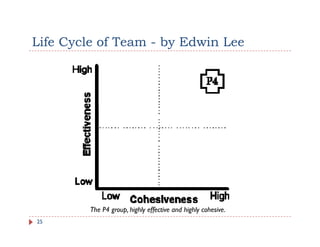
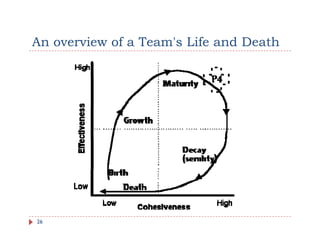
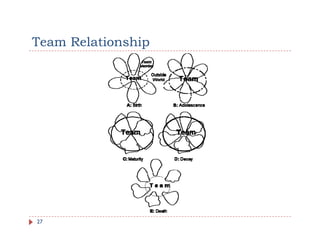
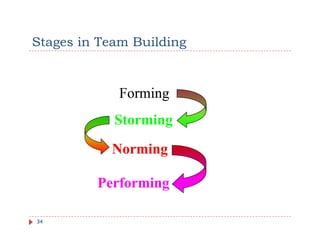
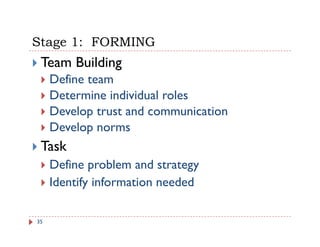
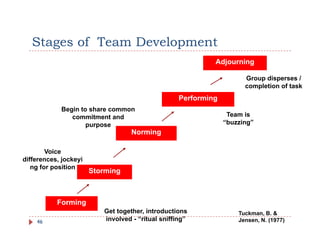
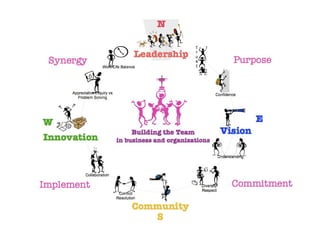
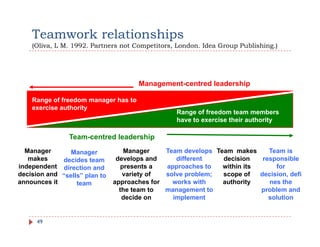
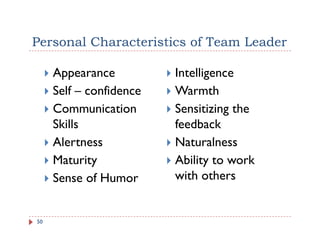
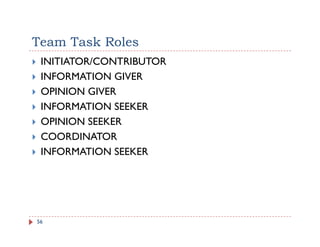
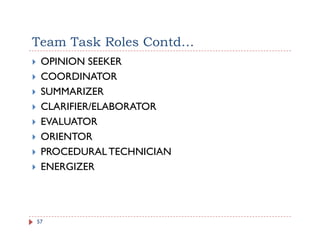
The document discusses team building and team effectiveness. It defines what a team is and outlines the benefits of teamwork. It describes Tuckman's model of team development, which includes forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning stages. Key aspects of team effectiveness are clear goals, roles, procedures, relationships, and leadership. The importance of team culture and characteristics of effective team leaders are also discussed.