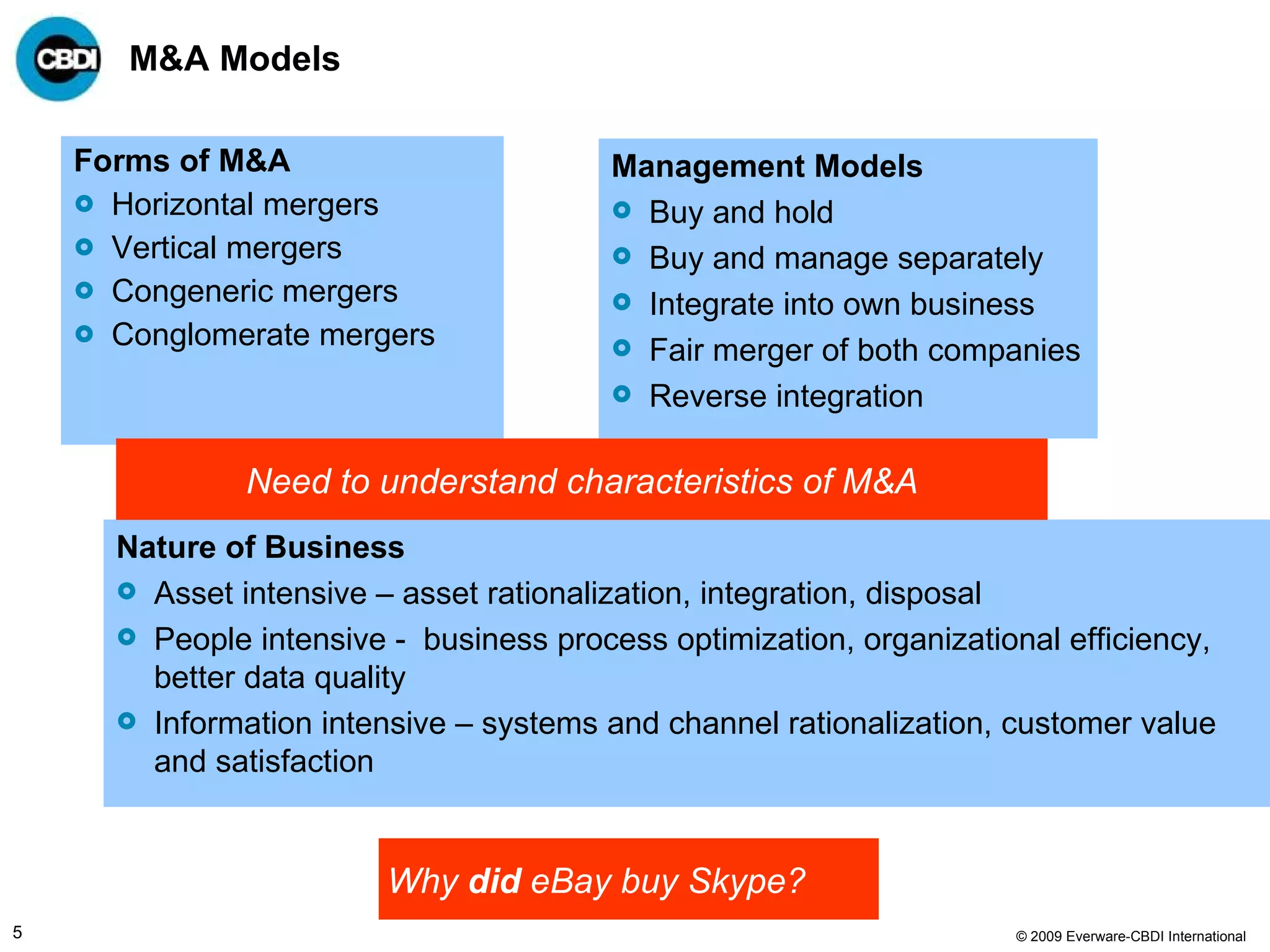
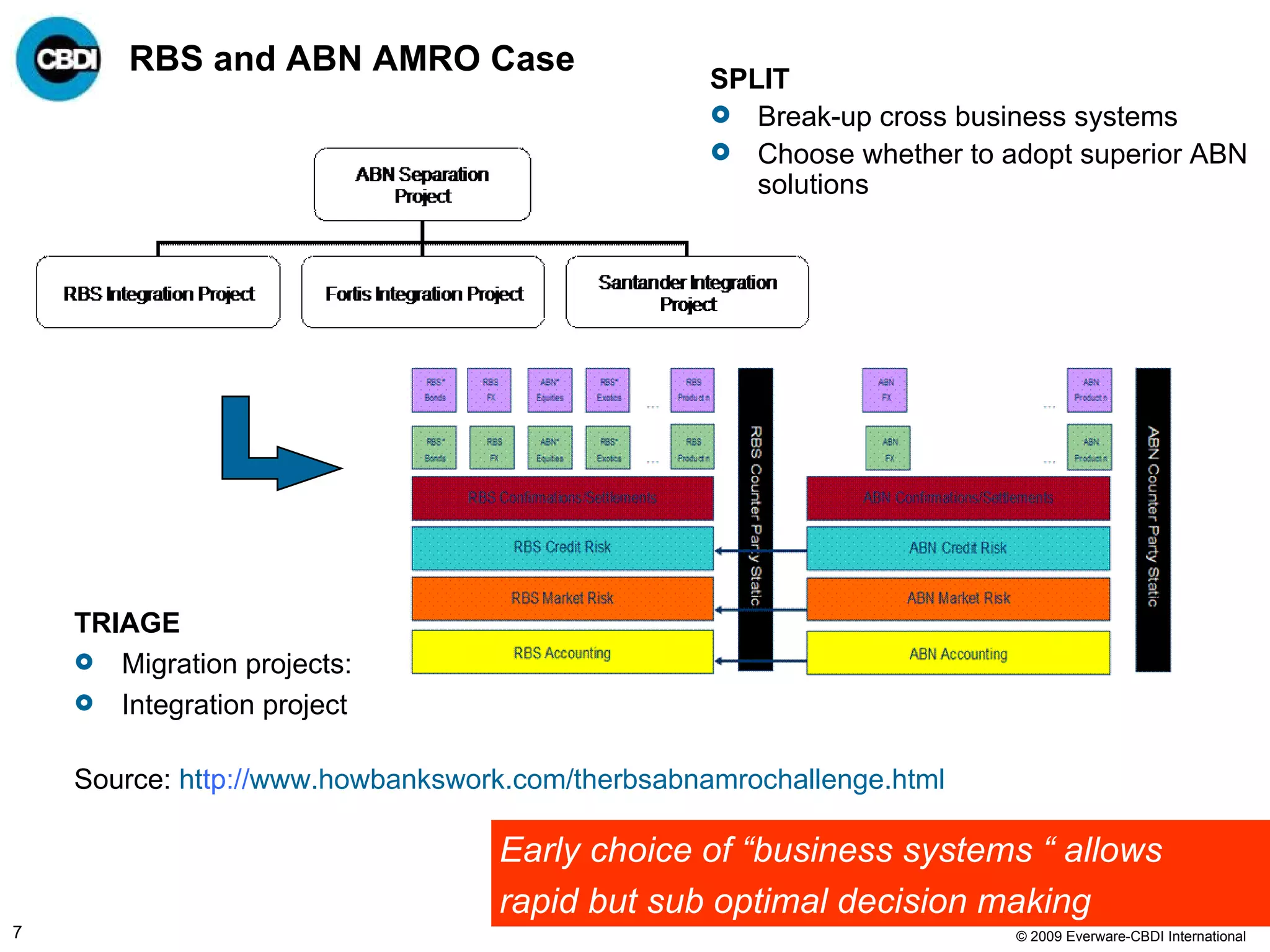
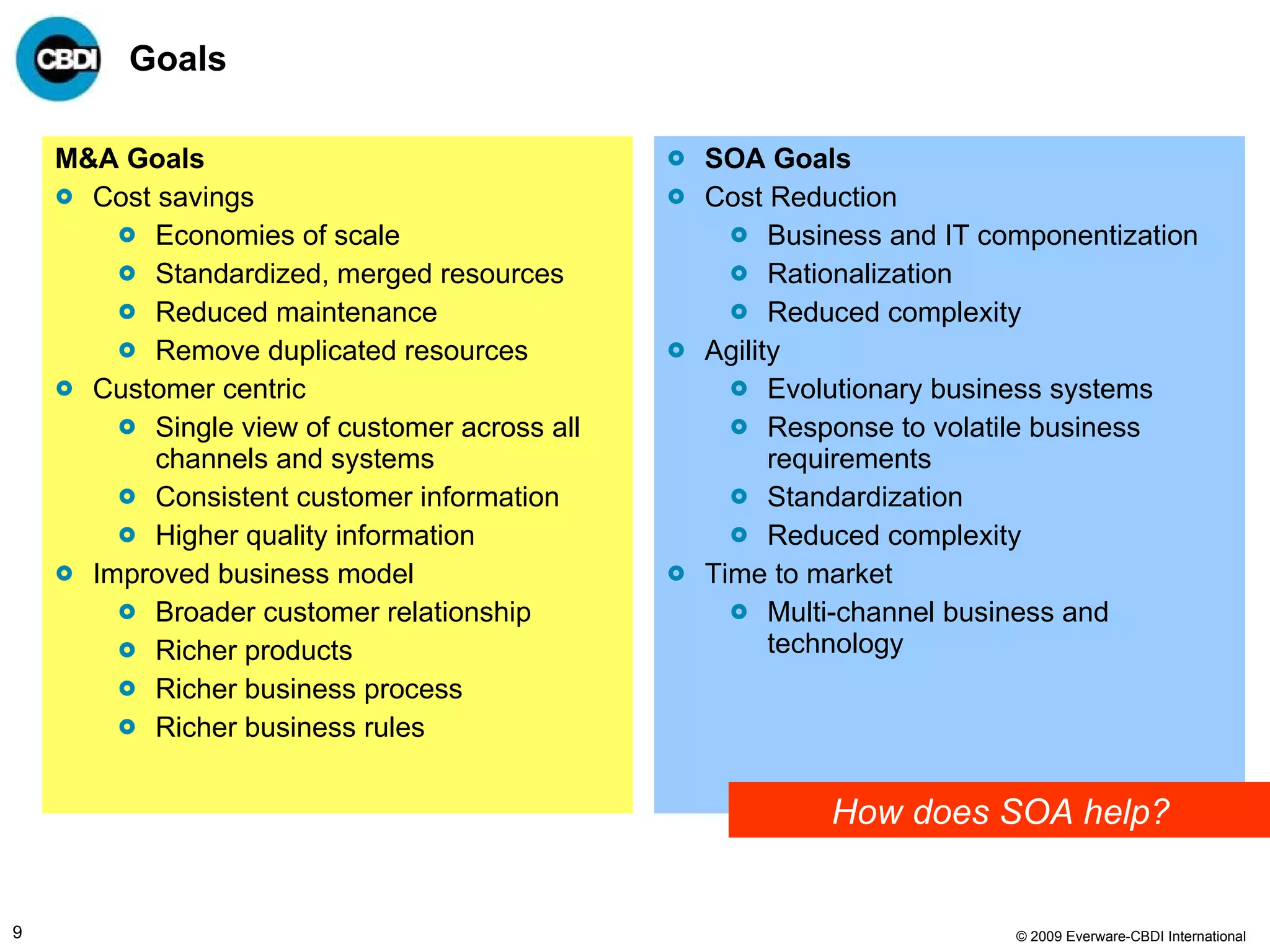
