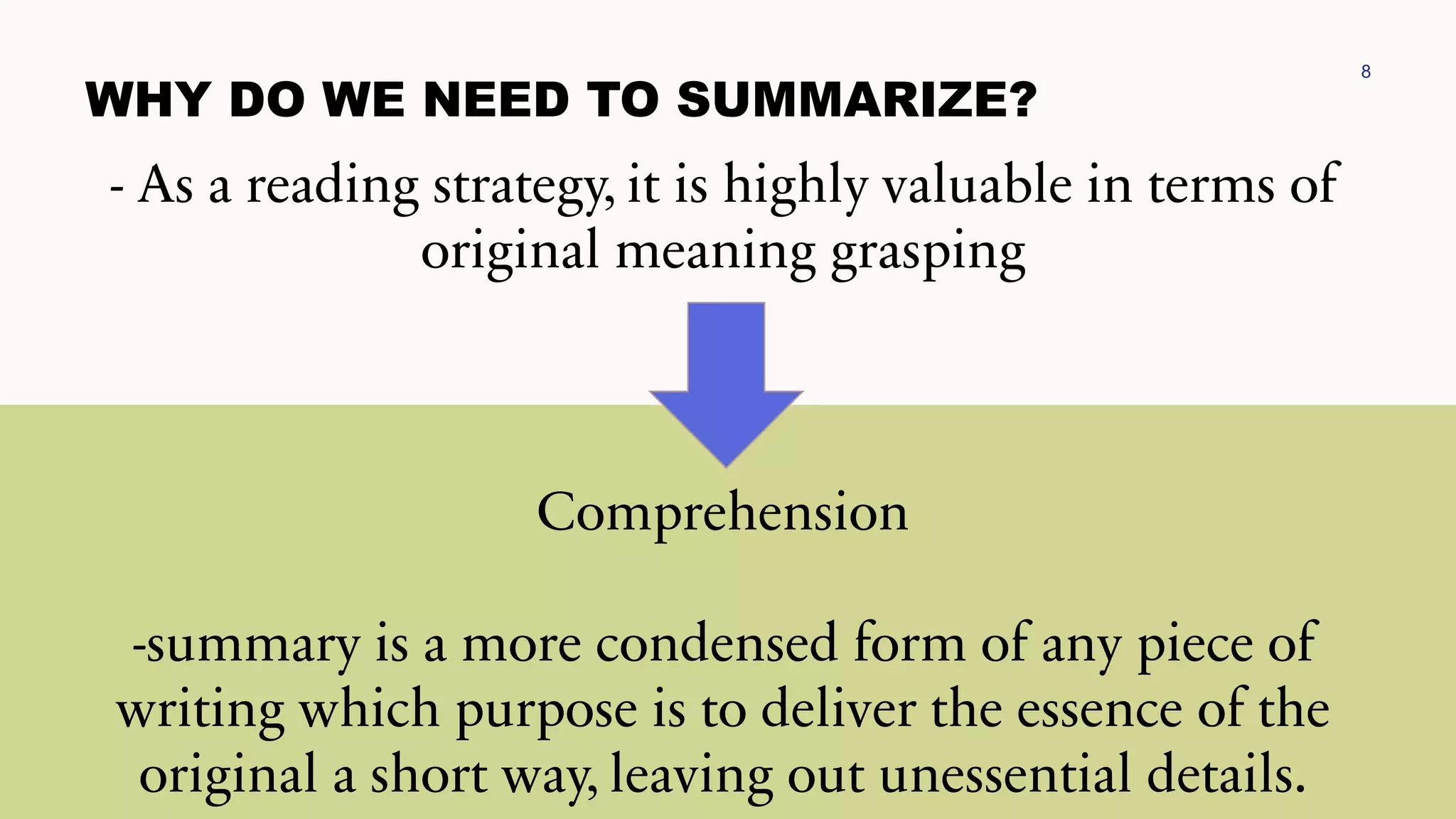
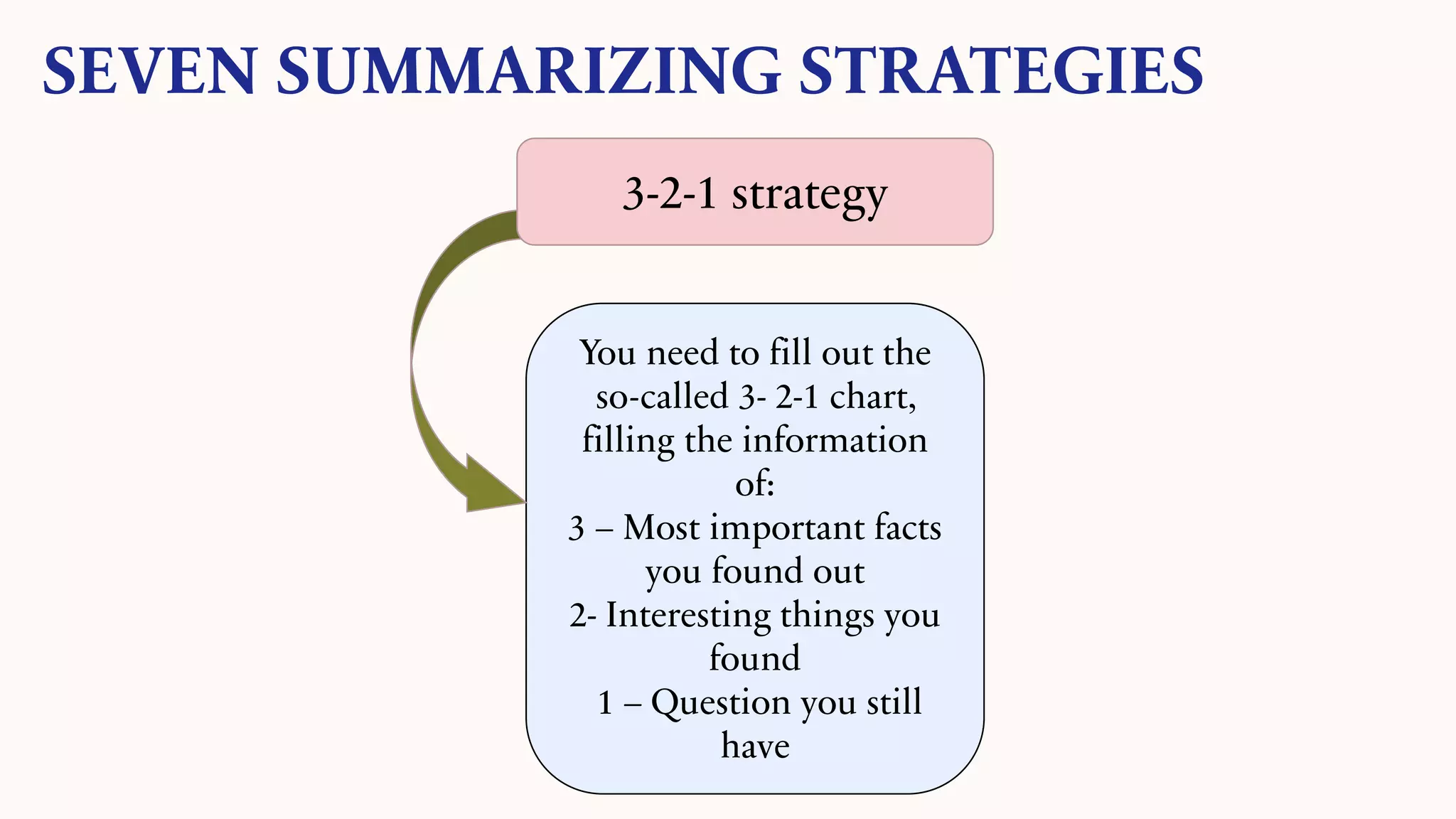
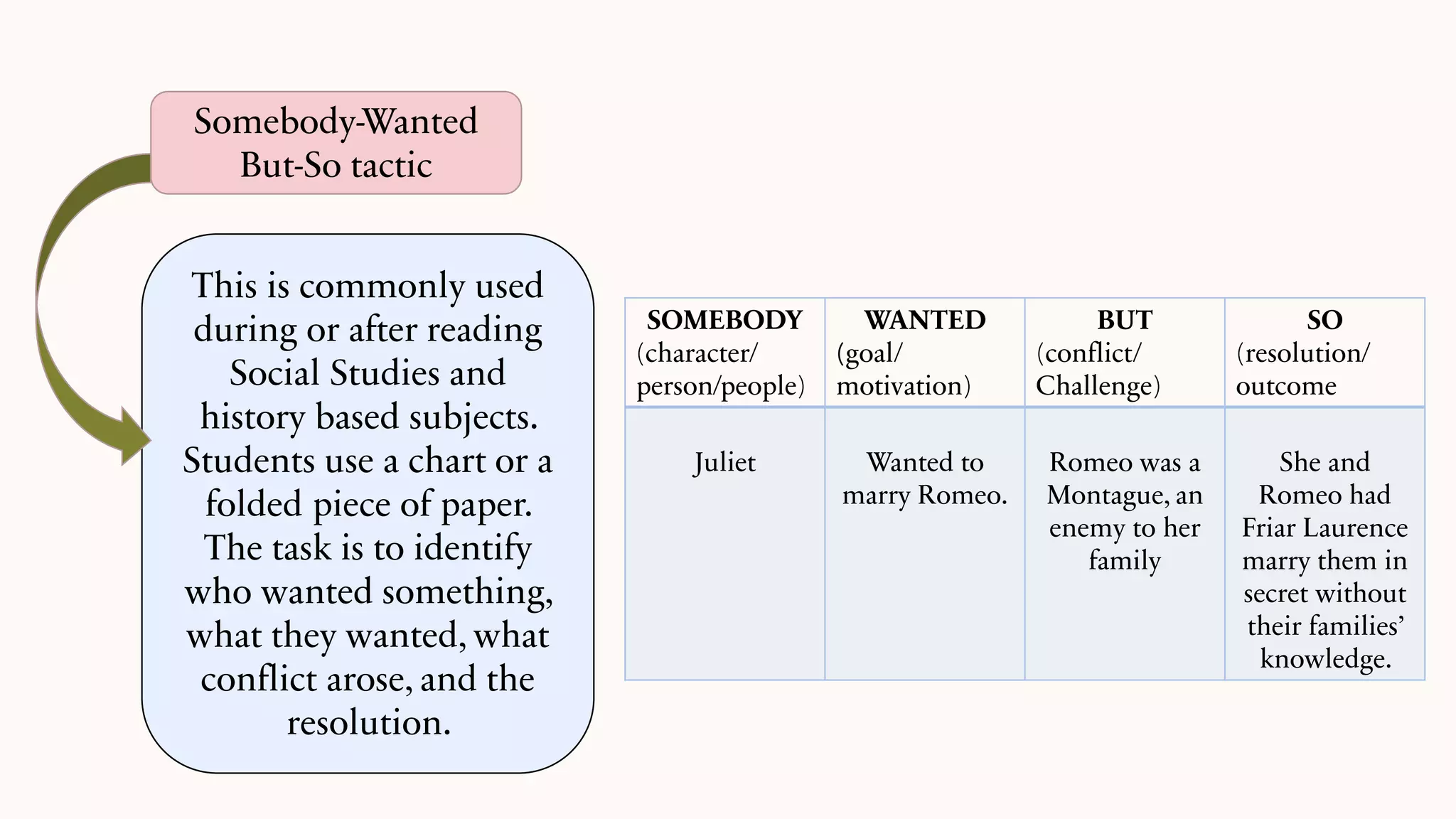
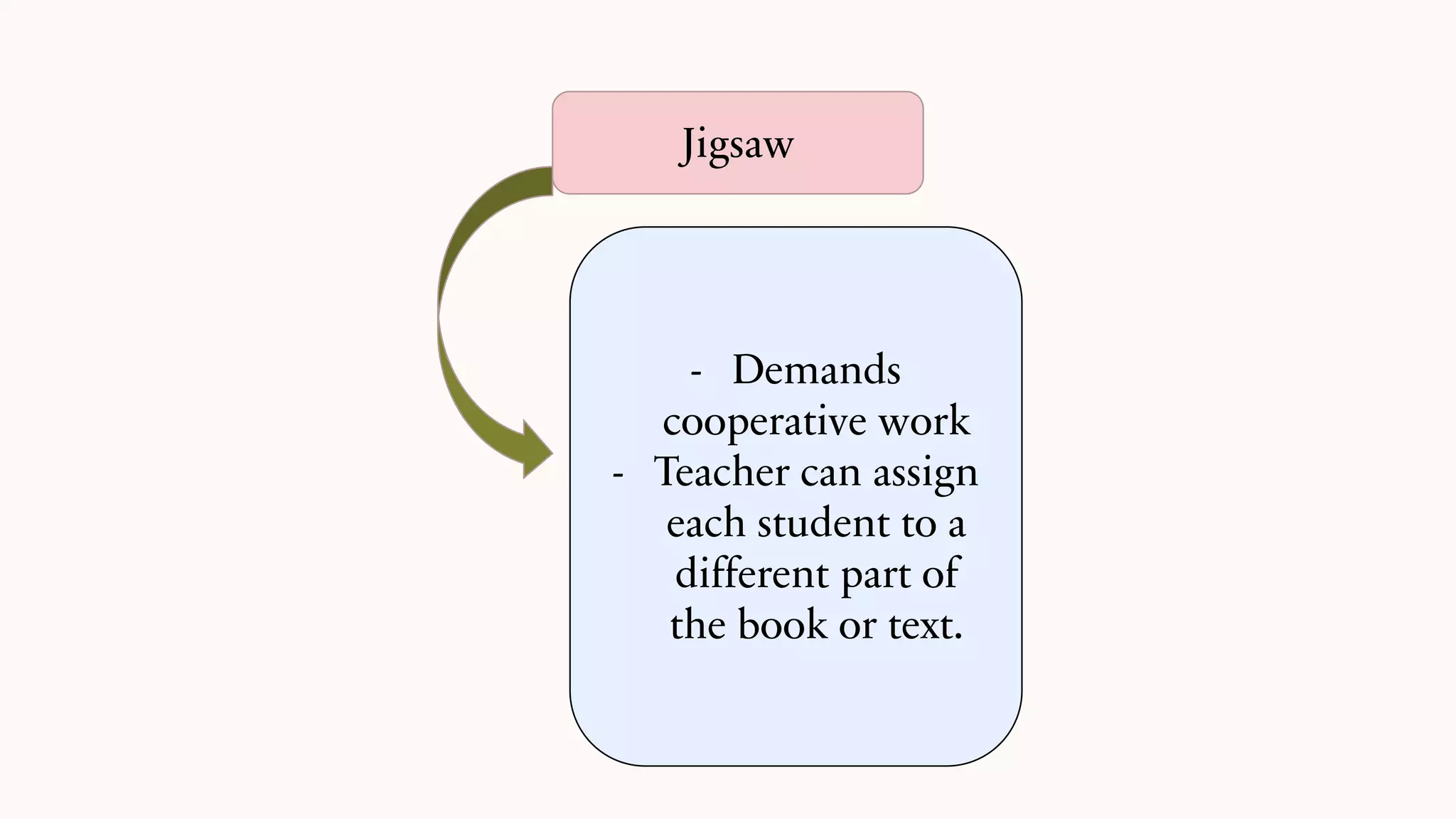
