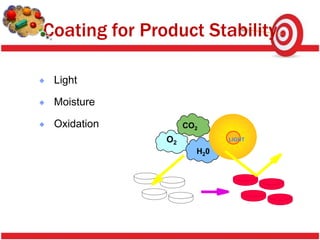
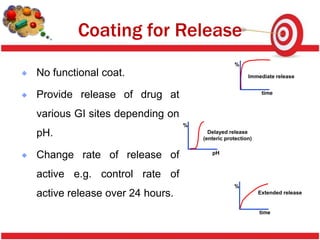
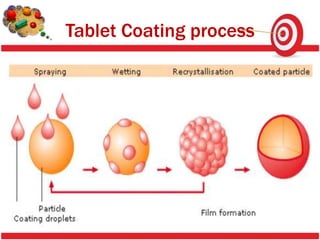
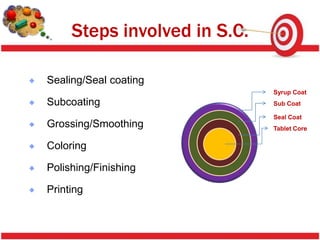
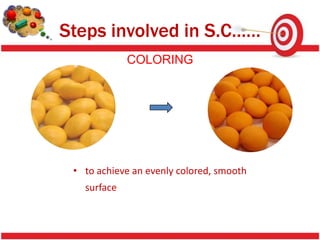
Tablet coating provides benefits like masking taste, protecting drugs from the environment, and modifying drug release. Sugar coating is a multistep process using sucrose to coat tablets. Defects in coating like chipping, sticking, cracking and color variation can occur due to factors like coating solution properties, processing parameters, and moisture. Proper control of these factors is needed to produce quality coated tablets.