The document summarizes several teaching methods for foreign languages:
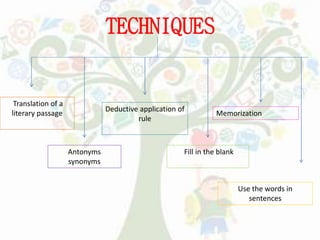
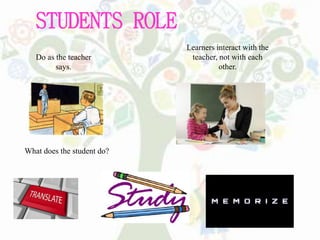
- Grammar Translation Method focuses on translation and grammar rules with little speaking practice.
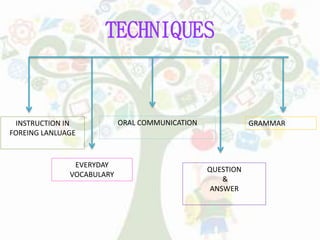
- Direct Method teaches vocabulary and concepts through visuals and interaction without translation.
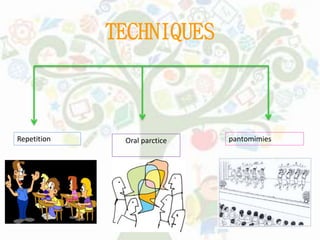
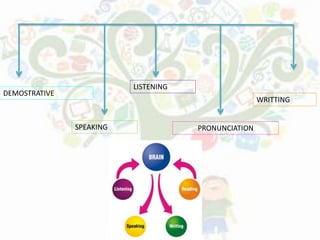
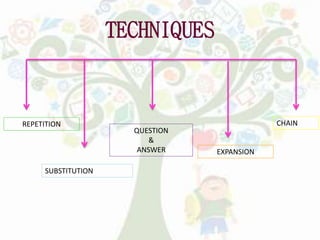
- Audiolingual Method emphasizes speaking through repetition of dialogs with less focus on grammar rules.
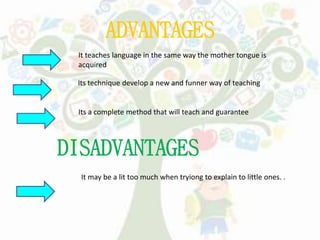
- Cognitive Code Learning connects new material to students' prior knowledge and helps them learn from their mistakes.