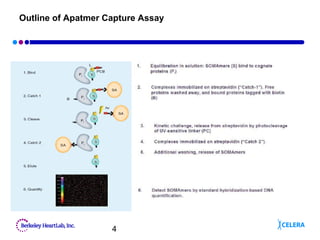
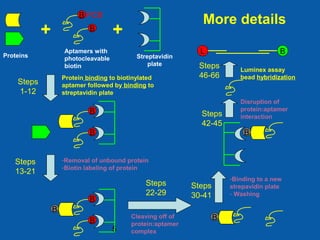
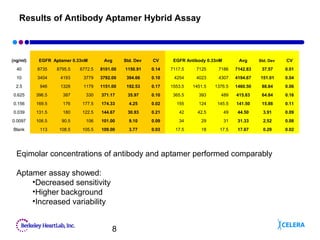
This document describes the development of an aptamer-based assay for the early detection of lung cancer. Aptamers are oligonucleic acid molecules that bind to specific target molecules and have advantages over antibodies. The current assay takes two days to complete and has high variability. To make it practical for clinical use, the assay needs to be completed in one day with lower variability. Future work will focus on shortening the assay time, optimizing aptamer conjugations and the use of biotinylated antibodies, and refining assay conditions. The goal is to develop a simple, fast assay that can help detect lung cancer early and improve treatment outcomes.