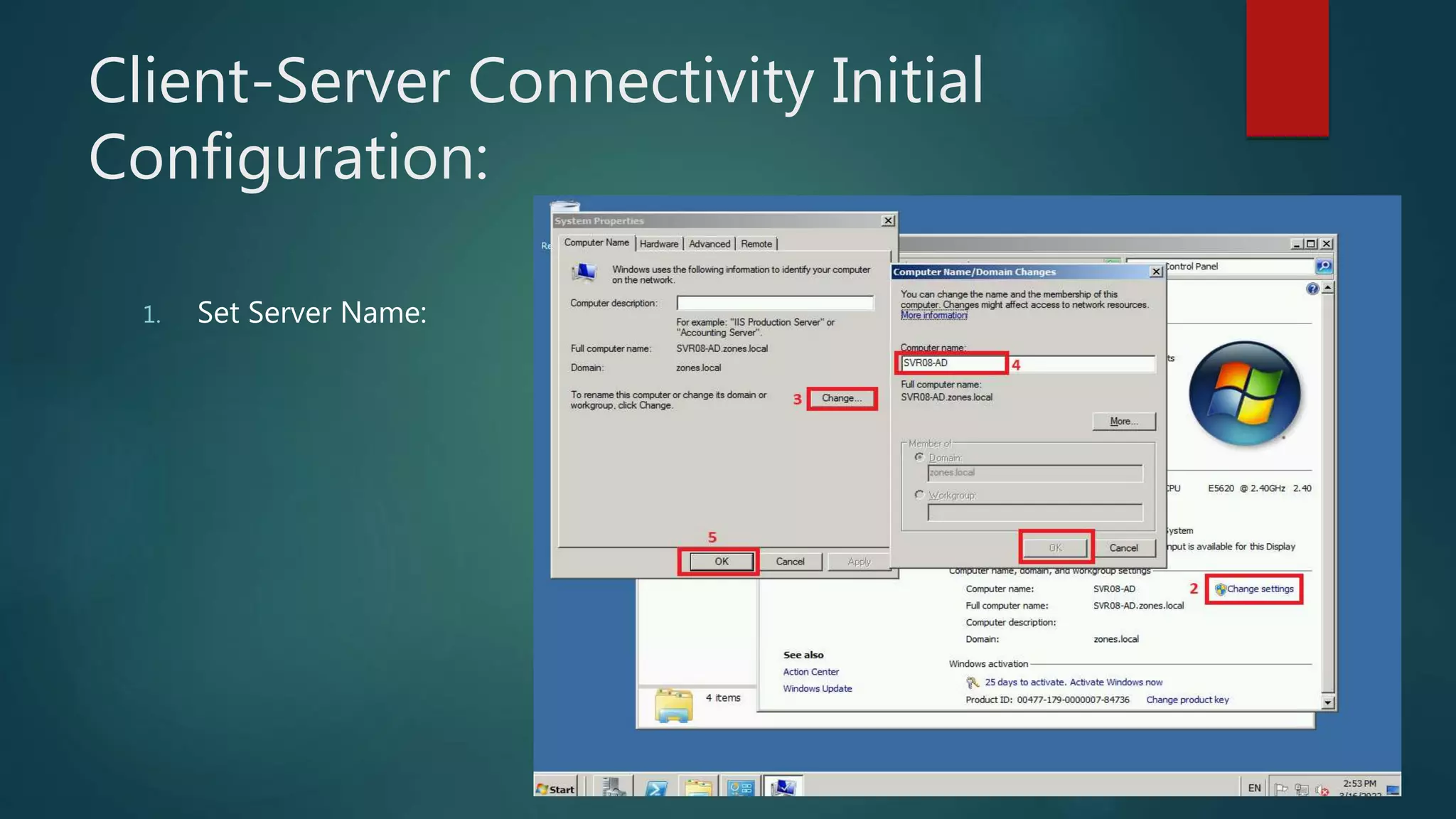
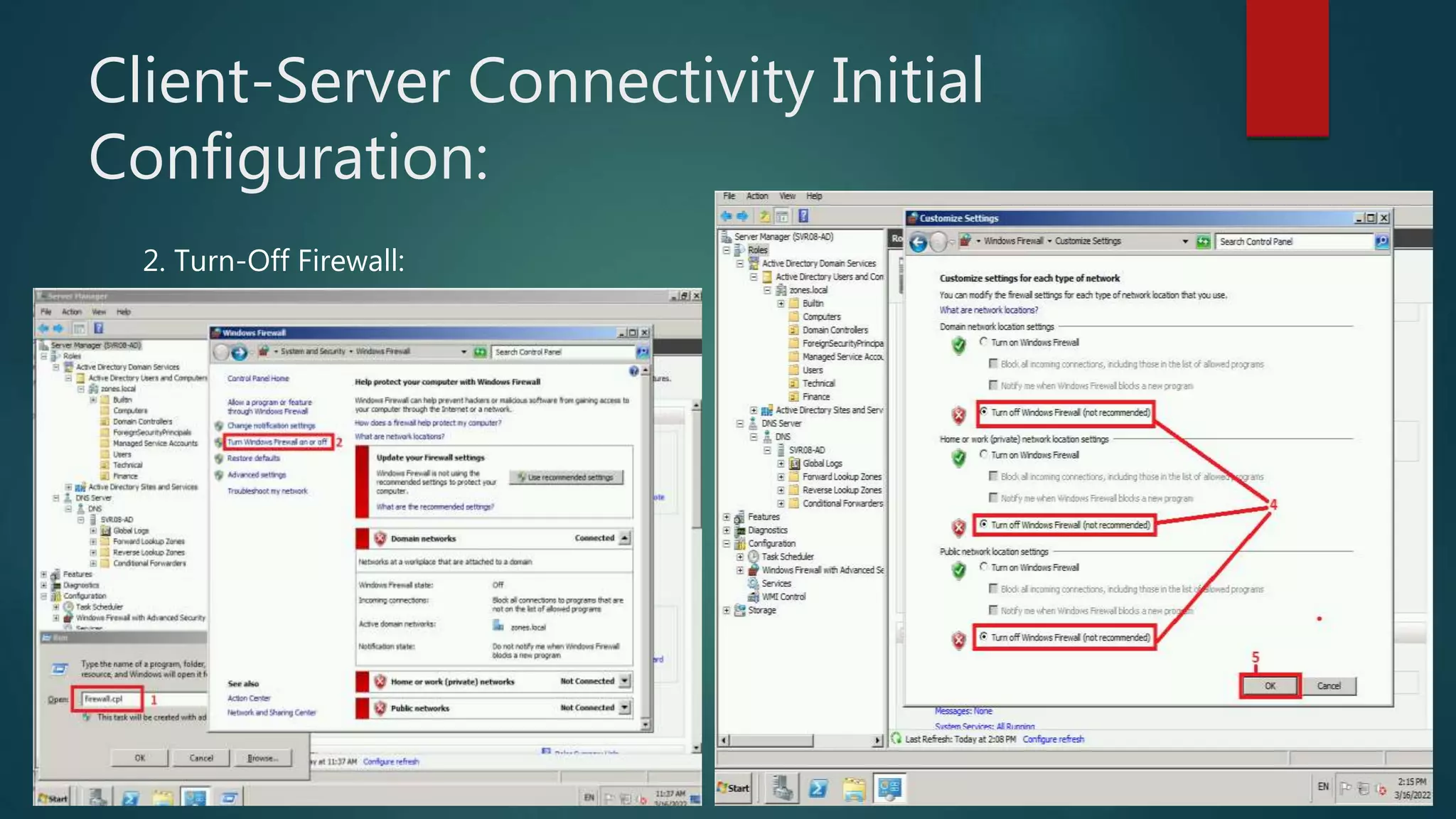
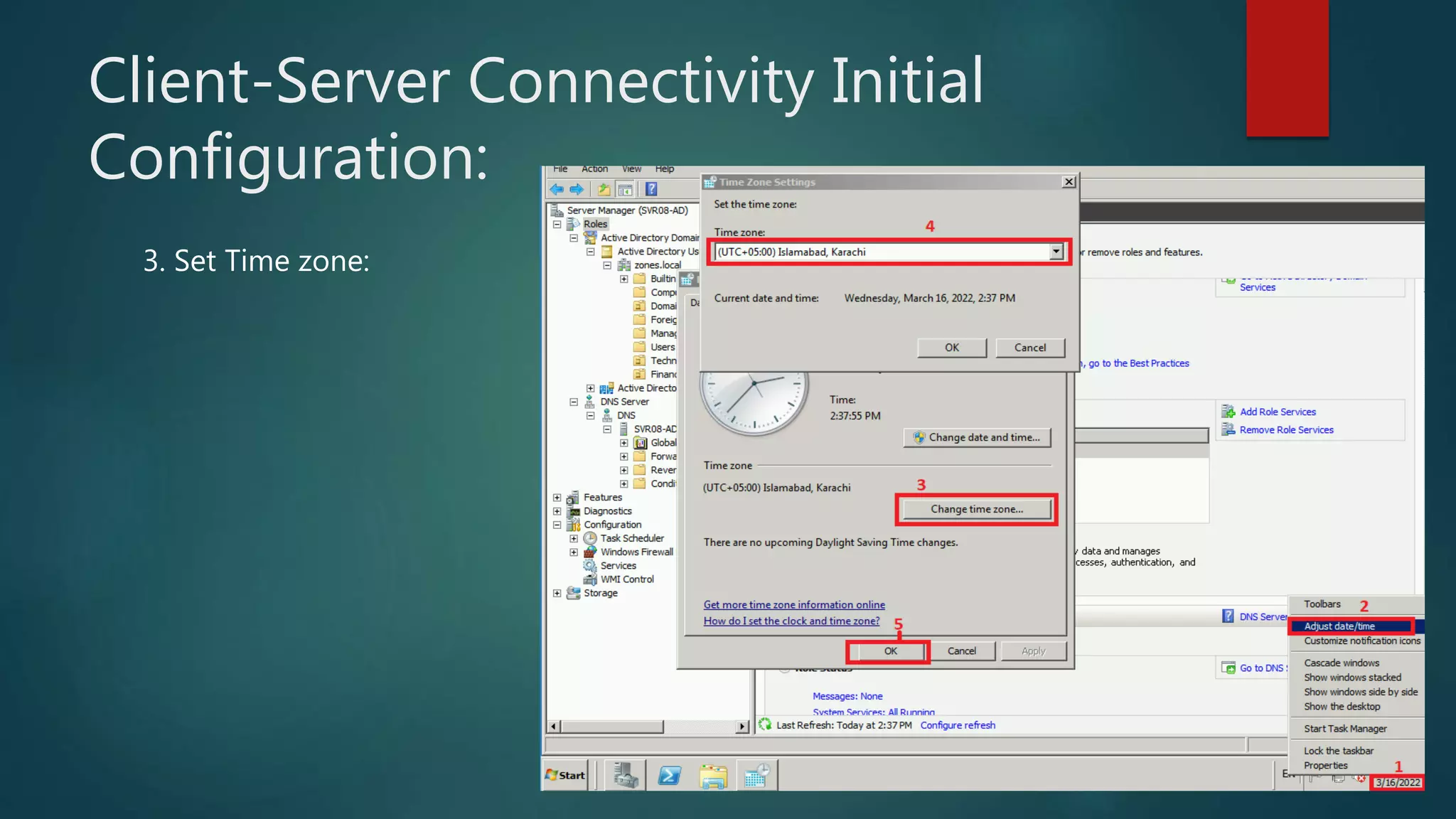
