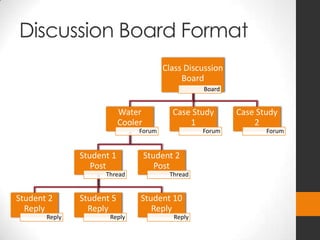
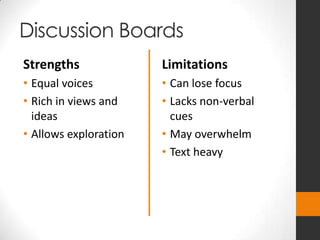
This document describes three tools - discussion boards, blogs, and wikis - that can be used to facilitate student engagement and formative assessment. Discussion boards are best for creating discourse on topics and allowing all voices to be heard. Blogs focus on an author's individual voice and message and can be used for reflection. Wikis support highly collaborative work where multiple students can edit a shared document. The presenter provides examples and guidance on how to best apply each tool based on learning objectives and desired student interactions.