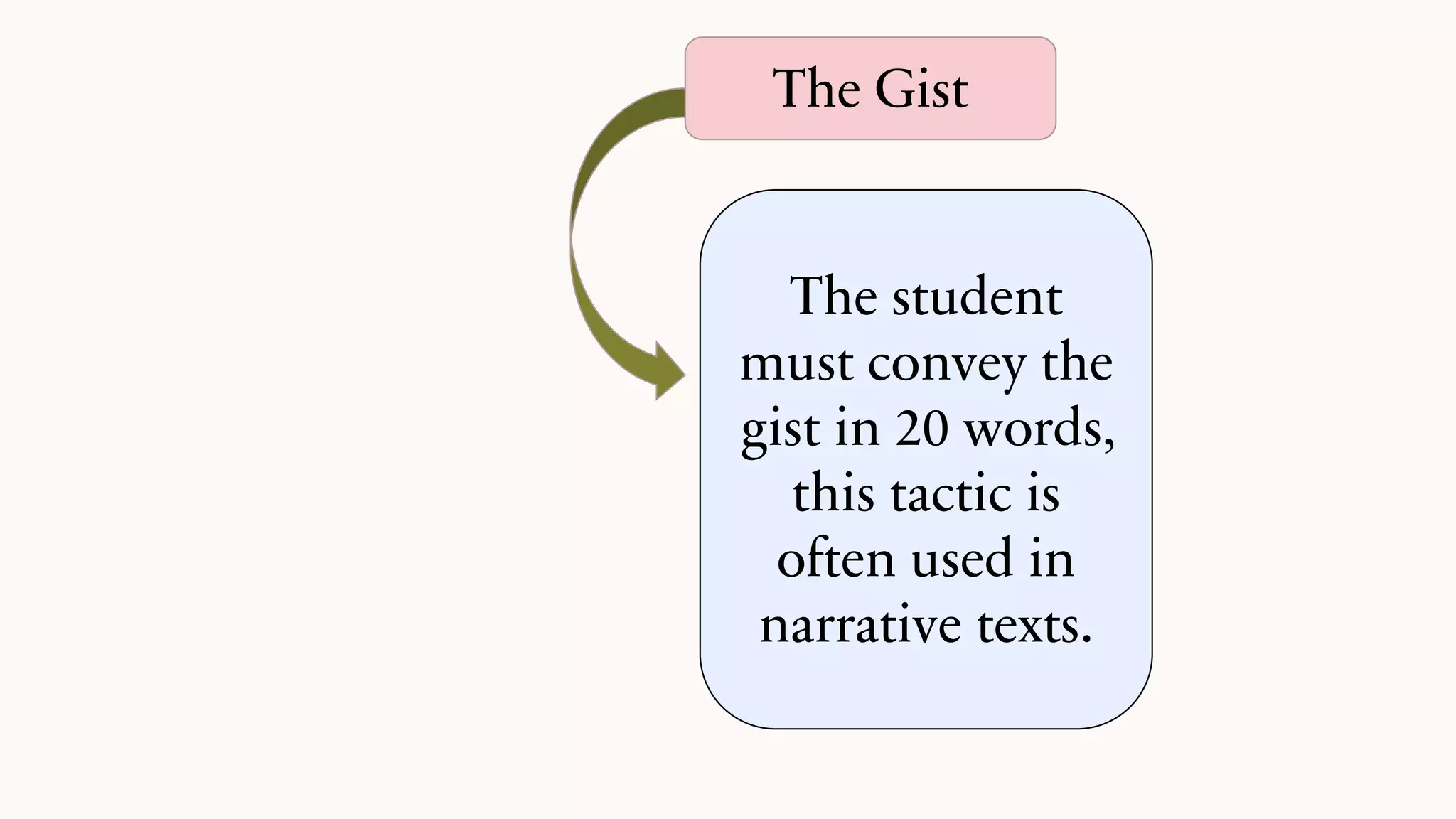
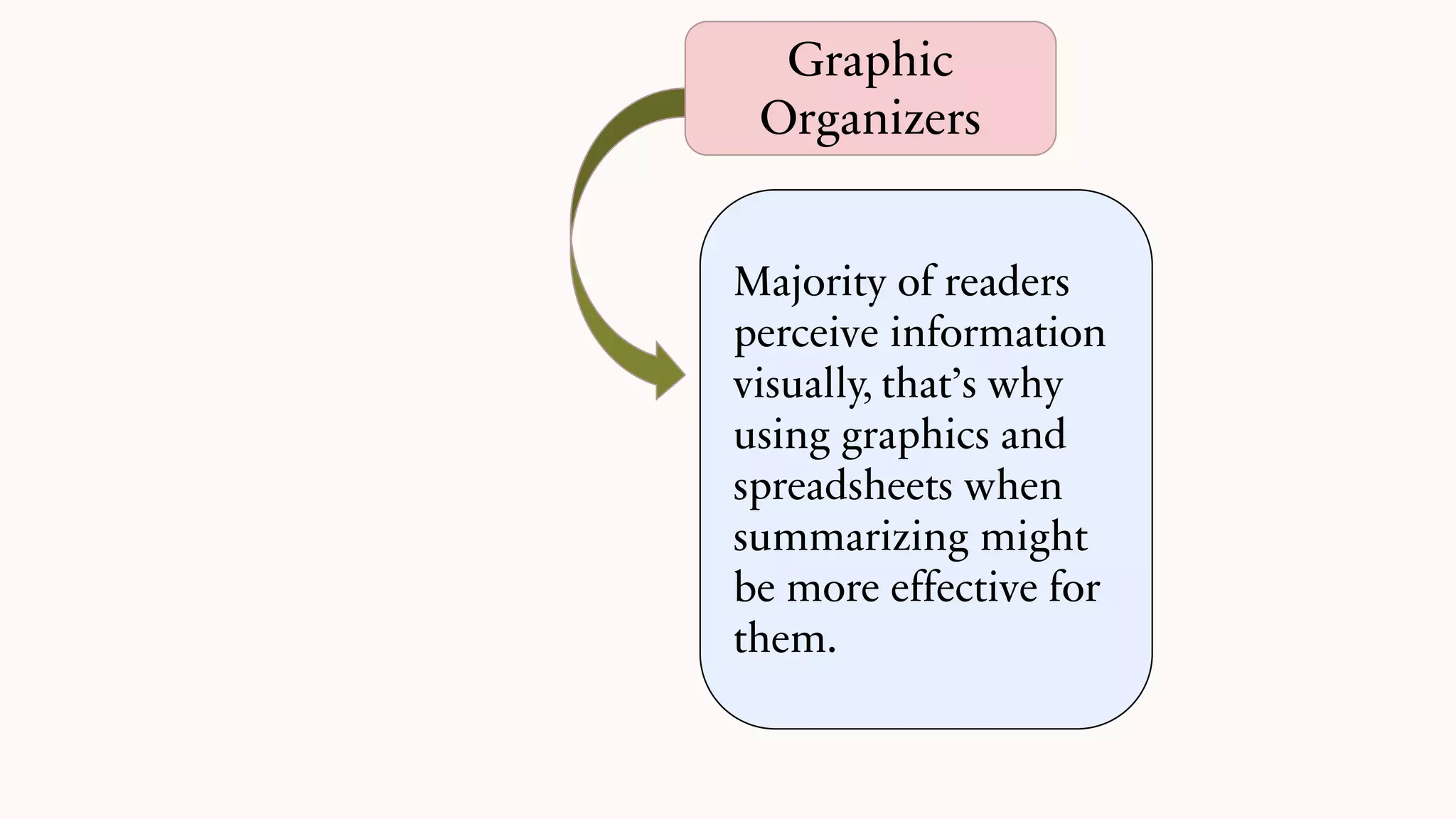
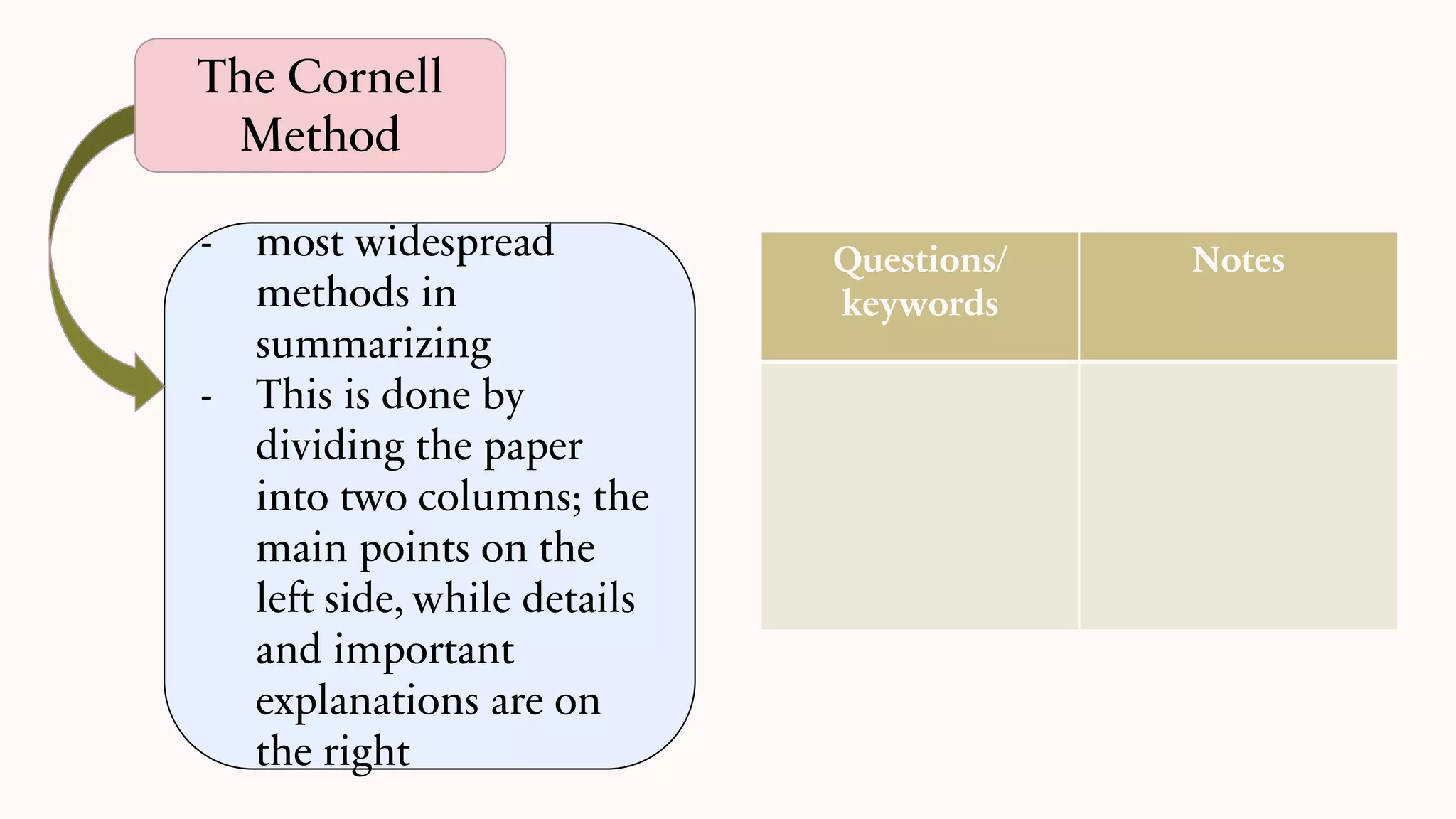
This document discusses techniques for summarizing academic texts. It defines summarizing as reducing a text to one-third or one-quarter of its original size while retaining the original ideas and key points. The purpose is to briefly present the context for an argument. Effective summarizing requires identifying the main idea and essential information in a text. It is an important skill that helps deepen understanding and learn to identify relevant details that support the main ideas. The document outlines several strategies for summarizing texts, including the 3-2-1 technique, somebody-wanted-but-so tactic, jigsaw method, ball tossing, using only 20 words to convey the gist, graphic organizers, and the Cornell note-taking method.