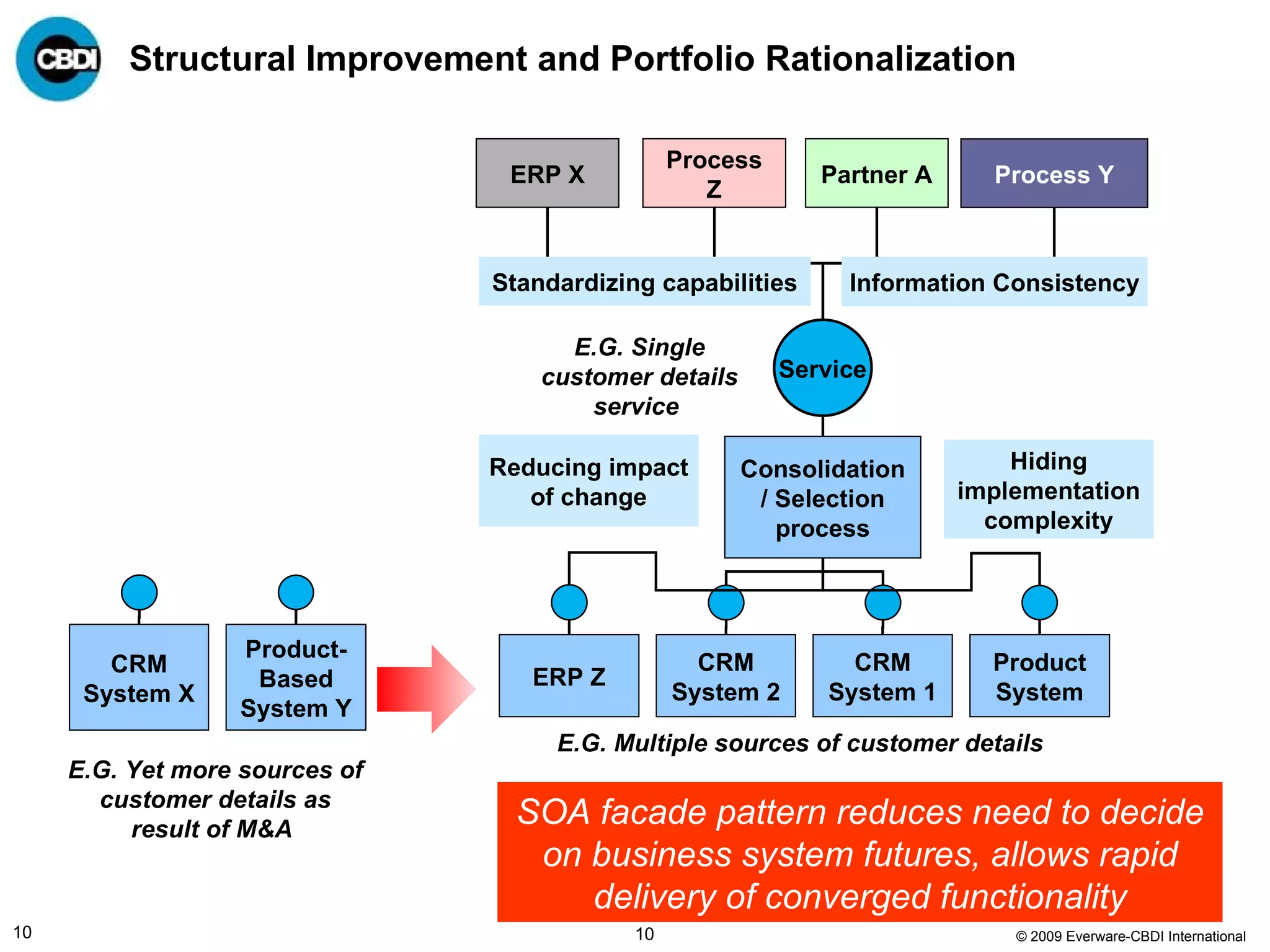
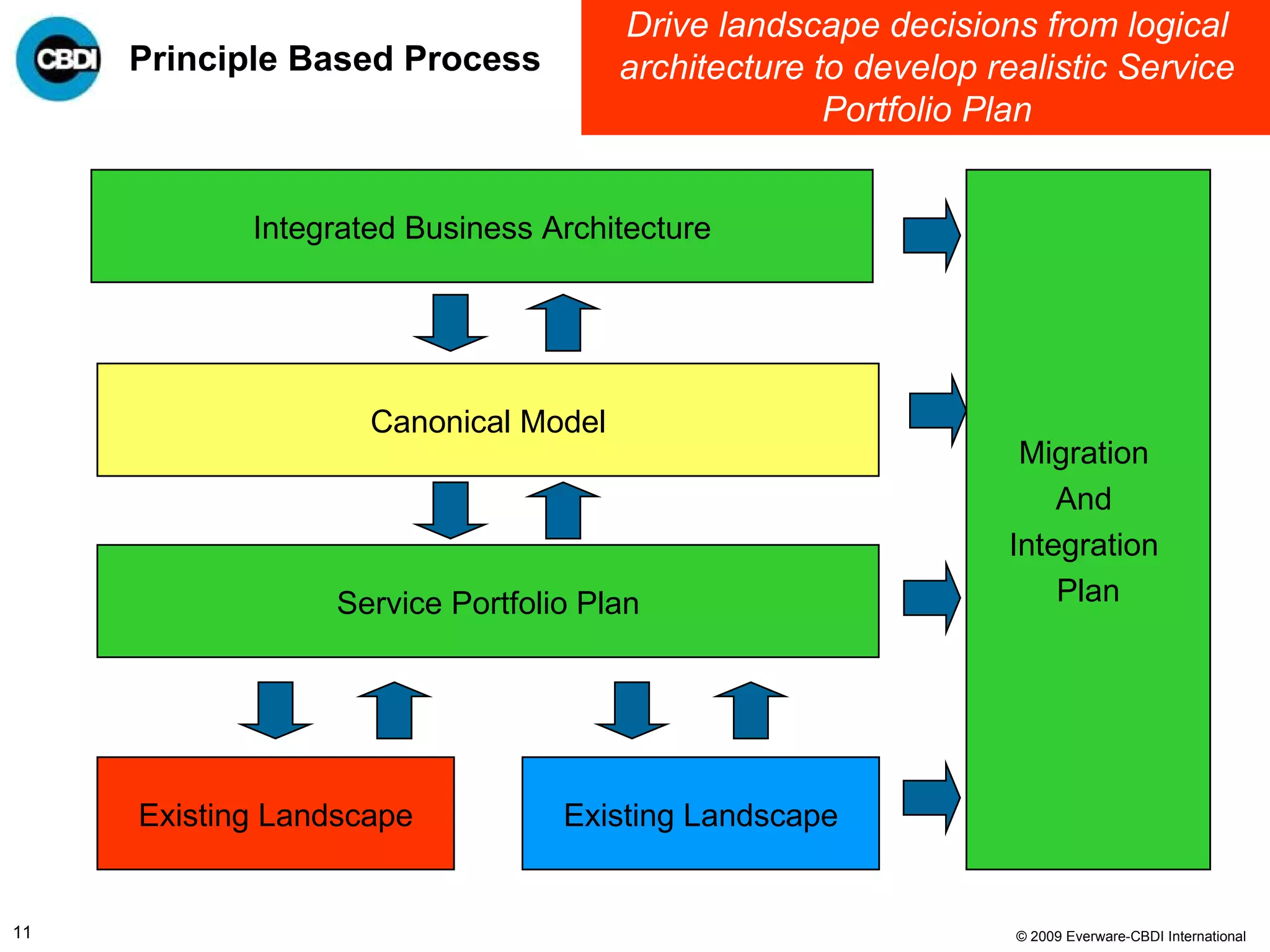
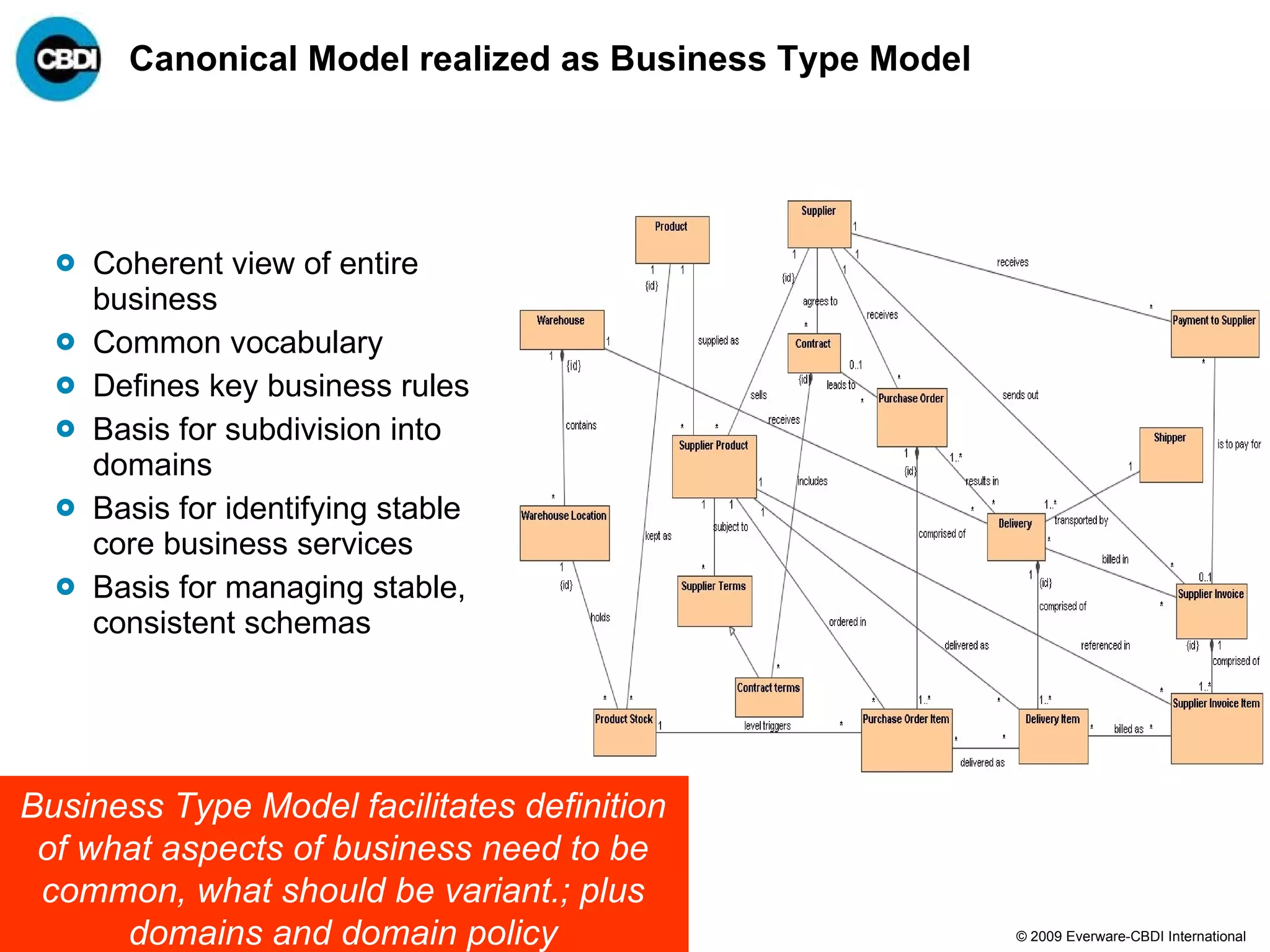
