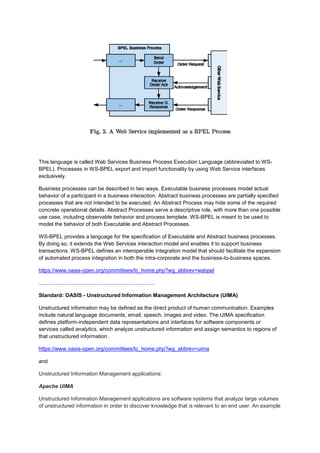
This document summarizes Gregg Barrett's recommendations for technology platforms and standards/frameworks for Q1 2012. It recommends evaluating the Microsoft platform using SQL Server, BizTalk Server, and SQL Server Integration Services for ETL capabilities. If Microsoft is not suitable, it recommends considering Adeptia, Informatica, Software AG, TIBCO, and Progress Software. It outlines several relevant standards and frameworks in areas like insurance, data modeling, business processes, financial reporting, and more. It provides links and descriptions for some of the key standards.



![RosettaNet Partner Interface Processes (PIPs) define business processes between trading partners.
PIPs fit into seven Clusters, or groups of core business processes, that represent the backbone of the
trading network. Each Cluster is broken down into Segments - cross-enterprise processes involving
more than one type of trading partner. Within each Segment are individual PIPs.
PIPs are specialized system-to-system XML-based dialogs. Each PIP specification includes a
business document with the vocabulary, and a business process with the choreography of the
message dialog.
http://www.rosettanet.org/TheStandards/RosettaNetStandards/PIPs/tabid/475/Default.aspx
…………………………………………………………….
Standard: OASIS - Reference Architecture Foundation for SOA
The OASIS Service Oriented Architecture Reference Model TC develops a reference model to
encourage the continued growth of different and specialized SOA implementations whilst preserving a
common layer of understanding about what SOA is.
This document specifies the OASIS Reference Architecture Foundation for Service Oriented
Architecture (SOA-RAF). It follows from the concepts and relationships defined in the OASIS
Reference Model for Service Oriented Architecture. While it remains abstract in nature, the current
document describes the foundation upon which specific SOA concrete architectures can be built.
The focus of the SOA-RAF is on an approach to integrating business with the information technology
needed to support it. These issues are always present but are all the more important when business
integration involves crossing ownership boundaries.
The SOA-RAF follows the recommended practice of describing architecture in terms of models, views,
and viewpoints, as prescribed in the ANSI/IEEE 1471-2000 (now ISO/IEC 42010-2007) Standard. The
SOA-RAF is of value to Enterprise Architects, Business and IT Architects as well as CIOs and other
senior executives involved in strategic business and IT planning.
The SOA-RAF has three main views: the Participation in a SOA Ecosystem view which focuses on
the way that participants are part of a Service Oriented Architecture ecosystem; the Realization of a
SOA Ecosystem view which addresses the requirements for constructing a SOA-based system in a
SOA ecosystem; and the Ownership in a SOA Ecosystem view which focuses on what is meant to
own a SOA-based system.
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) is an architectural paradigm that has gained significant attention
within the information technology (IT) and business communities. The SOA ecosystem described in
this document occupies the area between business and IT. It is neither wholly IT nor wholly business,
but is of both worlds. Neither business nor IT completely own, govern and manage this SOA
ecosystem. Both sets of concerns must be accommodated for the SOA ecosystem to fulfill its
purposes.
The OASIS Reference Model for SOA [SOA-RM] provides a common language for understanding the
important features of SOA but does not address the issues involved in constructing, using or owning a
SOA-based system. This document focuses on these aspects of SOA.
The intended audiences of this document and expected benefits to be realized include non-
exhaustively:
- Enterprise Architects - will gain a better understanding when planning and designing
enterprise systems of the principles that underlie Service Oriented Architecture;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roadmapv3-140630044451-phpapp01/85/Technology-Software-Architecture-for-P-C-Insurance-4-320.jpg)