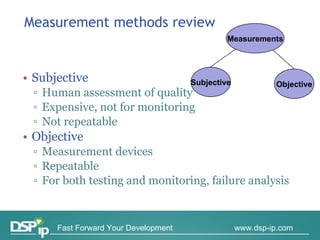
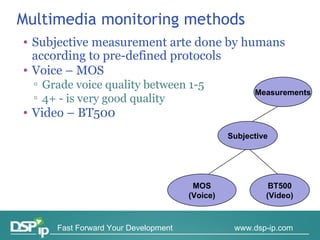
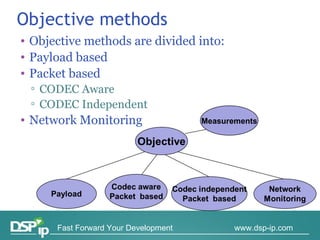
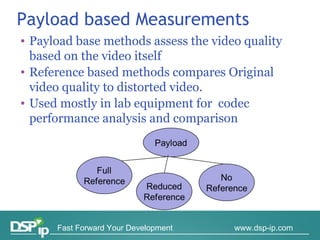
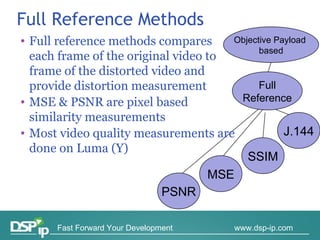
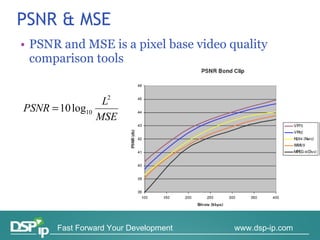
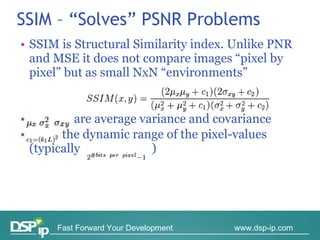
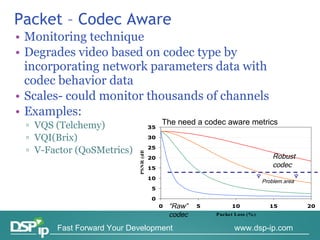
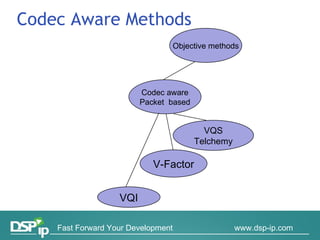
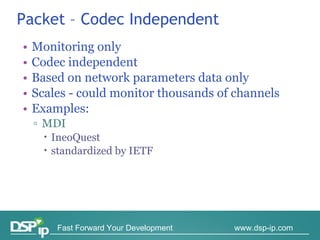
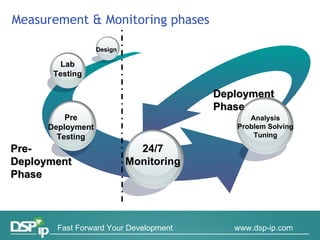
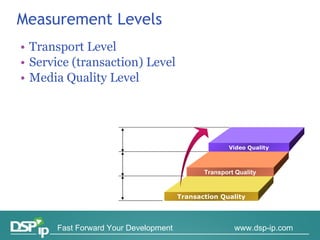
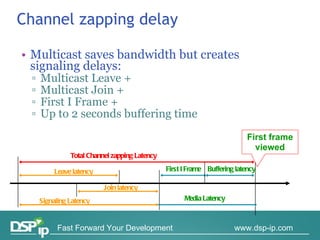
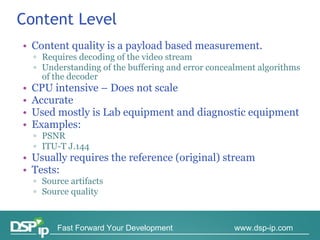
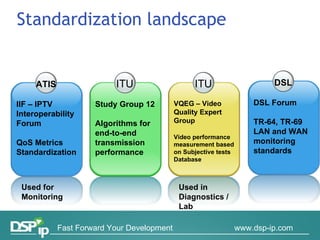
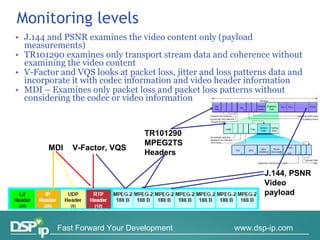
Video quality measurements can be performed using subjective, objective, and payload-based methods. Subjective methods involve human assessment while objective methods use measurement devices and are repeatable for testing and monitoring. Payload-based methods assess video quality by comparing the original and distorted video. Standardization bodies have defined various levels of measurement including transport, transaction, and content levels to analyze video quality from different perspectives.