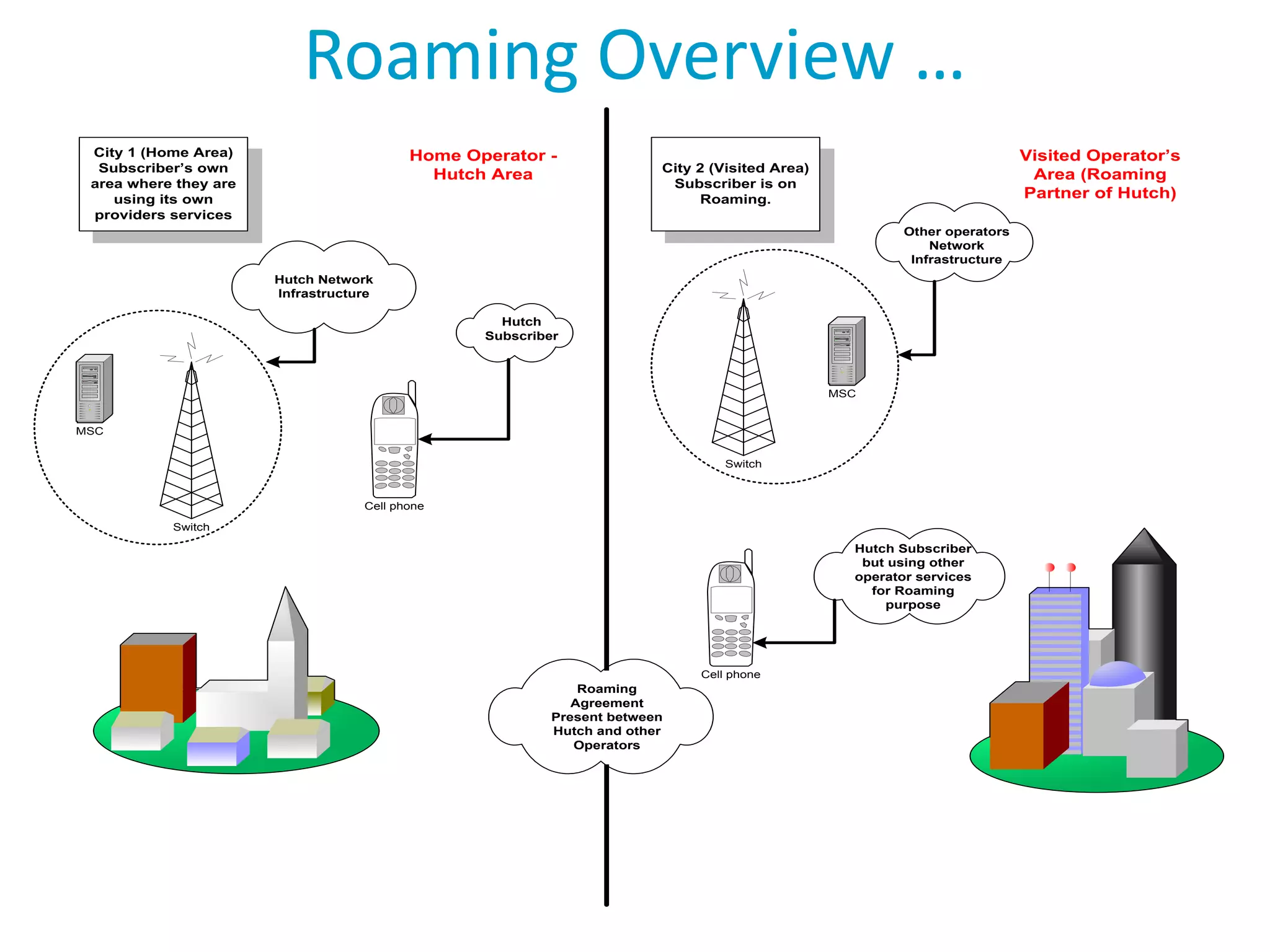
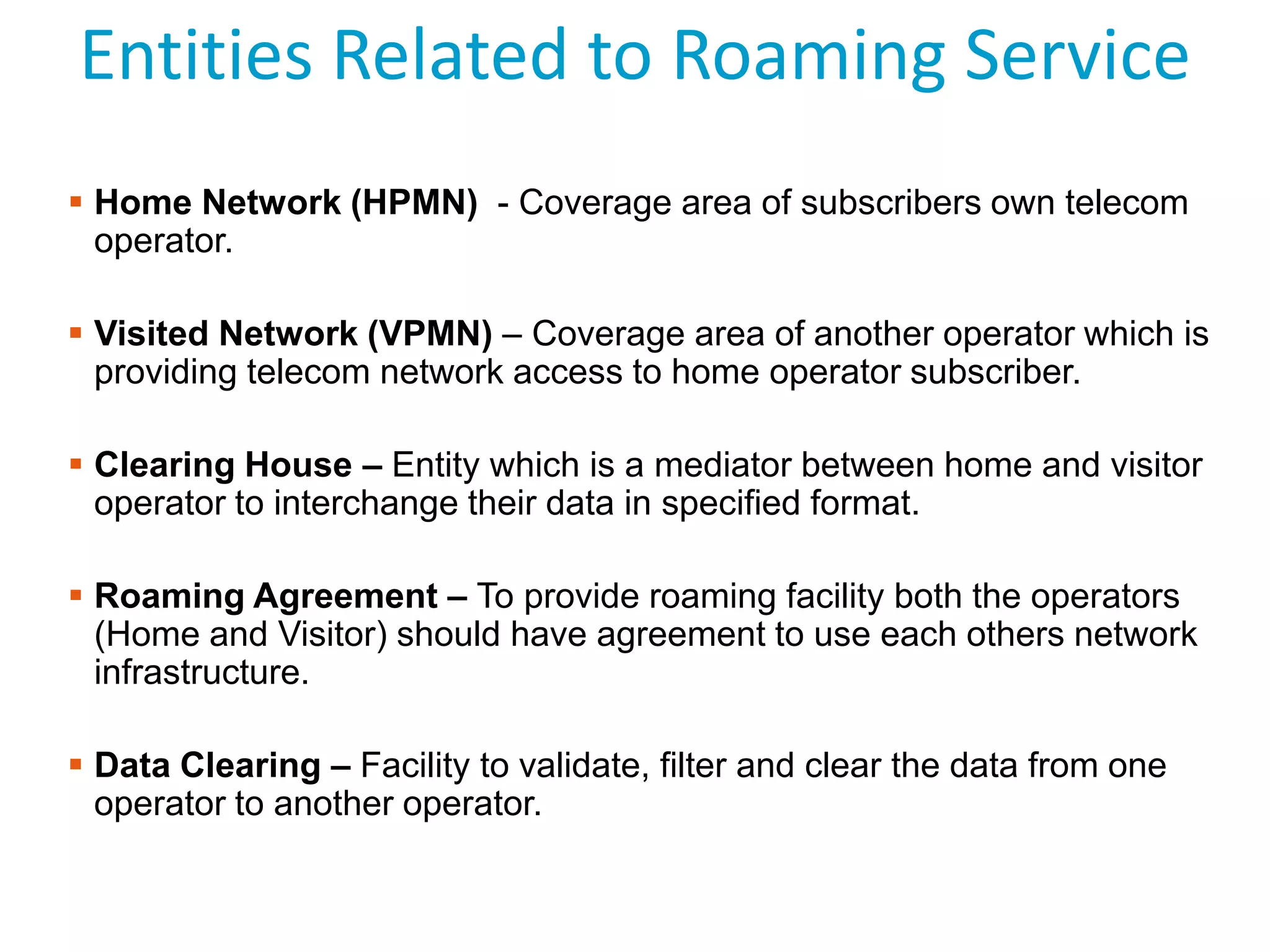
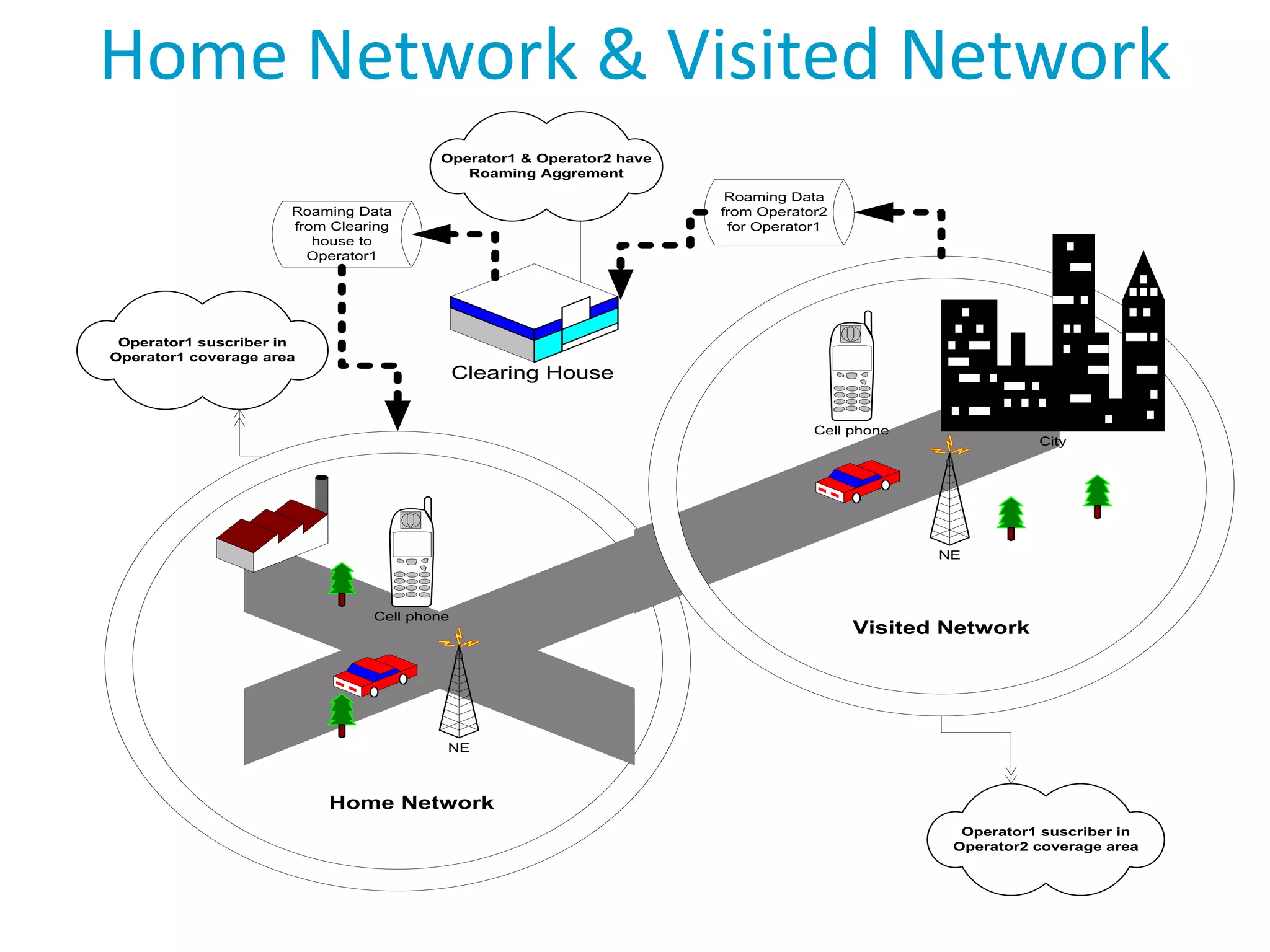
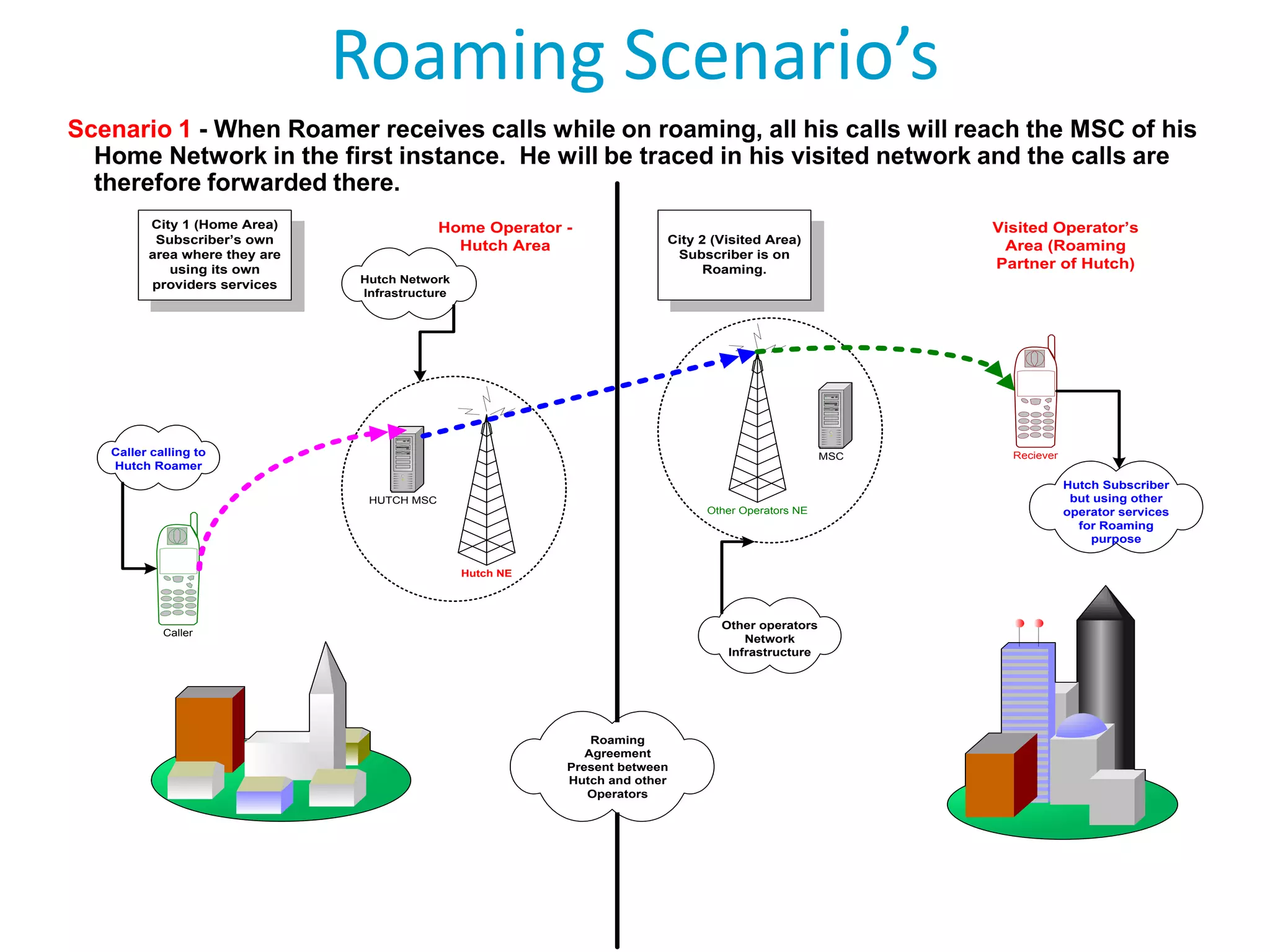