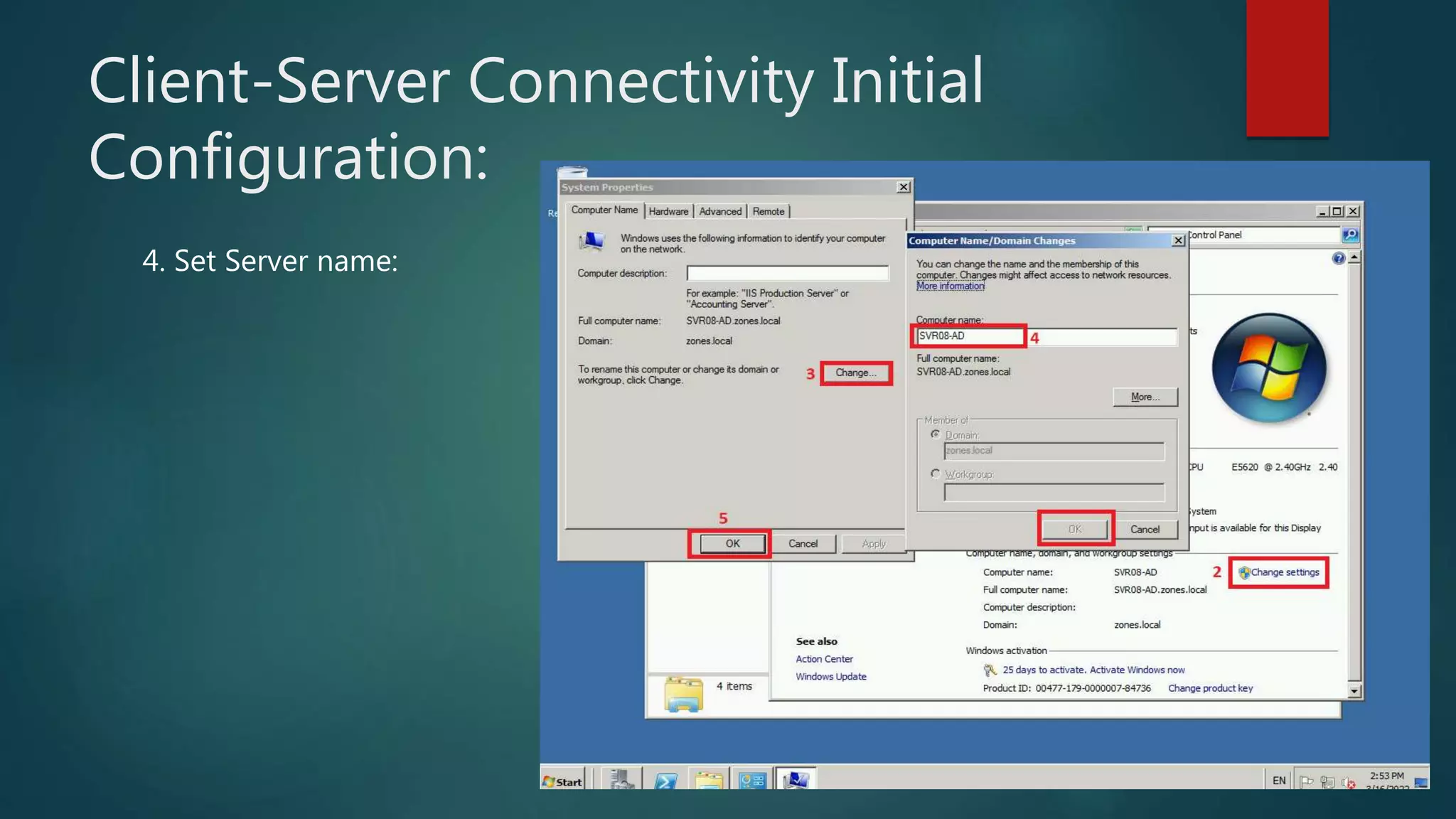
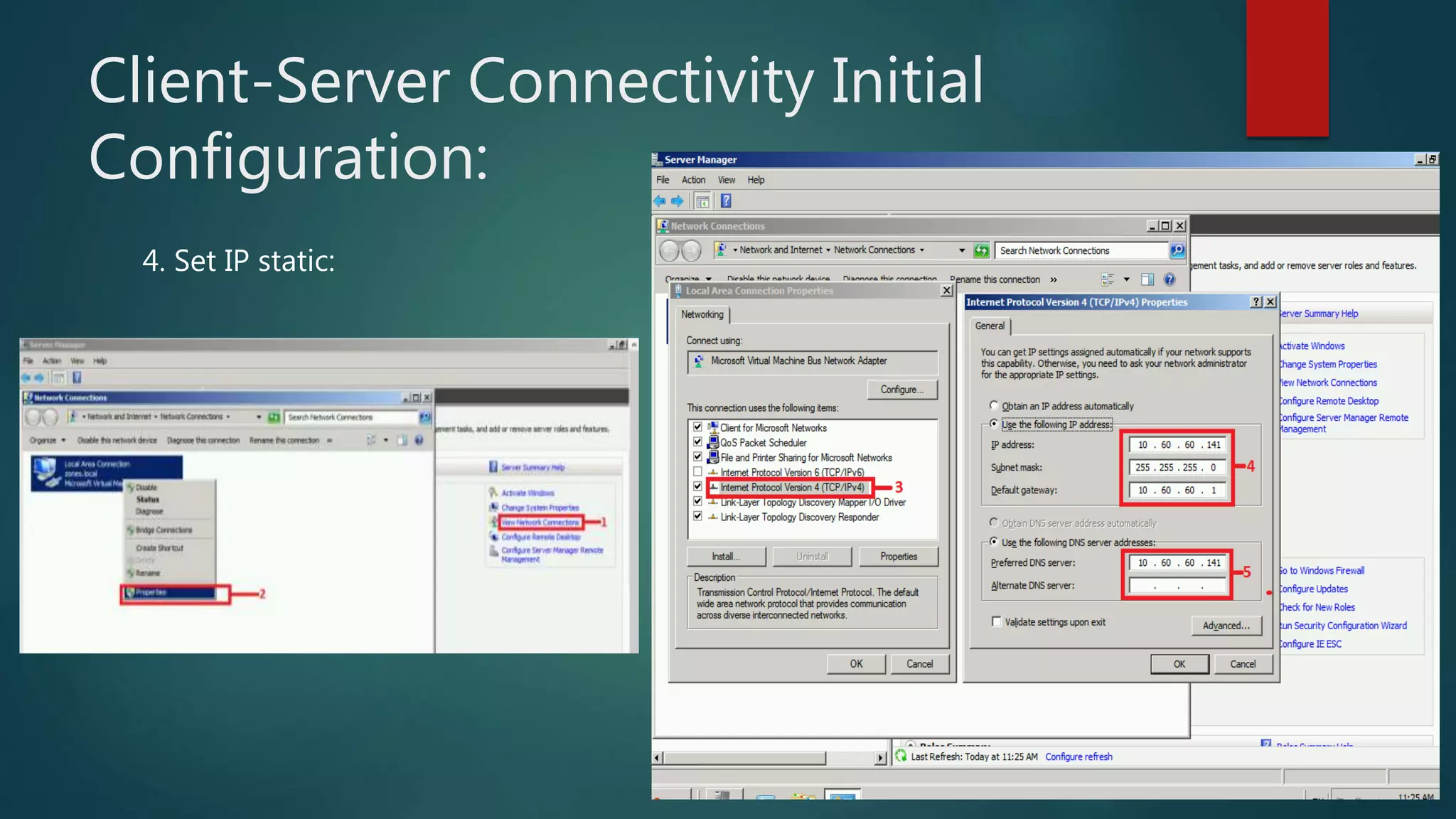
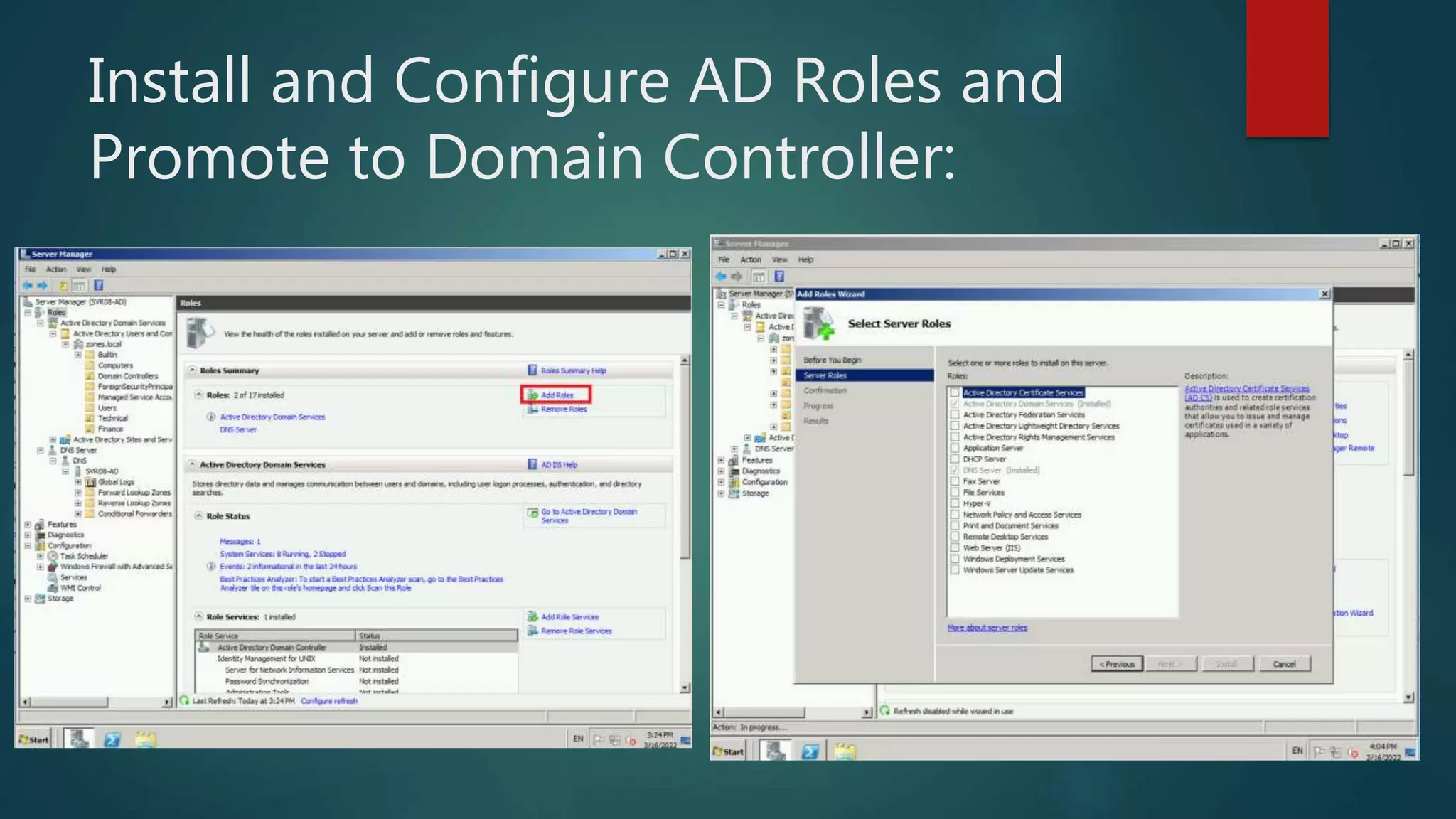
