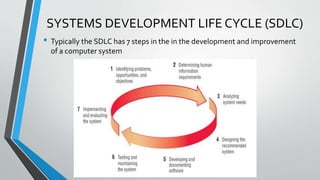
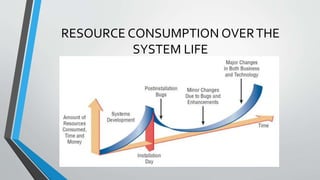
System analysis and design involves analyzing an organization's existing system or planned system and designing a better system to improve the organization. The key steps in system analysis and design are analyzing the system needs, designing the recommended system, developing and documenting the software, testing and maintaining the system, and implementing and evaluating the system. System analysts play an important role in information systems development projects by understanding business problems and applying technology to solve them.