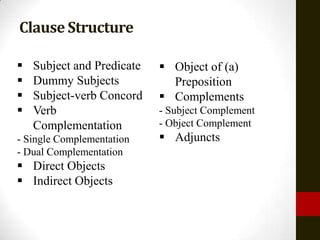
This document provides information about clause structure and adjective clauses in English grammar. It includes examples of:
- Subject and predicate clauses
- Direct and indirect objects
- Adjective pronouns like who, which, that and their uses for subjects, objects, and objects of prepositions
- Restrictive vs. non-restrictive adjective clauses
- Adjective pronouns whose, where, when and example sentences using them. Exercises are provided to practice these grammar points with answers explained.