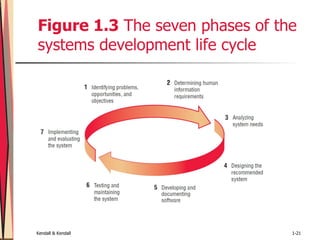
The document discusses the role of systems analysts and provides an overview of key concepts in systems analysis and design. It covers the types of systems analysts work with, the systems development life cycle, incorporating human-computer interaction considerations, and using computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools to aid analysts' work.