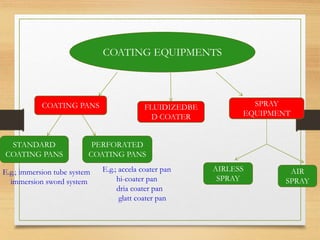
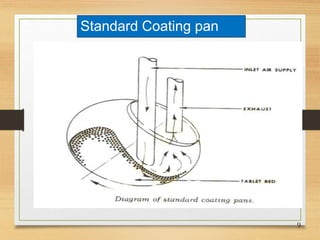
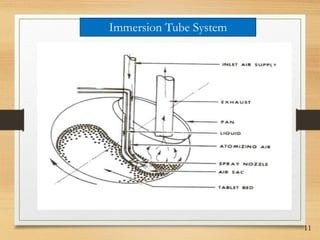
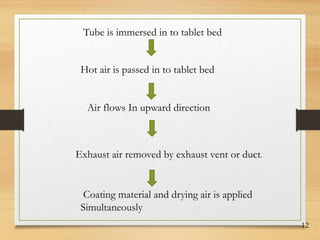
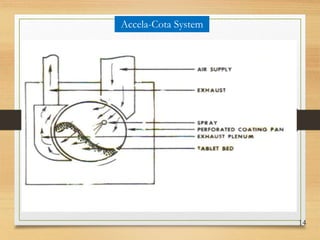
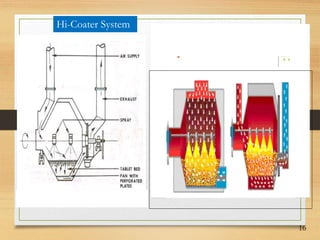
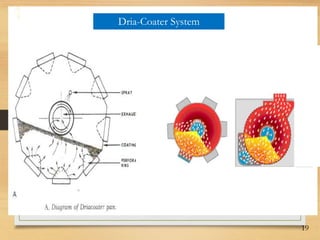
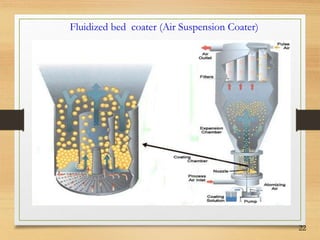
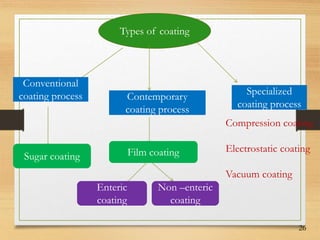
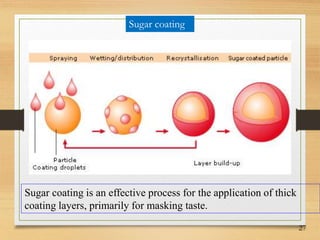
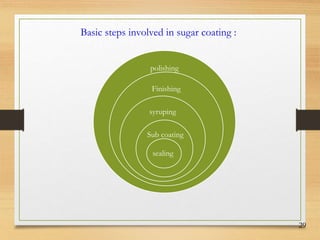
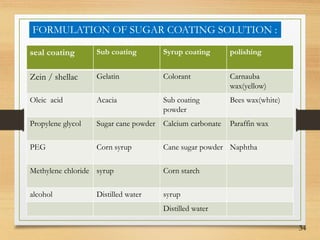
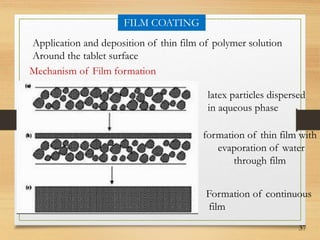
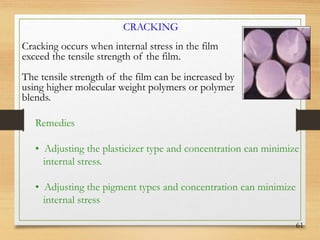
This document discusses tablet coating, including its objectives, properties, equipment, types, and parameters. The key objectives of tablet coating are to mask unpleasant tastes/odors, provide physical/chemical protection, improve patient acceptability, and control drug release. Common coating equipment includes standard coating pans, perforated pans, fluidized bed coaters, and various spray systems. Types of coatings include sugar coating, film coating, enteric coating, and compression coating. Important coating parameters are defects, materials used, and process variables.