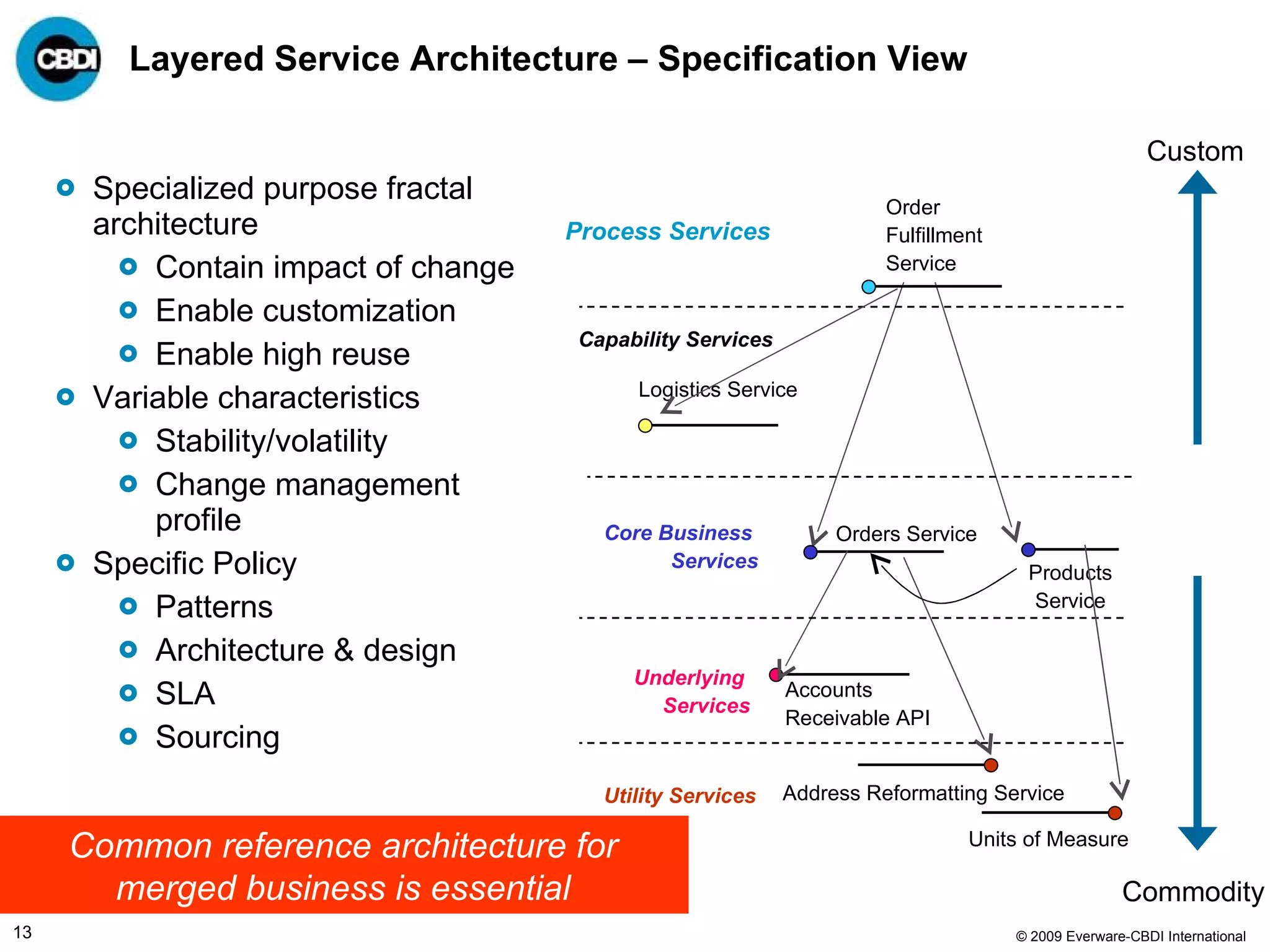
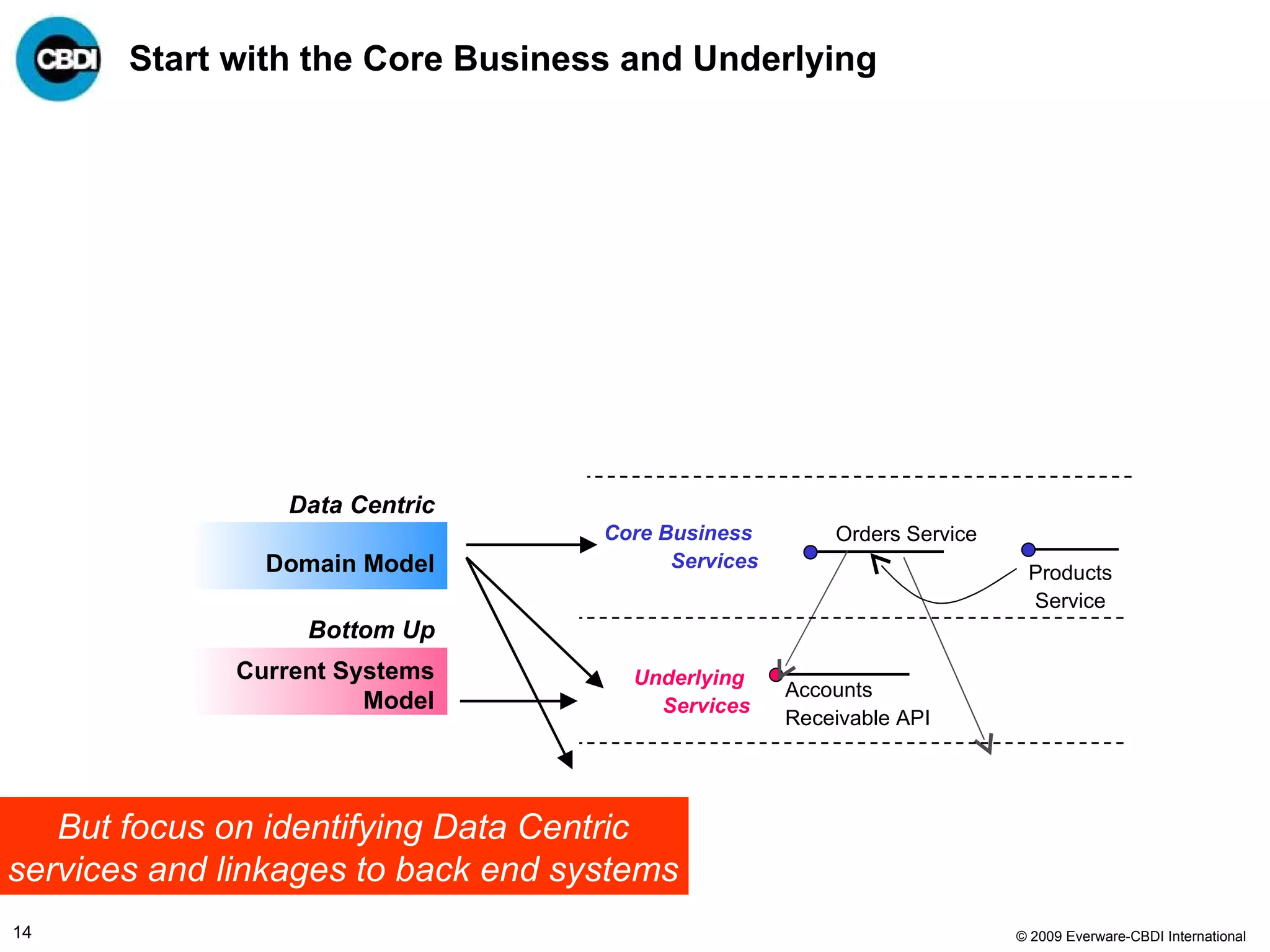
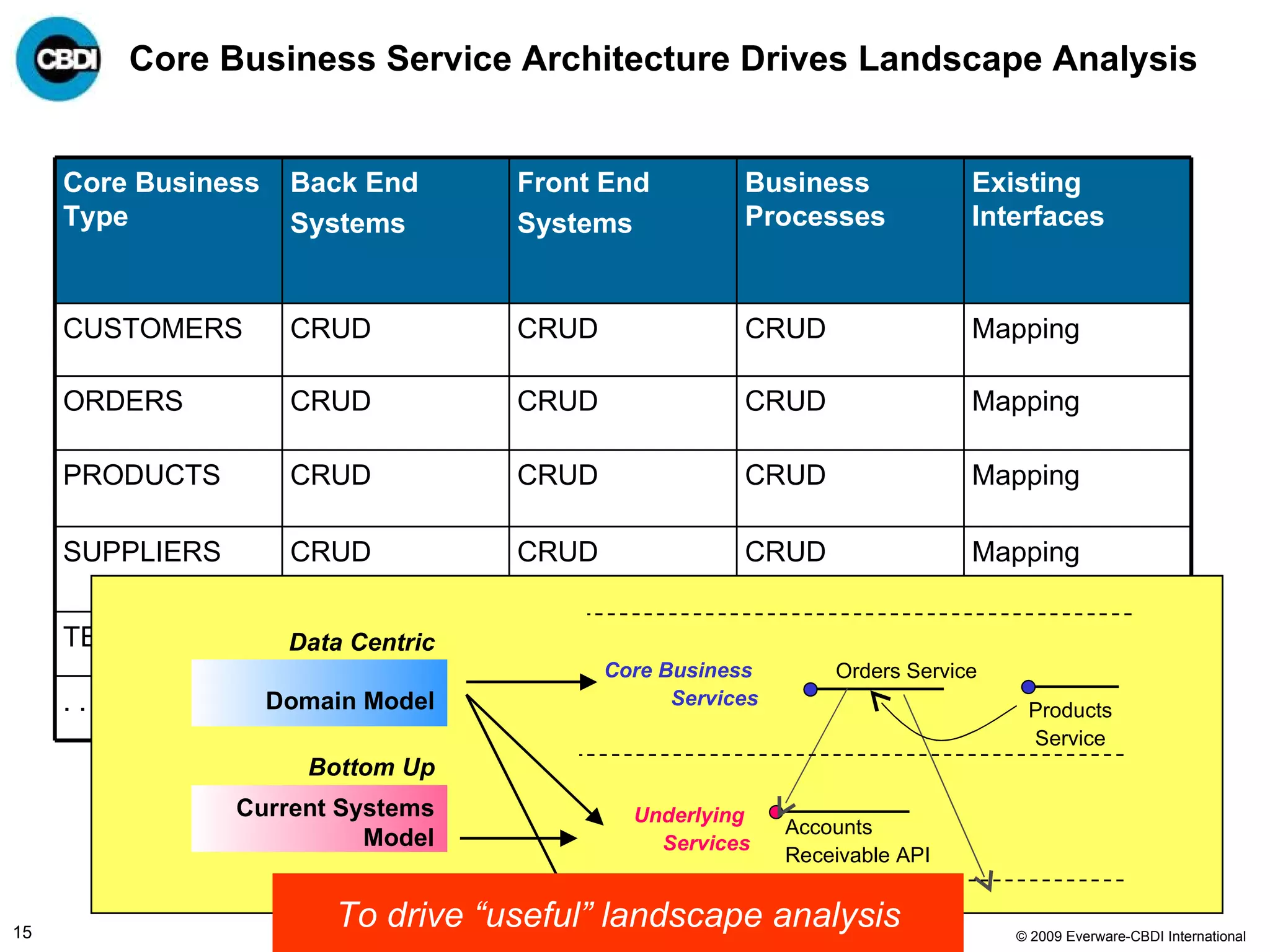
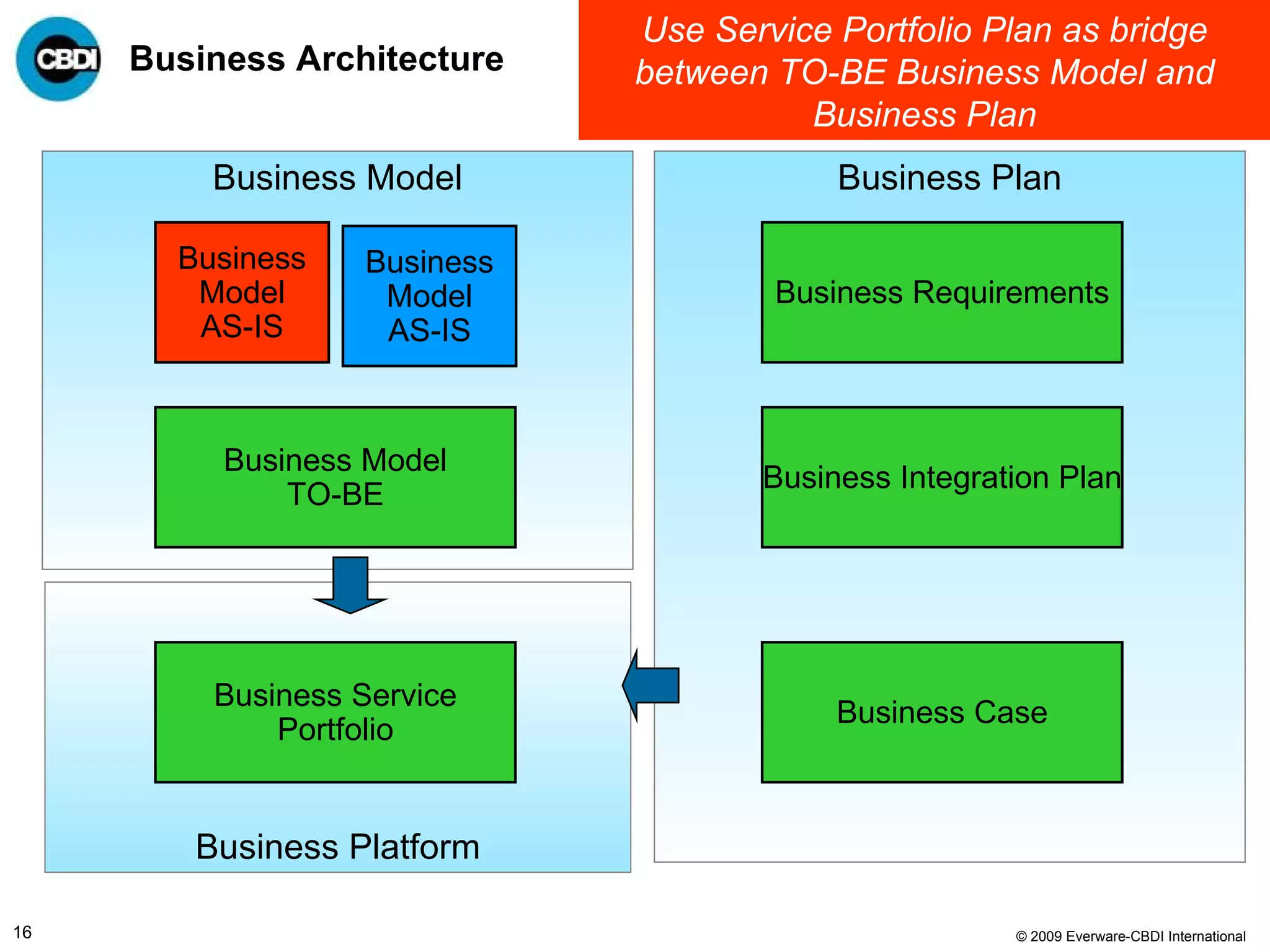
