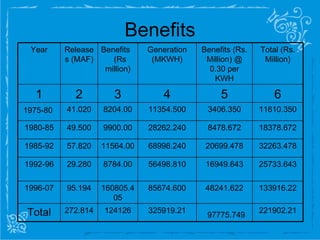
The document summarizes the Tarbela Dam project in Pakistan, which began construction in 1968. It describes the project's objectives of power generation and irrigation. It also outlines the project duration, constraints of cost and time, financing from various countries, construction details involving tunnels and spillways, power generation capabilities, and benefits provided.