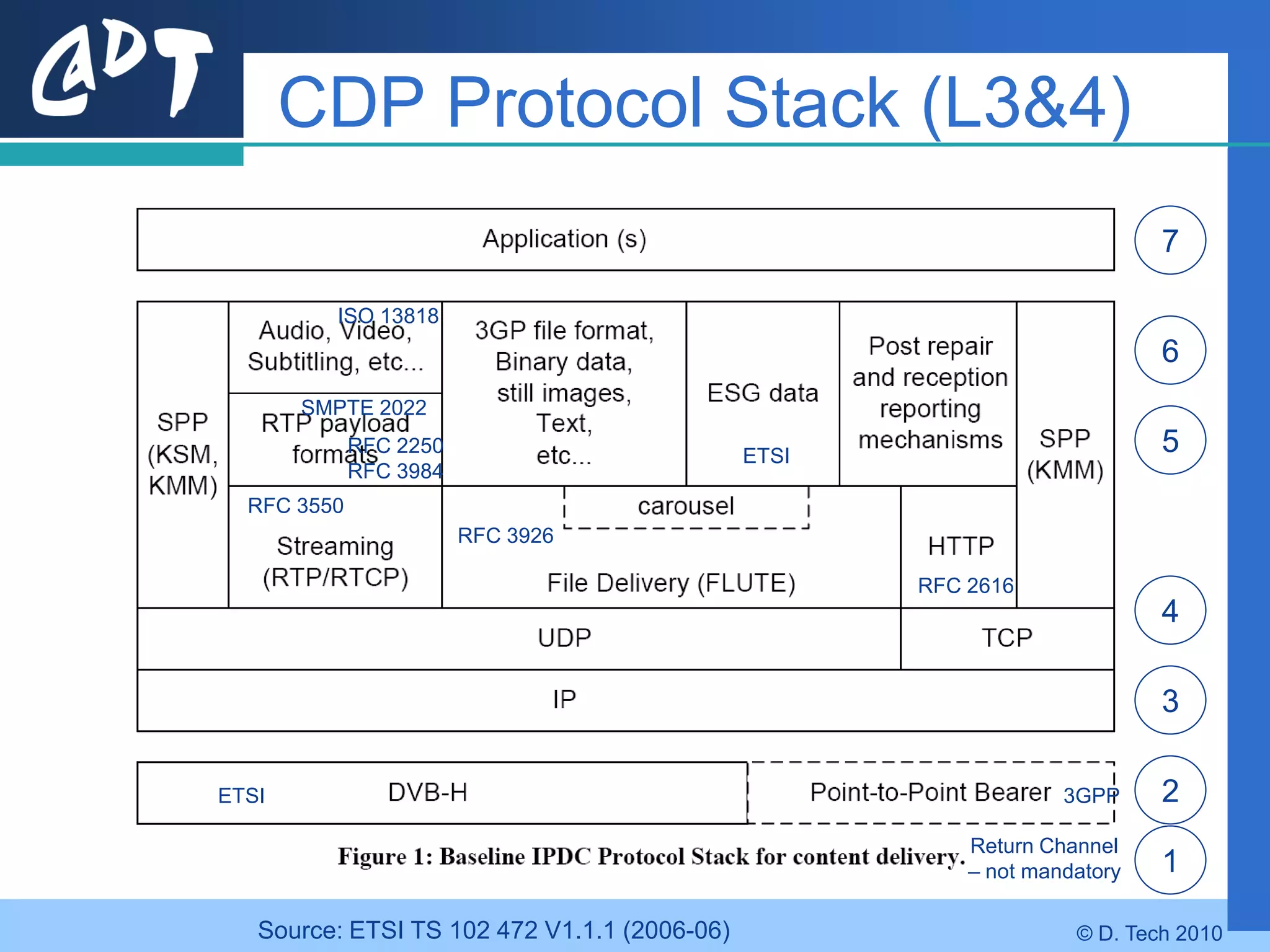
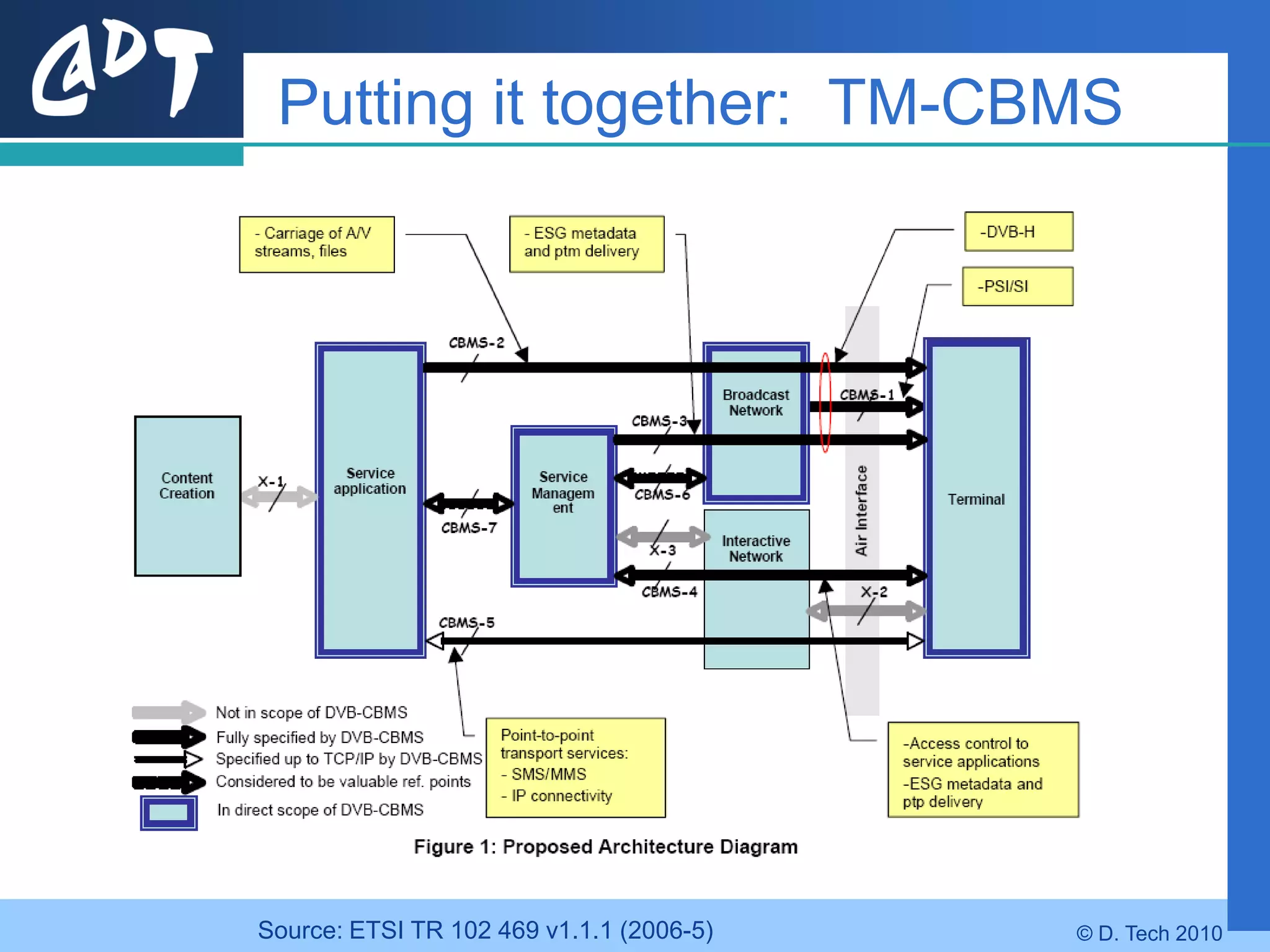
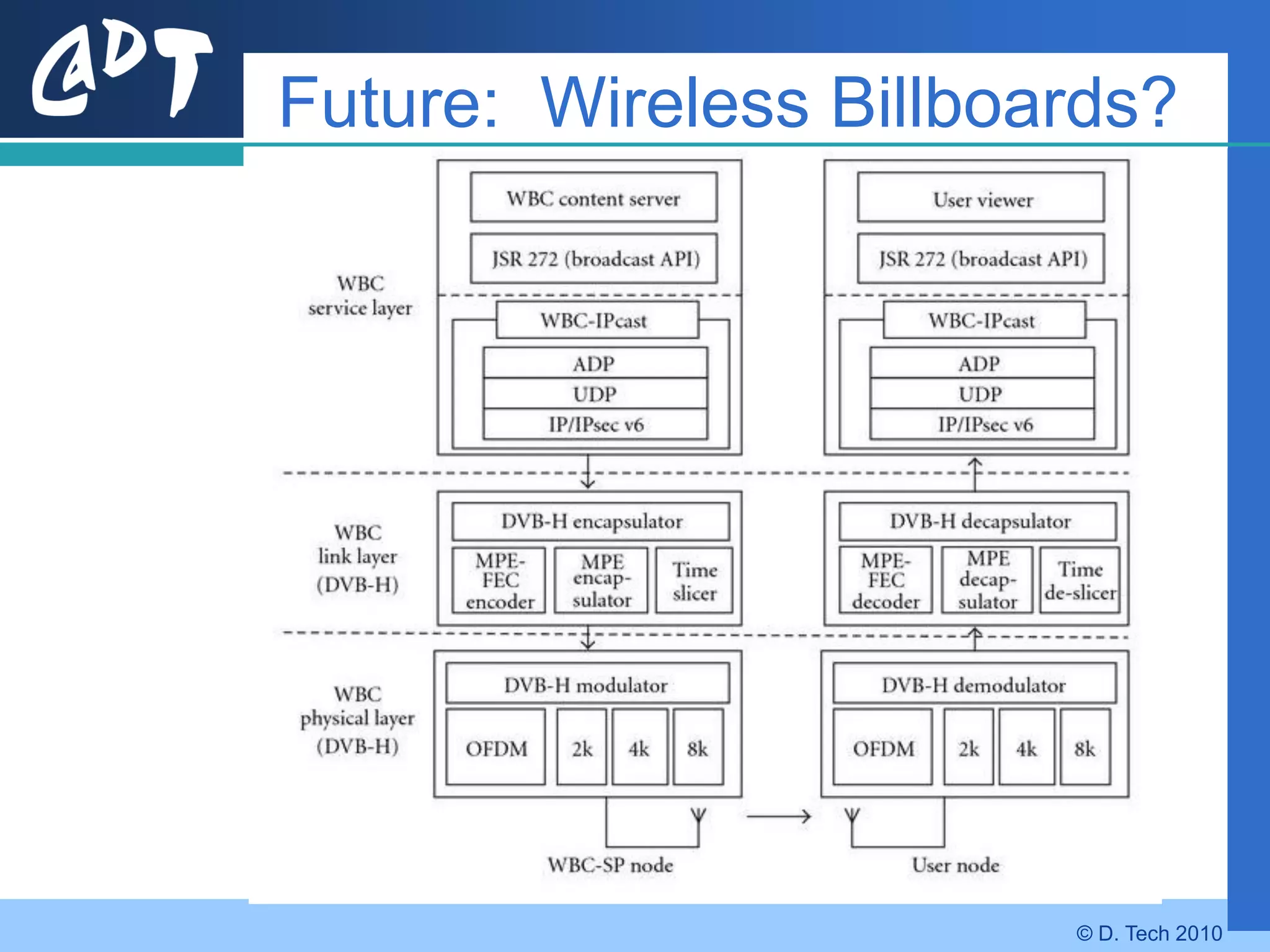
The document provides an overview of DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting - Handheld), a standard for delivering digital television and radio services to mobile devices. It discusses key aspects of DVB-H including its basis on DVB-T, use of IP packets, and innovations like time-slicing to reduce power consumption and larger 4K FFT modes to address Doppler effects from mobility. The document also reviews the DVB-H protocol stack and how it solves issues at the physical, data link and network layers for mobile reception.