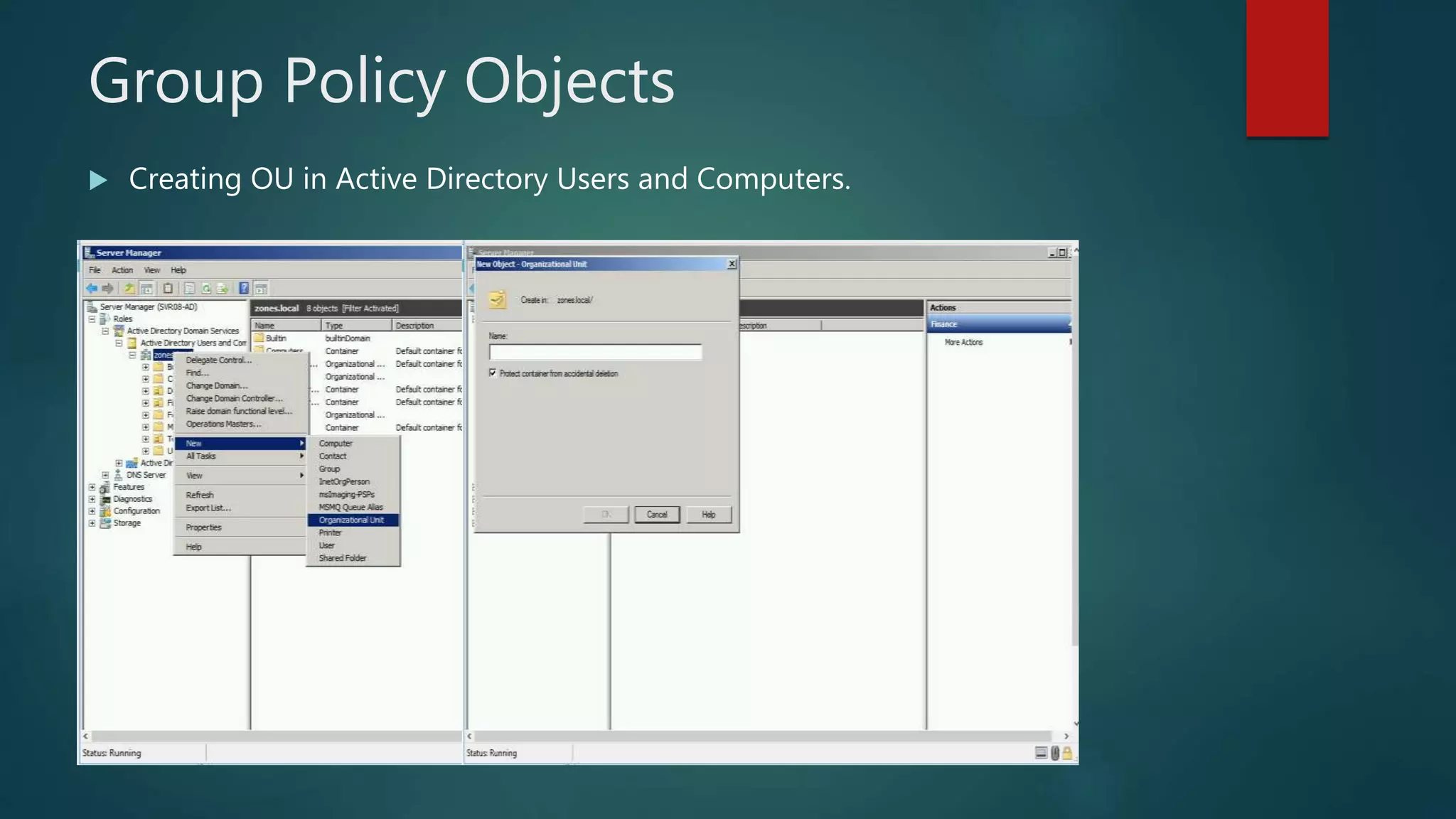
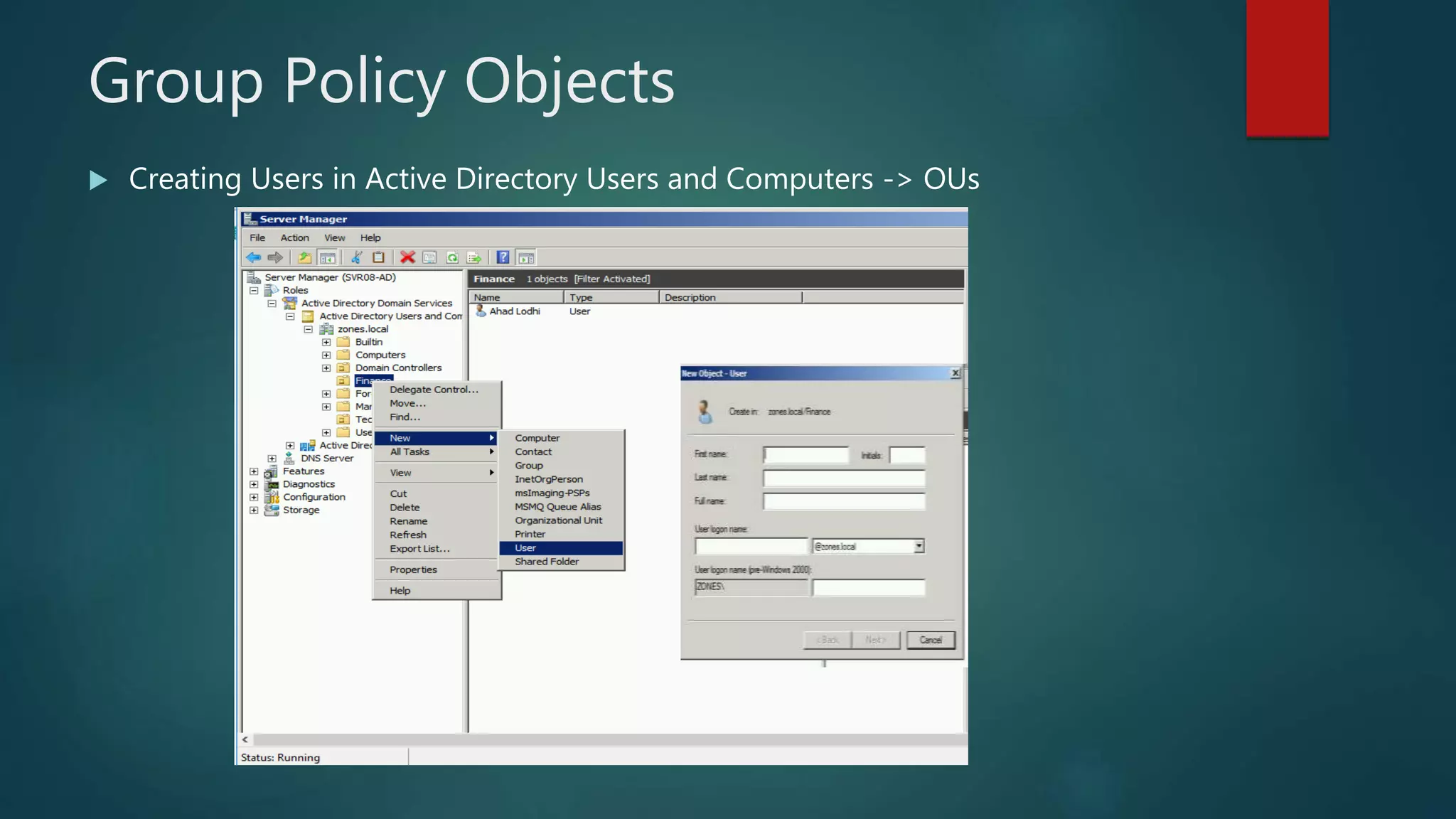