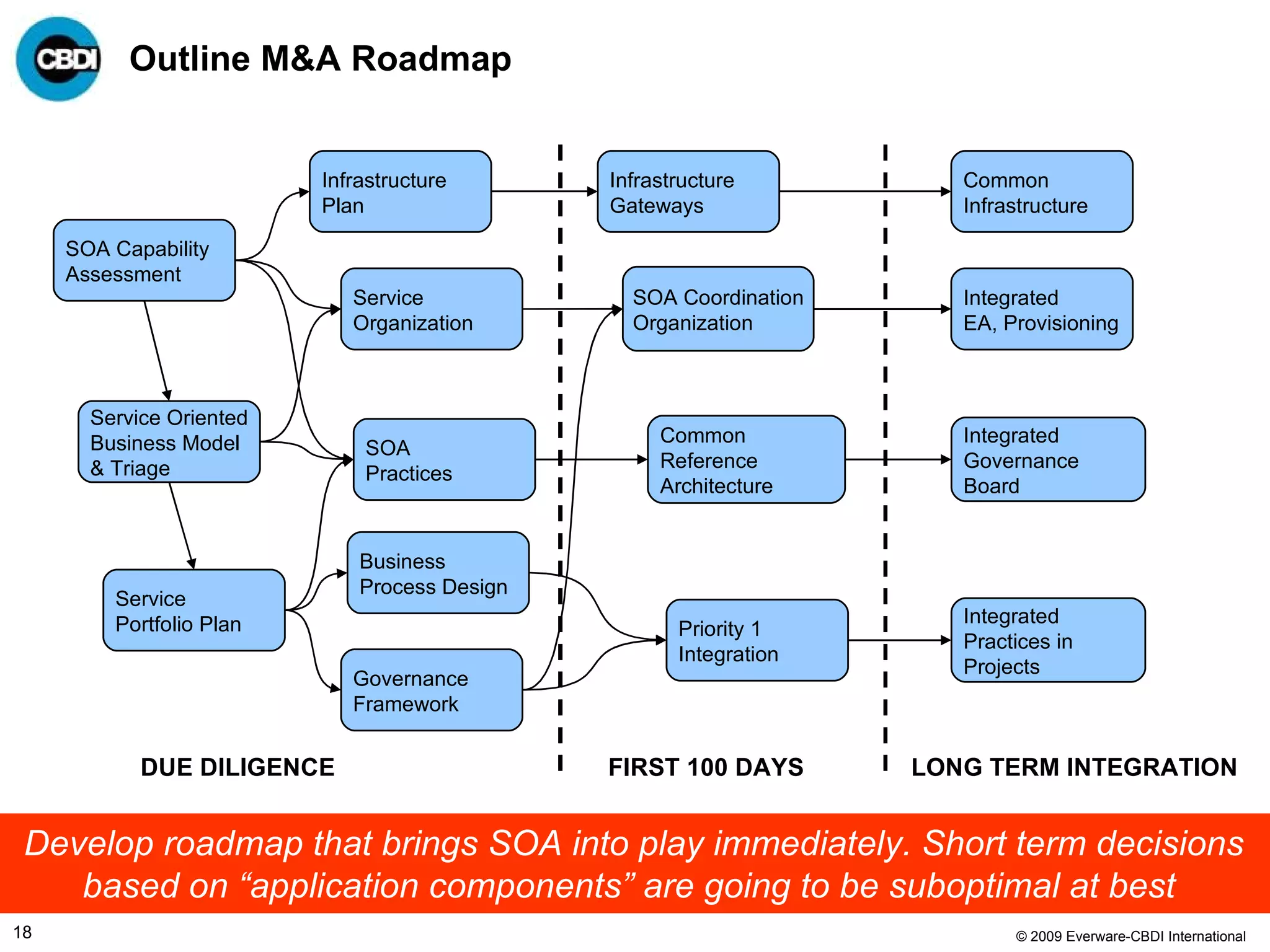
The document discusses the challenges and failures associated with mergers and acquisitions (M&A), highlighting that over 58% result in a net loss of shareholder value. It emphasizes the importance of effective utilization of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) for improving integration processes post-M&A and maximizing value creation through structured methodologies and better governance. The author suggests that leveraging SOA can address complexities and inefficiencies in M&A by providing a clear framework for integration, system rationalization, and improved data management.