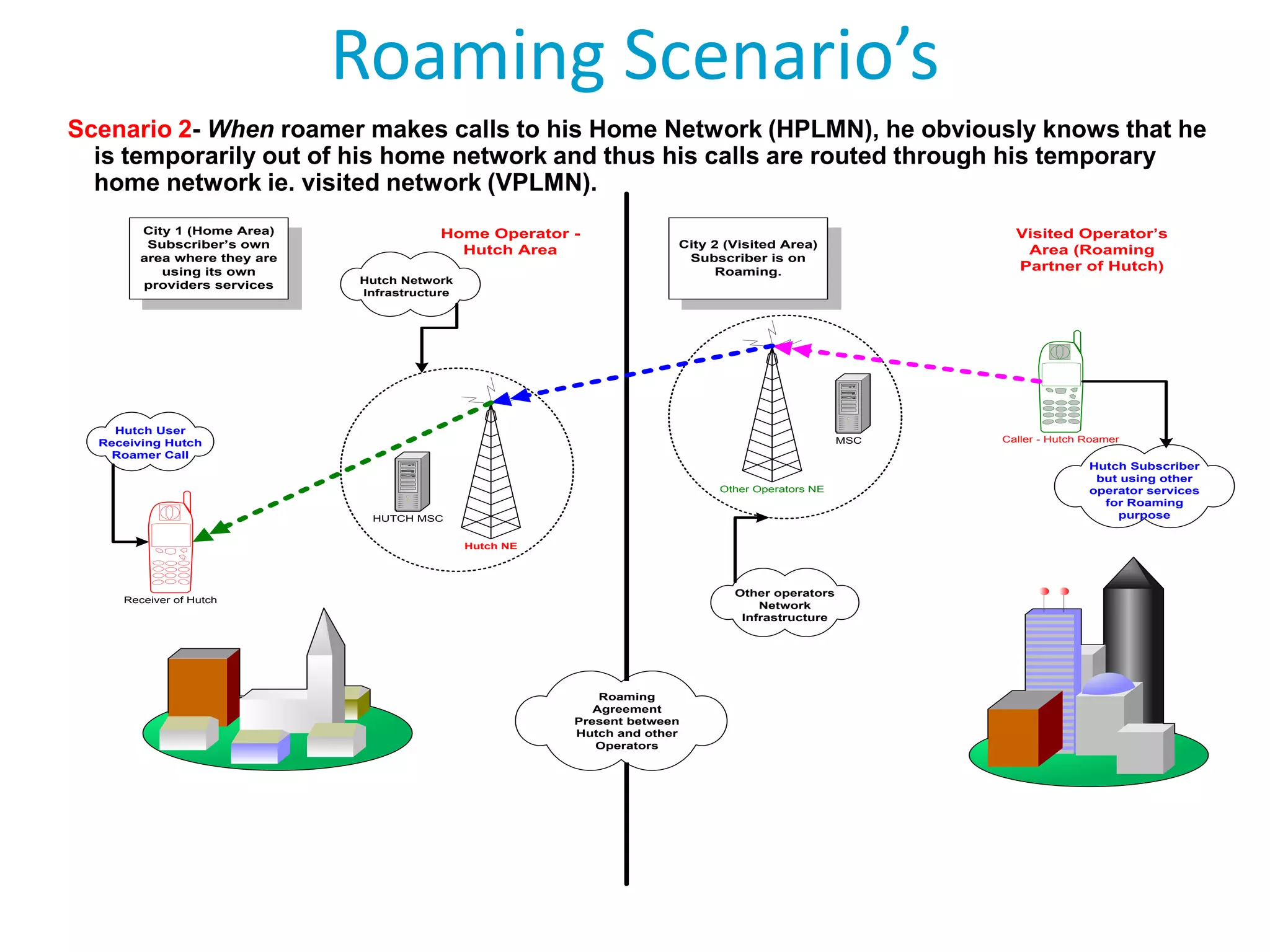
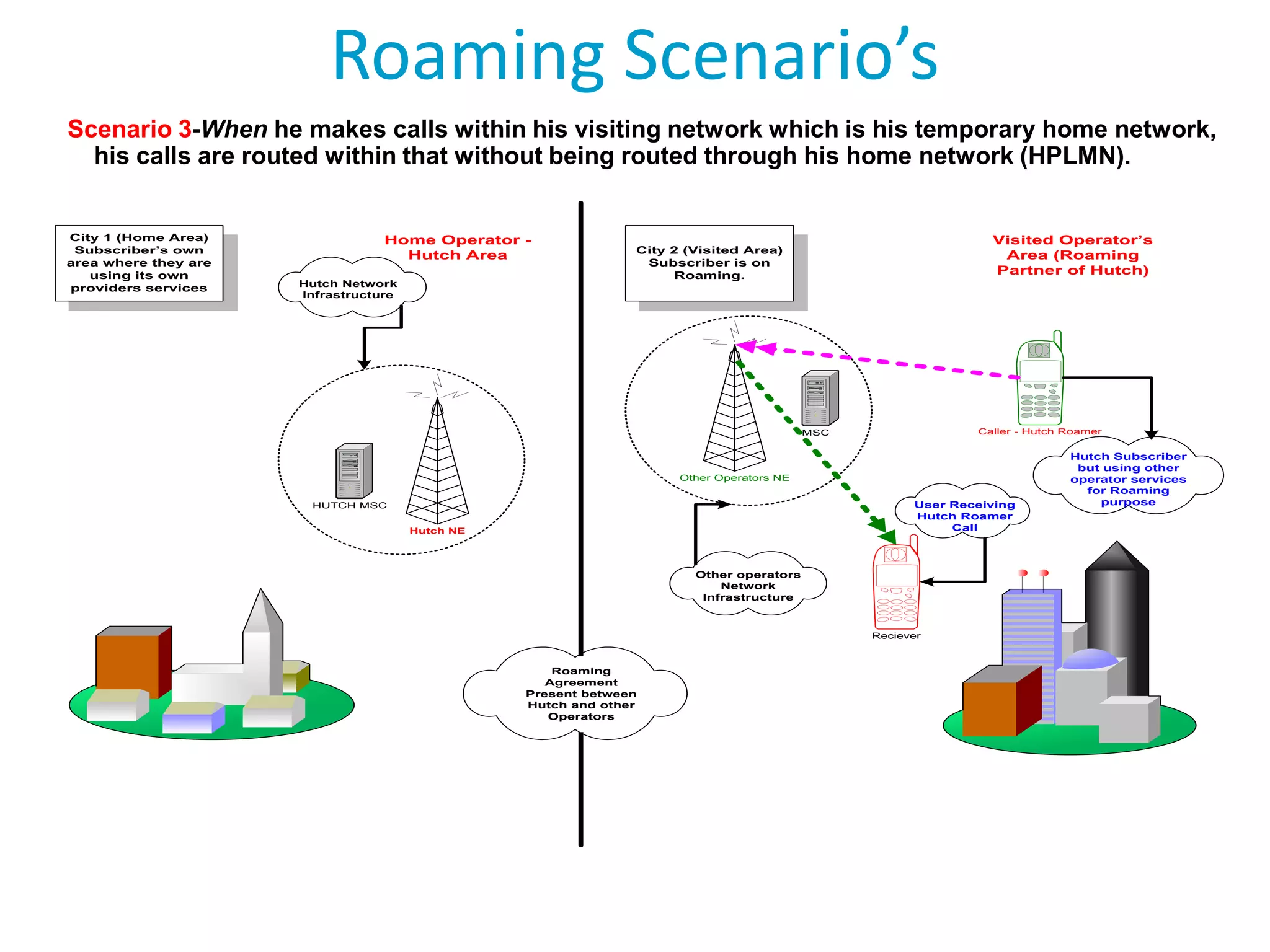
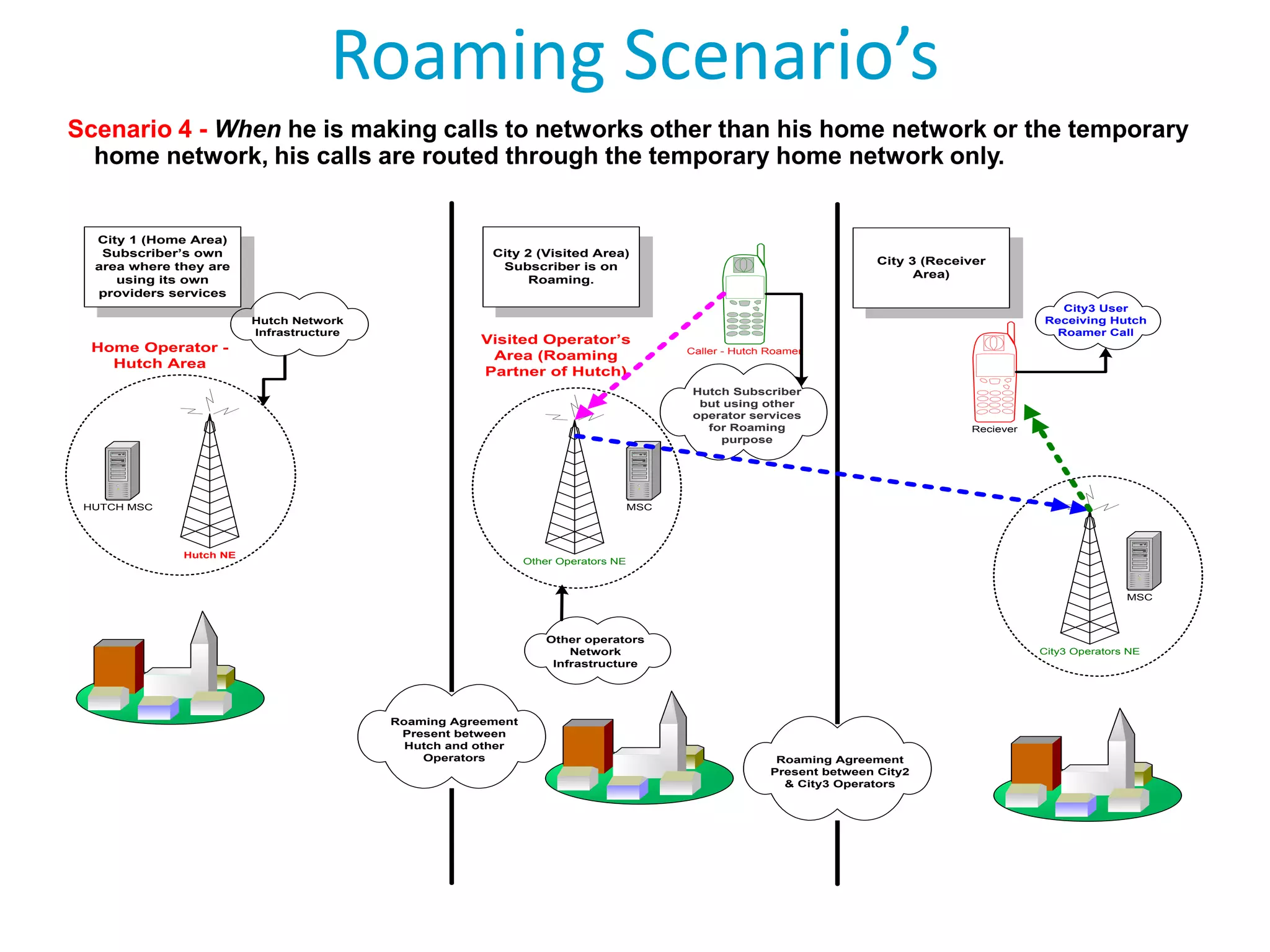
Roaming allows mobile subscribers to access voice and data services outside their home network coverage area by using a visited network. It requires roaming agreements between operators. There are several entities involved including home networks, visited networks, and clearing houses. Roaming can be national, international, or between different standards. Inbound roaming refers to customers of other operators using a home operator's network, while outbound refers to home customers using other networks. Roaming scenarios describe how calls are routed for subscribers roaming within and between networks. GSM technology benefits roaming by providing worldwide access across standards through a single number and device.