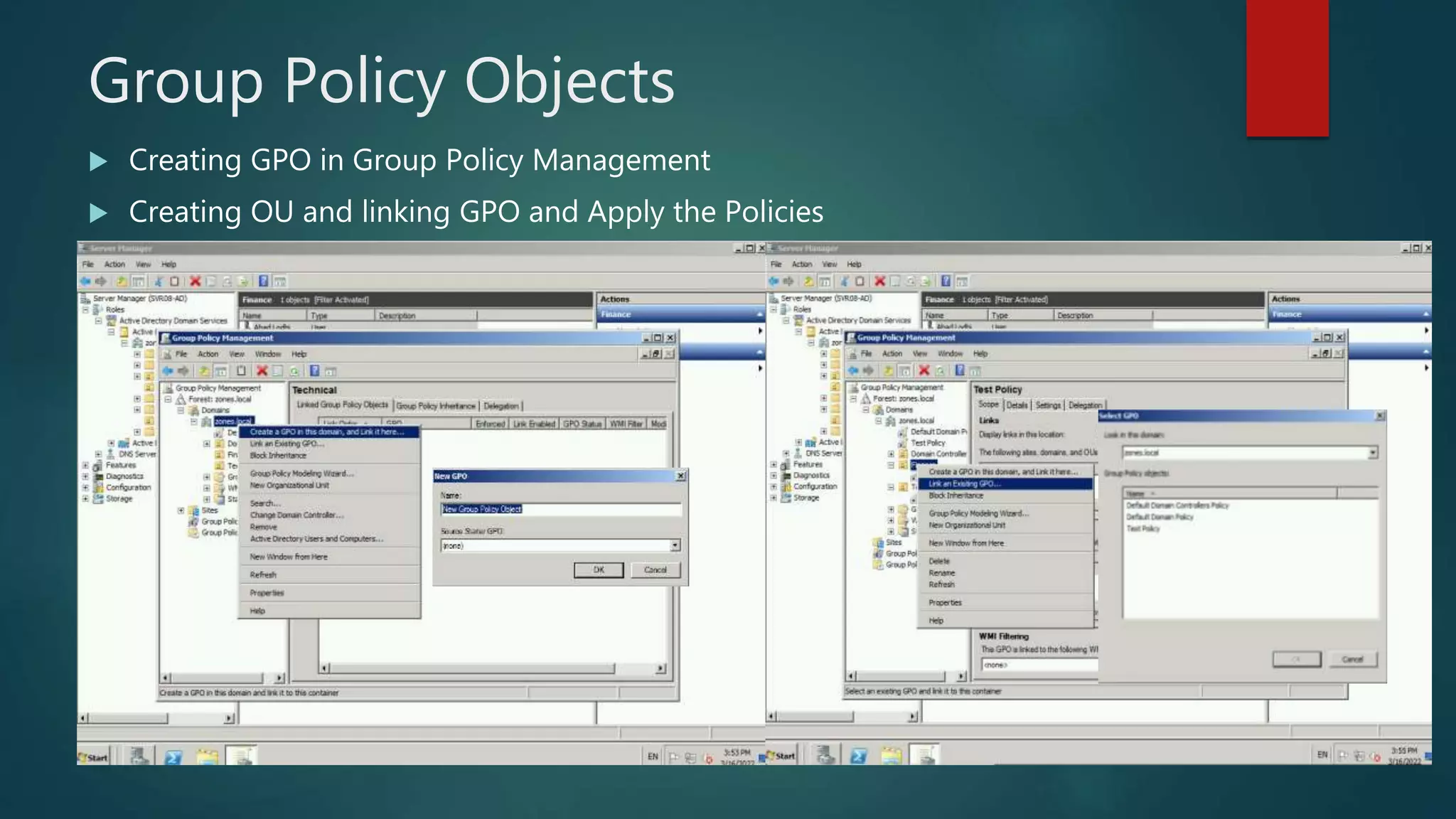
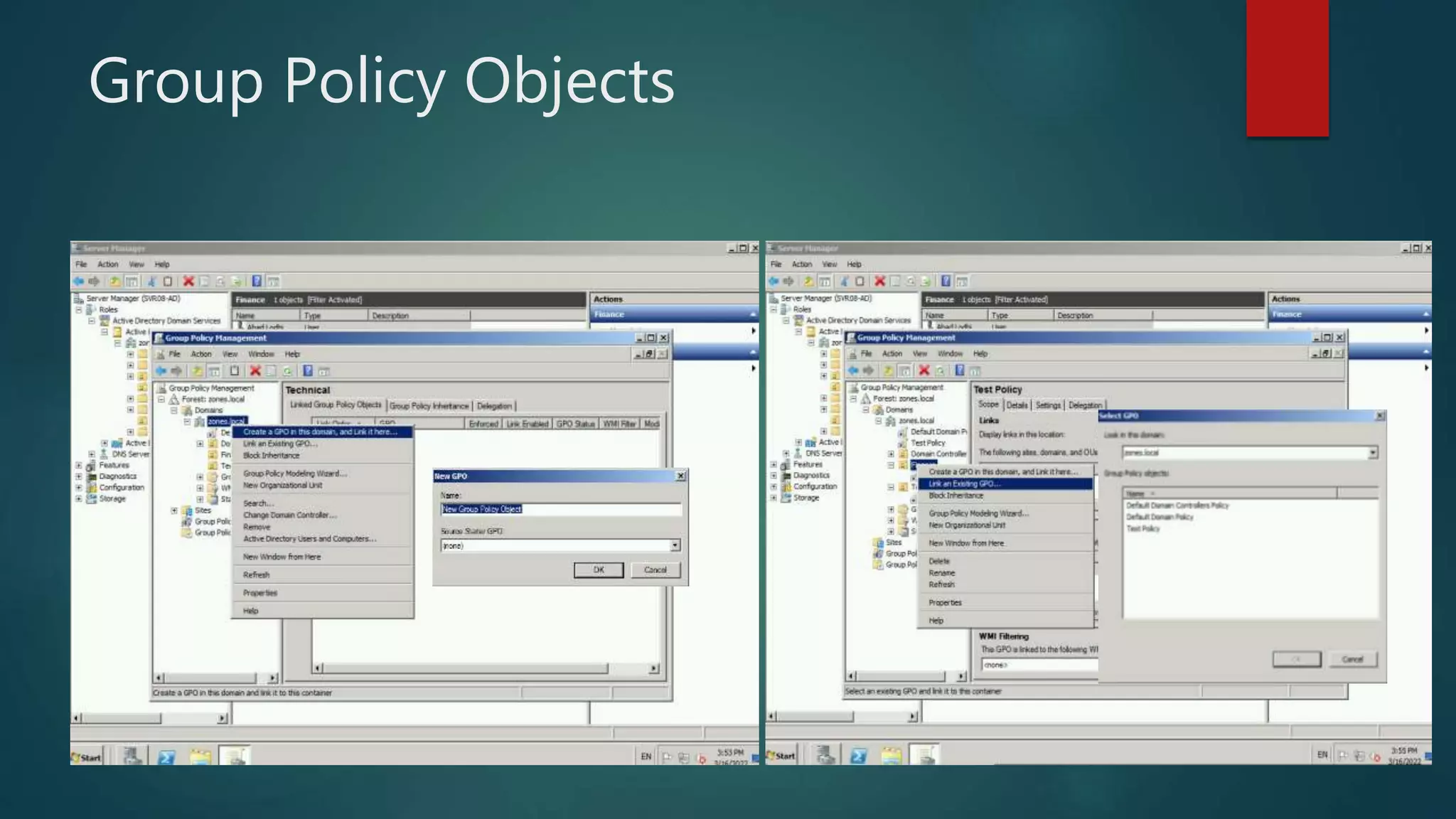
The document discusses the steps to transition from Windows Server 2008 R2 to Windows Server 2012 R2. It covers initial client-server connectivity configuration, installing and configuring Active Directory roles to promote the server to a domain controller, upgrading domain and forest functional levels, and demoting the old domain controller gracefully. Key terms like Active Directory, DNS, sites, domains, and forests are defined. Group policy object creation and application is also outlined.