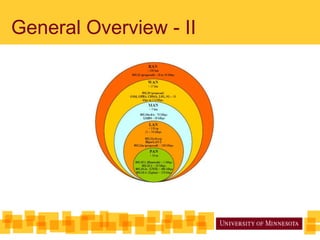
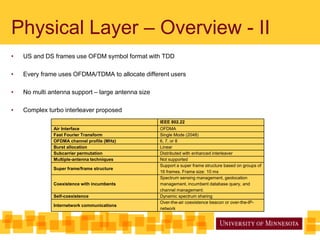
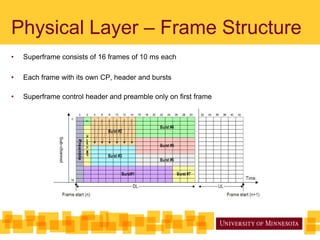
The document discusses IEEE 802.22, the first proposed standard for cognitive radio operation in TV bands, utilizing underutilized spectrum, known as TV white spaces, to meet the demand for higher data rates and coverage. It outlines the key features of cognitive radio, including spectrum sensing, channel bonding, and geolocation capabilities, which enable efficient use of wireless regional area networks (WRANs) in rural areas. Additionally, it details the physical layer specifications, modulation schemes, and performance comparisons with WiMAX, emphasizing the robust design to accommodate various environmental conditions.